IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: Recently, the U.S. Commission for International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) sought sanctions on Indian agencies over the ‘violation’ of religious freedom.
About U.S. Commission for International Religious Freedom (USCIRF):-
- USCIRF is an independent, bipartisan US federal government commission.
- It was established by the US government in 1998 after the inaction of the International Religious Freedom Act.
- It is Headquartered in Washington DC.
- It is dedicated to defending the universal right to freedom of religion or belief abroad.
- It is an advisory body to the US Congress.
- The recommendations of USCIRF are non-binding on the state department
- Traditionally, India does not recognize the view of USCIRF. .(UPSC PRELIMS: India’s designation by the USCIRF )
- It monitors the universal right to freedom of religion or belief (FoRB) abroad. UNCIRF Functions:-
- Advises Congress by working with Congressional offices, convening and testifying at hearings, and holding briefings on countries and thematic issues.
- Engages the Executive Branch by regularly meeting with Executive Branch officials.
- Monitors Religious Freedom Conditions Abroad. (UPSC PRELIMS: Religious Tolerance and Social Harmony)
- It makes policy recommendations to the President, Secretary of State, and Congress.
- Raises Public Awareness by holding public events, hosting podcast episodes, releasing public statements, and publishing op-eds.
- Issues an Annual Report & Other Publications that assess foreign countries that violate religious freedom in a systematic, ongoing, and/or egregious manner.
MUST READ: The hijab case and the essential practices doctrine
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2020)
International agreement/ set-up Subject
- Alma-Ata Declaration – Healthcare of the people
- Hague Convention – Biological and Chemical Weapons
- Talanoa Dialogue – Global Climate Change
- Under2 Coalition – Child Rights
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2,3 and 4 only
Q.2) The term “two-state solution” is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (2018)
- China
- Israel
- Iraq
- Yemen
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: Recently, De-dollarisation picked up pace in the aftermath of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
About De-dollarisation:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Dollarization and Ecuador (slideshare.net)
- De-dollarisation refers to the replacement of the U.S. dollar with other currencies as the global reserve currency.
- Reserve currency: refers to any currency that is widely used in cross-border transactions and is commonly held as reserves by central banks.
- De-dollarisation is a process of substituting the US dollar as the currency used for:
- Trading oil and/ or other commodities
- Buying US dollars for the forex reserves
- Bilateral trade agreements
- Dollar-denominated assets
History of Global Currency:-
- The British pound was the primary reserve currency during the 19th and early 20th centuries.
- After World War II, and the U.S. dollar became the dominant reserve currency.
- It has held this position since then, with over 60% of global foreign exchange reserves held in dollars as of 2021.
Reasons for the popularity of the US Dollar:-
- High Level of Trust: The global acceptability of the U.S. dollar as a reserve currency is primarily due to the popularity of U.S. assets among investors.
- Rule of Law: This trust may be due to the ‘rule of law’ in the U.S.
Need for De- Dollarisation:-
- Diversification of Risk: Holding a basket of currencies instead of just one currency (i.e., the US dollar) can help reduce the potential negative impact of a sudden currency devaluation or other economic shocks/political changes in the US. (UPSC PRELIMS: Currency manipulation)
- Increasing Trade and Investment: By using other currencies, countries can increase trade and investment with other countries that may not have a strong relationship with the US, which can open up new markets and opportunities for growth.
- Reducing US Monetary Policy Influence: By reducing the use of the US dollar, countries can increase their economic autonomy.
- Geopolitical Benefits: By reducing dependence on the US dollar, countries may be able to improve their geopolitical standing. (UPSC PRELIMS: Hyper globalisation)
Challenges of De dollarisation:–
- Market Volatility and Global Financial Crisis: A sudden shift away from the dollar could create market volatility and instability, as many countries and businesses are heavily reliant on the dollar for trade and investment and any change would lead to a potential global financial crisis.
- Trade Disruptions: A move away from the dollar could also disrupt international trade, as businesses and governments adjust to new currencies and exchange rate regimes.
- Exchange Rate Risk: De-dollarisation can expose countries to exchange rate risk, as they may have to convert their reserves into other currencies that are subject to volatility.
- Geopolitical Risks: A shift away from the dollar can be seen as a challenge to US economic and geopolitical power, which could lead to political tensions and even conflict.
International Efforts so far:-
- Bilateral currency swaps among countries, promotion of trade in national currencies, and the establishment of alternative payment systems.
- The BRICS’s New Development Bank encourages trade and investment in national currencies by disbursing up to 50% of its loans in national currencies since 2015.
- Russian banks have started using the China-based Cross-Border Interbank Payment System for international payments as they are debarred from the SWIFT international system.
- Some countries are also exploring the possibility of using cryptocurrencies for international trade and payments, as they offer a decentralized alternative to traditional payment systems.
National Efforts:-
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently unveiled a rupee settlement system for international trade by allowing special vostro accounts in designated Indian banks, a step towards internationalising the rupee.
- Similarly, India and Russia are considering the use of a third currency or the inclusion of a third country like the UAE to facilitate oil trade between the two countries.
MUST READ: India’s Digital rupee: CBDC
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2022)
- An increase in Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) indicates the appreciation of the rupee.
- An increase in the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) indicates an improvement in trade competitiveness.
- An increasing trend in domestic inflation relative to inflation in other countries is likely to cause an increasing divergence between NEER and REER.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2022)
- If the inflation is too high, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is likely to buy government securities.
- If the rupee is rapidly depreciating, RBI is likely to sell dollars in the market.
- If interest rates in the USA or European Union were to fall, that is likely to induce RBI to buy dollars.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: The Government shines on 11 parameters of the Twenty Point Programme released recently.
About Twenty Point Programme:-
- The Twenty Point Programme was initially launched by Prime Minister Indira Gandhi in 1975.
- It was subsequently restructured in 1982 and again in 1986.
- With the introduction of new policies and programmes it has been finally restructured in 2006 and it has been in operation at present.
- The Programmes and Schemes under TPP-2006 are in harmony with the priorities contained in the National Common Minimum Programme, the Millennium Development Goals of the United Nations and the SAARC Social Charter.
- Objective: to eradicate poverty and to improve the quality of life of the poor and the underprivileged population of the country.
- The monitoring of the programme at the centre has been assigned to the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, Government of India.
- The management information system relating to Twenty Point developed by the Ministry consists of a monthly Progress Report (MPR) and yearly Review of the Programme, Point-wise, Item-wise and State-wise.
The 20 points under TPP after restructuring in 2006 include:-
- Poverty eradication
- power to people
- Support to farmers
- Labour welfare (UPSC PRELIMS: India’s labour reforms )
- Food security
- Clean drinking water
- Housing for all
- Health for all
- Education for all
- Welfare of SC/ ST/ OBC and minorities
- Women welfare
- Child welfare
- Youth Development
- Improvement of slums
- Environment protection and afforestation
- Social security
- Rural Roads
- Energising rural areas
- Development of Backward areas
- IT enabled and e-governance (UPSC PRELIMS: Governance 4.0)
MUST READ: States
SOURCE: THE ECONOMIC TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
- Department of Science and Technology
- Ministry of Labour and Employment
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Q.2) Recently, India’s first ‘National Investment and Manufacturing Zone’ was proposed to be set up in (2016)
- Andhra Pradesh
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
- Uttar Pradesh
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the Indian Institute of Foreign Trade (IIFT) Kakinada began its admission process.
About the Indian Institute of Foreign Trade (IIFT):-
IMAGE SOURCE: An introduction to NAAC Accreditation | by Linways Team | Linways Technologies
- The Indian Institute of Foreign Trade (IIFT) was established in 1963 as an autonomous body.
- It works under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- The Institute was granted “Deemed to be University” status in 2002.
- The Institute was granted the prestigious AACSB accreditation in 2021.
- With this the IIFT figures amongst 900+ Business Schools of the world which have earned this accreditation.
- The National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) recognized IIFT as a Grada e ‘A’ Institution in 2005 as well as in 2015. (UPSC PRELIMS: Accreditation of HEIs)
- MBA (International Business), the flagship programme of IIFT.
Mission:-
- To create and foster a learning environment that enables participants to be leaders in international business with sensitivity towards society. ( Academic Collaboration between Indian and foreign Universities)
Objectives & Activities:-
- Impart professional education in modern management techniques relevant to international business.
- Enable the participants to appreciate the inter-relationship between the diverse and complex tasks of international business.
- Develop capacities among business executives for improved understanding of various trade and economic issues.
- Conduct high-quality research that addresses domestic as well as world trade and business issues. (UPSC CSE: National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL))
MUST READ: Academic Collaboration between Indian and foreign universities
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Regarding DigiLocker’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2018)
- It is a digital locker system offered by the Government under Digital India Programme.
- It allows you to access your e-documents irrespective of your physical location.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) SWAYAM’, an initiative of the Government of India, aims at (2018)
- promoting Self-Help Groups in rural areas
- providing financial and technical assistance to young start-up entrepreneurs
- promoting the education and health of adolescent girls
- providing affordable and quality education to the citizens for free
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defence
Context: Recently, the Army held a ‘Buland Bharat’ exercise in Arunachal to test synergy in simulated war conditions.
About Buland Bharat exercise:-
IMAGE SOURCE: Map of selected study sites in Tawang and West Kameng districts of… | Download Scientific Diagram (researchgate.net)
- Buland Bharat is an integrated surveillance and firepower training exercise.
- Objective: to test the simulated war conditions in high altitude areas at the Mandala High Altitude Firing Ranges in Arunachal Pradesh.
- The month-long training culminated in the test exercise in which troops and equipment were tested in simulated war conditions, in high altitude areas and in extreme weather conditions.
- During the exercise, synergised surveillance and firepower from infantry and artillery radars, weapon systems and direction of fire from the air were practised.
- Uninterrupted communication on multiple media was also tested at long distances.
- The exercise validated plans for bringing down integrated firepower by orchestrating synchronised firing by artillery guns and fire support components of the infantry, aimed toward the destruction of designated targets.
- It involved the synergised application of surveillance and firepower capabilities of the artillery and the infantry in close coordination with Special Forces, Aviation and Central Armed Police Forces deployed in West Kameng and Tawang districts of Arunachal Pradesh. (UPSC PRELIMS: Arunachal-Assam border dispute)
- The Gajraj Corps, under which the exercise was held, handles major responsibilities which span from counterinsurgency to the Line of Actual Control in West Arunachal Pradesh including the Tawang area. (UPSC PRELIMS: India-China Tawang clash )
MUST READ: Kaiser-i-Hind: Arunachal’s State butterfly
SOURCE: TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In which one of the following groups are all four countries members of G20? (2019)
- Argentina Mexico, South Africa and Turkey.
- Australia Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
- Indonesia Japan Singapore and South Korea
Q.2) Consider the following countries : (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
- 1, 2, 4 and 5
- 3, 4, 5 and 6
- 1, 3, 4 and 5
- 2, 3, 4 and 6
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, UGC launched the ‘CU-Chayan’ portal for faculty recruitment in Central varsities.
About CU-Chayan portal:-
- CU-Chayan portal is a new platform to hire faculty members in central universities.
- The portal will provide a consolidated list of job openings across all 46 central universities under the Union Ministry of Education. (UPSC CSE: Governor’s Role in Universities)
- Central universities will still be responsible for advertising job openings, accepting applications, screening applicants, conducting interviews, and hiring faculty members, just as they did before.
- However, all of these tasks will be managed through the admin dashboard for each university on the portal.
Process:-
- Applicants will find a consolidated list of openings across the central universities, personalized dashboards to help manage the application process, and filters such as location, designation, subject, experience, and education level to view openings that suit them.
Benefits for Applicants and Universities:-
- Both applicants and universities will benefit from it as it provides a simple interface to apply for job openings.
- The portal will also throw up real-time data on vacancies, applications under consideration, and whether the reservation policy is being followed or not. (UPSC MAINS: reservation in education institutions)
- It will fast-track the recruitment process without centralizing the faculty hiring for the central universities.
About UGC:-
- UGC came into existence in 1953.
- It became a statutory body by an Act of Parliament in 1956.
- Background:-
- UGC was formed in 1946 to oversee the work of the three Central Universities of Aligarh, Banaras and, Delhi.
- In 1947, the Committee was entrusted with the responsibility of dealing with all the then existing Universities.
- After independence, the University Education Commission was set up in 1948 under the Chairmanship of S. Radhakrishnan and it recommended that the UGC be reconstituted on the general model of the University Grants Commission of the United Kingdom.
- The UGC was formally established in November 1956, by an Act of Parliament.
- Objective: for the coordination, determination and maintenance of standards of teaching, examination and research in university education.
- The head office of the UGC is located in New Delhi.
- It is charged with coordination, determination and maintenance of standards of higher education.
- It provides recognition to universities in India.
- It disburses funds to such recognized universities and colleges.
MUST READ: Common University Entrance Test (CUET)
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) What is the aim of the programme ‘Unnat Bharat Abhiyan’? (2017)
- Achieving 100% literacy by promoting collaboration between voluntary organizations and the government’s education system and local communities.
- Connecting institutions of higher education with local communities to address development challenges through appropriate technologies.
- Strengthening India’s scientific research institutions in order to make India a scientific and technological power.
- Developing human capital by allocating special funds for health care and education of rural and urban poor, and organizing skill development programmes and vocational training for them.
Q.2) Recognition of Prior Learning Scheme’ is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to (2017)
- Certifying the skills acquired by construction workers through traditional channels.
- Enrolling the persons in Universities for distance learning programmes.
- Reserving some skilled jobs to rural and urban poor in some public sector undertakings.
- Certifying the skills acquired by trainees under the National Skill Development Programme
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: The Election Commission of India (ECI) recently issued an advisory urging star campaigners to “maintain the dignity of the political discourse.”
About Star Campaigners:-
- A star campaigner is a celebrity vote seeker in an election for a party.
- This person can be anyone, a politician or even a film star.
- There is no law governing who can or cannot be made a star campaigner. (UPSC PRELIMS: Election Commission)
- They are nominated by the concerned political parties specifying their constituencies and duration of the status.
Terms and Conditions:-
- Numbers of Star Campaigners:
- A ‘recognised’ National or State party declared as such by the ECI can nominate a maximum of 40-star campaigners.(UPSC PRELIMS: What does it take to become a National Party in India?)
- An unrecognised political party can nominate a maximum of 20-star campaigners.
- Section 77 (b) of The Representation of People’s Act, 1951 says that most of the expenses incurred by the campaigner “shall not be deemed to be an expenditure in connection with the election”.
- In other words, all expenses will be borne by the respective political party.
- For example, expenses borne by star campaigners on account of travel by air or by any other means of transport shall not be deemed as expenditure in connection with the election.
- The manual to the Model Code of Conduct states that for the benefit of availing Section 77 (1) of The RP Act, a permit for the mode of transport for every star campaigner will be issued centrally and against their name.
-
- It is also mandatory for this permit to be stuck on a prominent and visible place on the vehicle.
- If a star campaigner campaigns specifically for one candidate:-
- If a candidate or her election agent shares the stage with a star campaigner at a rally, then the entire expenditure on that rally, other than the travel expenses of the star campaigner, is added to the candidate’s expenses.
- Even if the candidate is not present at the star campaigner’s rally, but there are posters with her photographs or her name on display, the entire expenditure will be added to the candidate’s account.
- This applies even if the star campaigner mentions the candidate’s name during the event.
- When more than one candidate shares the stage, or there are posters with their photographs, then the expenses of such rally/meeting are equally divided between all such candidates.
Prime Minister as Star Campaigner:-
- The MCC guidelines say when a prime minister or a former prime minister is a star campaigner, the expenditure incurred on security including bullet-proof vehicles will be borne by the government and will not be added to the election expenses of the party or the individual candidate. (UPSC PRELIMS: Elections & MCC)
- However, if another campaigner travels with the prime minister, the individual candidate will have to bear 50% of the expenditure incurred on the security arrangements.
MUST READ: Election Symbol
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to anti-defection law in India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The law specifies that a nominated legislator cannot join any political party within six months of being appointed to the House.
- The law does not provide any time frame within which the presiding officer has to decide a defection case.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2021)
- In India, there is no law restricting the candidates from contesting in one Lok Sabha election from three constituencies.
- In the 1991 Lok Sabha Election, Shri Devi Lal contested from three Lok Sabha constituencies.
- As per the existing rules, if a candidate contests in one Lok Sabha election from many constituencies, his/her party should bear the cost of bye-elections to the constituencies vacated by him/her in the event of him/her winning in all the constituencies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recent studies by researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have explained how the dengue virus causes the Dengue Fever.
About Dengue Fever:-
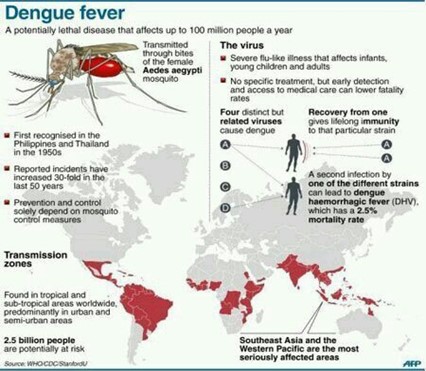
IMAGE SOURCE: Dengue Fever INFO – Bing images
- Dengue Fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease.
- It is caused by the dengue virus belonging to the Genus Flavivirus.
- It is transmitted by several species of female mosquito within the genus Aedes, principally Aedes aegypti.
- This mosquito also transmits chikungunya, yellow fever and Zika infection. (UPSC PRELIMS: Zika Virus Disease )
- There are 4 distinct, but closely related, serotypes of the virus that cause dengue: DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3 and DEN-4.
Symptoms:-
- Sudden high fever
- severe headaches
- pain behind the eyes
- severe bone, joint, and muscle pain, etc.
Diagnosis and Treatment:-
- Diagnosis of dengue infection is done with a blood test.
- There is no specific medicine to treat dengue infection.
- Dengue Vaccine:-
- The dengue vaccine CYD-TDV or Dengvaxia was approved by the US Food & Drug Administration in 2019.
- It was the first dengue vaccine to get the regulatory nod in the US. (UPSC PRELIMS: Malaria Vaccine )
- Dengvaxia is basically a live, attenuated dengue virus which has to be administered in people ages 9 to 16 who have laboratory-confirmed previous dengue infection and who live in endemic areas.
- Vaccine manufacturer Indian Immunologicals Limited (IIL) is developing India’s first Dengue vaccine and has received permission for a Phase-1 trial.
- The vaccine is being produced in collaboration with the National Institutes of Health in the US.
MUST READ: Tomato Flu
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent the COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Serum Institute of India produced a COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using an mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using a vector-based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen-based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing? (2013)
- Chikungunya
- Hepatitis B
- HIV-AIDS
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Society and associated issues)
Context: The annual State of World Population report 2023 by the UN Population Fund (UNFPA) stated that India’s population is expected to surpass that of China by the middle of this year at the latest.
Key facts about India’s population: Fertility Decline
- According to National Family Health Survey (NFHS), fertility rate falling below the replacement level for the first time to 2.0 in 2021.dropped from 2.2 to 2.0.
- Only five States have a fertility rate above the replacement rate: Bihar (3), Meghalaya (2.9), Uttar Pradesh (2.4), Jharkhand (2.3), and Manipur (2.2)
- At the time of Independence, India’s fertility rate was six per woman, and it had taken 25 years to reach five, with the government launching the first ever family planning program in the world in 1952.
- India’s fertility further declined to four in the 1990s when Kerala became the first State in India to have a fertility rate below replacement.
- Increased use of contraception, more years of average schooling, better health care, and an increase in the mean marriage age of women are of the reasons behind the steady dip in fertility rate.
Population vs Economic development:
- Starting point of this debate is Thomas Malthus’ argument in 1798.
- Malthusianism is the theory that population growth is potentially exponential while the growth of the food supply or other resources is linear, which eventually reduces living standards to the point of triggering a population decline.
- This event, called a Malthusian catastrophe.
- Since then, however, the world population has grown eight times to reach 8 billion.
- During the 1950s and 60s, “the general view of economists was that high birth rates and rapid population growth in poor countries would divert scarce capital away from savings and investment, thereby placing a drag on economic development.
- However, between the 1970s and 1990s, several studies “failed to detect a robust relationship between national population growth rates and per capita income growth”.
- The global view reverted in the 1990s when researchers again found a clear “negative association between population growth and economic performance”.
- During this time, World was also introduced to the concept of “demographic dividend”e., high economic growth when there is a bulge in the working-age population (roughly speaking, population between 15 and 65 years).
Opportunities for India:
- A larger workforce: A growing population means a larger workforce, which, if trained and employed, can contribute to economic growth and development.
- Domestic market: A larger population can create a larger domestic market, which can drive economic growth by increasing demand for goods and services.
- Innovation and technological advancements: A larger population can provide a greater pool of knowledge and expertise, and a more diverse range of perspectives and ideas, which can lead to innovation and technological advancements.
- Investment in infrastructure: Population growth can create opportunities for investment in infrastructure, education, and health, which can further stimulate economic development.
- Cultural richness: A larger population can lead to cultural richness and diversity. With a diverse population comes a range of languages, traditions, and cultural practices, which can contribute to a vibrant and dynamic society.
- Diplomatic influence: A larger population can give a country greater diplomatic influence on the world stage.
- As one of the world’s most populous countries, India has significant diplomatic influence and can use its demographic size as a bargaining tool in international negotiations.
Issues associated with over population:
- Strain on resources: A growing population can put a strain on natural resources, such as water, food, and energy.
- It can lead to environmental degradation, scarcity, and conflict.
- Unemployment: A larger population can create a mismatch between the supply and demand of jobs, leading to high unemployment rates, particularly among young people
- Poverty: Population growth can exacerbate poverty, particularly in rural areas and among marginalized communities.
- This can create social and economic inequality and limit access to education, healthcare, and other basic needs.
- Overcrowding: A larger population can lead to overcrowding, particularly in urban areas.
- This can create poor living conditions, increased pollution, and health hazards.
- Infrastructure: A growing population can put a strain on infrastructure, such as transportation, housing, and sanitation.
- This can lead to inadequate services and poor living conditions.
- Health: A larger population can increase the spread of disease and illness, particularly in areas with poor healthcare infrastructure.
- It can lead to public health crises and decreased life expectancy.
- Education: Population growth can put a strain on education systems, particularly in terms of providing quality education to all.
- This can limit social and economic mobility and contribute to inequality.
- Migration: A larger population can lead to migration, particularly to urban areas, which can create social and economic challenges, such as increased crime rates and inequality.
Way Forward:
Population growth constantly acts as a hurdle in effectively addressing the problem of poverty, hunger and malnutrition and in providing a better quality of health and education, with limited resources. It is, therefore, important to understand that in order to have a better future for all on a healthy planet, attainment of the SDGs is critical.
Family planning is an effective tool to ensure a stable rise in the population, which in turn is crucial for the achievement of some of these SDGs. The Government at all levels — Union, State and local, citizens, civil societies as well as businesses — must take the responsibility to promote awareness and advocate the sexual and reproductive rights of women and encourage the use of contraception.
This would go a long way in ensuring that every child who is born would prove to be an asset for the country, as all the research shows that investing in family planning and well-being measures have significant benefits over per Rupee spent vis-à-vis other investments.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding the Indian Institute of Foreign Trade (IIFT):
- It aims to create and foster a learning environment that enables participants to be leaders in international business with sensitivity towards society.
- It works under the Ministry of Finance
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which of the following statements is not correct regarding the University Grants Commission (UGC):
- It is a statutory body
- The head office of the UGC is located in Hyderabad
- It provides recognition to universities in India.
- UGC was formed in 1946 to oversee the work of the three Central Universities of Aligarh, Banaras and, Delhi.
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding star campaigners in Indian elections:
- A ‘recognised’ National or State party declared as such by the ECI can nominate a maximum of 50-star campaigners.
- If a candidate or his/her election agent shares the stage with a star campaigner at a rally, then the entire expenditure on that rally, other than the travel expenses of the star campaigner, is added to the candidate’s expenses.
- when a prime minister or a former prime minister is a star campaigner, the expenditure incurred on security including bullet-proof vehicles will be borne by the government and will not be added to the election expenses of the party or the individual candidate.
- There is no law governing who can or cannot be made a star campaigner.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 2 and 3 only
- 2 3 and 4 only
- 1 3 and 4 only
- All of the above
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 4th May 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 3rd May – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – c












