IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: The recent train tragedy in Odisha has brought to the surface the need for KAVACH in preventing rail accidents. Kavach was not available on this route.
About KAVACH:-

IMAGE SOURCE: newssimplified.in
- KAVACH is an Automatic Train Protection (ATP) electronic system designed to help the Indian Railways achieve Zero Accidents.
- Objective: to achieve safety in train operations across Indian Railways.
- Development:-
- It has been indigenously developed.
- It is developed by the Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) in collaboration with the Indian industry.
- Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO): it is a research and development organisation under the Ministry of Railways.
- Working of KAVACH:-
- It has a set of electronic devices and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) devices installed in locomotives, in the signalling system as well as the tracks. (UPSC CSE: RFID)
- These connect to each other using ultra-high radio frequencies to control the brakes of trains.
- It also alerts drivers, all based on the logic programmed into them. (UPSC MAINS: KAVACH)
- It is a Safety Integrity Level 4 (SIL-4) certified technology.
- Safety Integrity Level (SIL): it comes from two voluntary standards used by plant owners/operators to quantify safety performance requirements for hazardous operations.
- There are four SIL Levels (1-4).
- A higher SIL Level means a greater process hazard and a higher level of protection.
- KAVACH is the world’s cheapest automatic train collision protection system.
- Initial development of Kavach started in 2012 under the name Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS) and completed development on 2022.
- First successful trial: between Gullaguda–Chitgidda Railway stations of South Central Railway in 2022.
- The Budget of 2022-23 had proposed rollout of Kavach in 2000 kms.
Salient features:-
- Automatic activation of the train braking system if the driver fails to control the train speed.
- Preventing collision between two Locomotives equipped with a functional KAVACH system.
- Sending continuous updates of Movement. (UPSC CSE: Mobile Train Radio Communication (MTRC) )
- Auto Whistling while approaching Level Crossing Gates
- Sending SoS Messages during emergency situations.
- Centralised live monitoring of train movements through the Network Monitor System.
MUST READ: Vande Bharat 2.0
SOURCE: BUISINESSLINE
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following communication technologies: (2022)
- Closed-circuit Television
- Radio Frequency Identification
- Wireless Local Area Network
Which of the above are considered Short-Range devices/technologies?
- 1 and 2 only.
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of (2020)
- Digital security infrastructure
- Food security infrastructure
- Health care and education infrastructure
- Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography, Environment and Ecology
Context: The Government recently, permitted the import of pet coke as a raw material for lithium-ion batteries.
About Pet Coke:-

IMAGE SOURCE: bulkcarrierguide.com
- Pet Coke is one of the industrial by-products produced during oil refining.
- It is dark solid carbon material.
- It is used as a source of energy and carbon for various industrial applications.
- It is abundantly used in India in several manufacturing industries such as cement, steel and textile.
- It is significantly cheaper than coal, has high calorific value and is easier to transport and store.
- There are two kinds of pet coke produced during oil refining viz.
- Fuel-grade pet coke (80%) and
- Calcined pet coke (20%).
- India is the world’s biggest consumer of pet coke. (UPSC CSE: Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR) )
- Local producers: Indian Oil Corp, Reliance Industries and Bharat Petroleum Corp.
- Cement companies in India account for about three-fourths of the country’s pet coke use.
Environment and Health Hazards of Pet Coke:-
- Pet coke is a much more potent pollutant than coal.
- It contains a whopping 74,000 PPM of sulphur content, which is released into the atmosphere as emissions, which is much higher than vehicular emissions.
- It is also a source of fine dust, which can get through the filtering process of the human airway and lodge in the lungs, which can cause serious health problems.
- It releases sulphur, nitrous oxide, mercury, arsenic, chromium, nickel, and hydrogen chloride, which contribute to global warming. (UPSC CSE: COP 27).
Lithium
- It is a soft, silvery-white metal.
- It is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element.
- It has the highest specific heat capacity of any solid element.
- It is a good conductor of electricity.
- It is flammable and can even explode when exposed to air and water.
- Lithium is a crucial building block of the lithium-ion rechargeable batteries.
- Currently, India is heavily dependent on import of these cells and the move to ink sourcing pacts for lithium is seen as a move to reduce its dependency on China, which is a key source of both the raw material and cell.
Lithium-ion batteries
- A lithium-ion battery or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery.
- Working: Li-ion batteries use an intercalated (Intercalation is the reversible inclusion or insertion of a molecule into materials with layered structures) lithium compound as one electrode material.
- The battery consists of electrolyte, which allows for ionic movement, and the two electrodes are the constituent components of a lithium-ion battery cell.
- Lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharge and back when charging.
Applications:-
- Power electric vehicles (EVs), laptops and mobile phones.
- Applications in electronic gadgets, Telecommunication, Aerospace, Industries.
- Power source for electric and hybrid electric vehicles.
Advantages of Li-Ion battery:-
- It is light weighted and is one-third the weight of lead acid batteries.
- It is nearly 100% efficient in both charging and discharging as compared to lead battery, which has 70% efficiency.
- It completely discharges i.e. 100% as compared to 80% for lead acid.
- It has life cycle of 5000 times or more compared to just 400-500 cycles in lead acid.
- It also maintains constant voltage throughout entire discharge cycle whereas voltage in lead acid battery drops consistently throughout its discharge cycle.
- It is much cleaner technology and is safer for environment.
- It can be wireless.
Disadvantages of Li-ion Batteries:-
- Long charging times.
- Safety issues: instances of batteries catching fires have been there.
- Expensive to manufacture
MUST READ: Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) Countries
SOURCE: BUISINESS STANDARD
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Monazite is a source of rare earth.
- Monazite contains thorium.
- Monazite occurs naturally in the entire Indian coastal sands in India.
- In India, Government bodies only can process or export monazite.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) In the Guidelines, statements: the context of WHO consider the Air Quality following (2022)
- The 24-hour mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 15 ug/m³ and the annual mean of PM 2.5 should not exceed 5 µg/m³.
- In a year, the highest levels of ozone pollution occur during periods of inclement weather.
- PM10 can penetrate the lung barrier and enter the bloodstream.
- Excessive ozone in the air can trigger asthma.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1 and 4 only
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1 and 2 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: The Environmental Information, Awareness, Capacity Building and Livelihood Programme (EIACP) Centres have spread the message on LiFE during the World Environment Day celebrations held recently.
About The Environmental Information, Awareness, Capacity Building and Livelihood Programme (EIACP):-
IMAGE SOURCE: nbrienvis.nic.in
- It is a Central Sector sub-scheme being implemented in alignment with Mission LiFE. . (UPSC CSE: EIACP)
- Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
- In 2023, The Environmental Information System (ENVIS) was renamed EIACP (Environmental Information, Awareness, Capacity Building and Livelihood Programme).
- ENVIS: came into existence as in 1983.
- The focus of ENVIS was to provide environmental information to decision-makers, policy planners, scientists and engineers, research workers, etc. all over the country.
- EIACP is being implemented in alignment with Mission LiFE. (UPSC CSE: LIFE – LIfestyle for Environment)
- Objective: it serves as a one-stop platform for the dissemination of environmental information, informed policy formulation on various facets of the environment and facilitation of alternate livelihoods through green skilling.
- 60 EIACP Centres are actively engaged in promoting awareness about sustainable actions that individuals can undertake.
- ENVIS: came into existence as in 1983.
Environment Education Programme (EEP)
- It is a Central Sector sub-scheme.
- Objective: for imparting non-formal environment education through inter alia initiatives for strengthening Eco-club activities in schools and colleges.
- Sharing the common goal of promoting a sustainable lifestyle.
- Implementation: It is implemented in full alignment with Mission LiFE, through State/UT-level Implementing Agencies.
- Implementing Agencies of EEP have organized some unique and eco-friendly initiatives like nature camps, eco-art workshops, clay & pottery workshop, promotion of eco-friendly green wedding ideas, awareness campaigns on medicinal plants, campaigns in marketplaces against single-use plastics etc.
- Eco-clubs are used as an effective medium to spread messages on LiFE.
Mission LIfestyle for Environment (Life):-
- Background: At the 2021 UN Climate Change Conference (UNFCCC COP26), Hon’ble Prime Minister of India Shri Narendra Modi announced Mission LiFE.
- Aim: to bring individual behaviours at the forefront of the global climate action
- LiFE envisions replacing the prevalent ‘use-and-dispose’ economy with a circular economy, which would be defined by mindful and deliberate utilisation.
- Approach:-
- Focus on Individual Behaviours: Make Life a mass movement (Jan Andolan) by focusing on behaviours and attitudes of individuals and communities.
- Co-create Globally: Crowdsource empirical and scalable ideas from the best minds of the world, through top universities, think tanks and international organisations.
- Leverage Local Cultures: Leverage climate-friendly social norms, beliefs and daily household practices of different cultures worldwide to drive the campaign.
- Objectives :-
- It aims to promote an environmentally conscious lifestyle that focuses on ‘mindful and deliberate utilisation’ instead of ‘mindless and wasteful consumption’.
- It aims to utilise the power of collective action.
- It aims to nudge individuals across the world to undertake simple climate-friendly actions in their daily lives.
- It aims to create and nurture a global network of individuals, namely ‘Pro-Planet People’ (P3).
- Pro-Planet People’ (P3): to have a shared commitment to adopt and promote environmentally friendly lifestyles.
- It seeks to leverage the strength of social networks to influence social norms surrounding climate.
MUST READ: National Clean Air Programme
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1)The “Common Carbon Metric” supported by UNEP, has been developed for (2021)
- Assessing the carbon footprint of building operations around the world.
- Enabling commercial farming entities around the world to enter carbon emission trading.
- Enabling governments to assess the overall carbon footprint caused by their countries.
- Assessing the overall carbon footprint caused by the use of fossil fuels by the world in a unit of time.
Q.2) “R2 Code of Practices” constitute a tool available for promoting the adoption of (2021)
- Environmentally responsible practices in the electronics recycling industry.
- Ecological management of ‘’Wetlands of International Importance” under the Ramsar Convention.
- Sustainable practices in the cultivation of agricultural crops in degraded lands.
- ‘’Environmental Impact Assessment’’ in the exploitation of natural resources.
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: The long-standing issue of Iran and Afghanistan’s water conflict arose again as clashes broke out along the border recently.
About Iran and Afghanistan’s water conflict:-
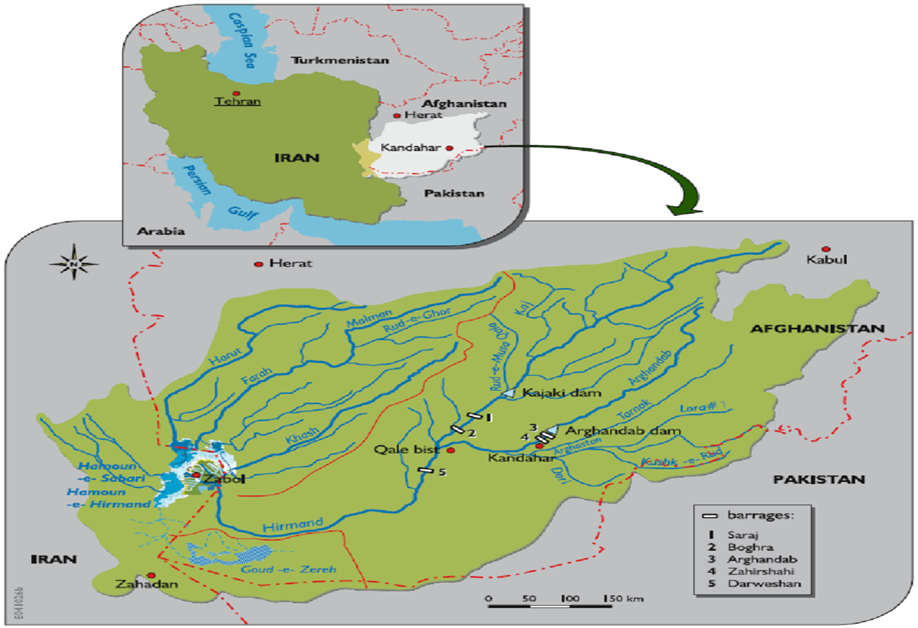
IMAGE SOURCE: ResearchGate
Background:-
- Afghanistan and Iran signed the Helmand River Treaty in 1973.
- Objective: to regulate the allocation of river water.
- However, the accord was neither ratified nor fully implemented, causing disagreements and tensions to persist.
- Disagreements:-
- Iran accuses Afghanistan of violating water rights: Iran has consistently accused Afghanistan of infringing upon its water rights, claiming that it receives significantly less water than agreed upon in the 1973 treaty.
- Afghanistan blames climatic factors for reduced water flow: Afghanistan has refuted Iran’s allegations, citing climatic factors such as reduced rainfall and diminished river water volumes as the primary causes of the current situation.
- Concerns over Afghanistan’s dam and irrigation projects: Iran expresses concerns over Afghanistan’s construction of dams, reservoirs, and irrigation systems along the Helmand River, fearing that these initiatives negatively affect water flow into Iran.
Current situation:-
- Water shortages and other problems: Sistan-Baluchistan region of Iran faces severe water shortages, contributing to economic and social difficulties in one of Iran’s poorest areas.
- Setting up an inquiry commission: to address the recent border clash, Iran and Afghanistan have agreed to establish a commission of inquiry to investigate the incident.
- Short-term focus on internal problems: Both Iran and the Taliban prioritize short-term solutions and focus on internal issues rather than actively resolving the water dispute.
- Both Iran and the Taliban show little interest in addressing the mismanagement of water resources and environmental challenges in the region.
River Hirmand/Helmand
- The Helmand is Afghanistan’s longest river.
- Origin: near Kabul (Afghanistan) in the western Hindu Kush mountain range. (UPSC CSE: India-Afghanistan)
- Drainage: It flows in a south-westerly direction through desert areas.
- It empties into Lake Hamun, which straddles the Afghanistan-Iran border.
- Lake Hamun is the largest freshwater lake in Iran. (UPSC CSE: Chabahar port)
- The Lake has experienced a drastic decline in water levels, attributed to factors such as drought and the construction of dams.
- Economic Importance: Lake Hamun supports agricultural activities, livelihoods, and economic sectors in the surrounding areas.
MUST READ: India, Iran and Afghanistan
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following countries: (2022)
- Azerbaijan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Tajikistan
- Uzbekistan
- Turkmenistan
Which of the above has borders with Afghanistan?
- 1, 2 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
- 3, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
The region often mentioned in the news: Country
- Anatolia Turkey
- Amhara Ethiopia
- Cabo Delgado Spain
- Catalonia Italy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: A recent global study on moss reveals that they are far more vital to Earth’s ecosystems than previously known.
About Moss:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Flickr
- Mosses are small, soft, flowerless Plants.
- Scientific Classification:-
- Kingdom – Plantae
- Division – Bryophyta
- They have Stomata.
- Stomata: cells specialized for photosynthetic gas exchange.
- They are some of the oldest land plants and existed as early as the Permian Period (299 to 251 million years ago).
- Unlike most other plants, mosses do not have roots. Instead, they have rhizoids, which are small hair like structures.
- Distribution: They are found all over the world, from lush tropical rainforests to the driest deserts.
- They are found growing in cracks along roads and pathways, on the trunks of trees, on rocks and buildings, and importantly, on the
- They are found even in
Salient Features:-
- Non-Vascular Plants: Mosses lack a Vascular system i.e. xylem and phloem.
- Habitat Indicators: Mosses can also be extremely useful as Habitat Indicators.
- Ability to revive with very Less Water: Mosses are an amazingly resilient and versatile group of Plants.
- Absence of Flowers and Seeds: They do not have flowers or seeds.
- Presence of Multicellular Rhizoid: Mosses are the only Plants that have a Multicellular Rhizoid.
- Rhizoid: a root-like subterranean tissue that absorbs water and nutrients from the soil.
- Radial Symmetry: if they are cut down, the long axis of an individual gives two similar halves.
- Tendency to grow in Clusters: They commonly grow close together in clumps or mats.
Importance of Mosses:
- Mosses function like sponges, using their capillary spaces to hang on to water.
- They help to soak up rainfall, maintain moisture in the soil below and keep conditions around them humid. This enables other plants around them thrive, such as in habitats like marshes and woodland.
- Mosses also play a vital role in the development of new ecosystems. They are among the first plant colonisers of disturbed sites, such as when an area is deforested or affected by forest fires. They stabilise the soil surface and retain water, helping new plants to grow.
- Mosses can affect the temperature of the soil, both warming it up and cooling it down depending on the environment.
- In hot places, they can protect tree roots by shading and insulating the soil from high temperatures. In the Arctic, they have an opposite effect on temperature. They can prevent the warmth of the sun from reaching the ground and reduce the speed at which ice thaws, keeping it cooler for longer.
- Some mosses are luminous. Some mosses have adapted to low light conditions and are even found growing in caves. One of the most well-known cave mosses is Schistostega pennata, also known as dragon’s gold, which shines an emerald green colour.
MUST READ: New genus of parasitic flowering plant
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to “Gucchi” sometimes mentioned in the news, consider the following statements: (2022)
- It is a fungus.
- It grows in some Himalayan forest areas.
- It is commercially cultivated in the Himalayan foothills of north-eastern India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following are nitrogen-fixing plants? (2022)
- Alfalfa
- Amaranth
- Chickpea
- Clover
- Purslane (Kulfa)
- Spinach
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3, 5 and 6 only
- 2, 4, 5 and 6 only
- 1, 2, 4, 5 and 6
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the National Statistical Office released provisional estimates of national income.
About National Statistical Office:-
- The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) merged with the Central Statistical Office (CSO) to form the National Statistical Office (NSO) in 2019.
- National Sample Survey Office (NSSO): formerly called the National Sample Survey Organisation was the largest organization in India conducting periodic socio-economic surveys.
- Central Statistics Organisation of India: was responsible for the coordination of statistical activities in India, and evolving and maintaining statistical standards.
- NSO is under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI).
Functions:-
- Acts as the nodal agency for the planned development of the statistical system in the country.
- Lays down and maintain norms and standards in the field of statistics.
- Coordinates the statistical work in respect of the Ministries/Departments of the Government of India.
- Prepares national accounts as well as publishes annual estimates of national products, Government and Private final consumption expenditure, Capital Formation, Savings, etc.
- Compiles and releases Consumer Price Index (CPI). (UPSC CSE: CPI)
- Maintains liaison with International Statistical Organizations.
- Compiles and brings out reports as per international/regional commitments.
- Compiles and releases the Index of Industrial Production (IIP) every month. (UPSC CSE: IIP)
- Provides statistical information to assess and evaluate the changes in the growth, composition and structure of the organized manufacturing sector.
MUST READ: National Statistical Commission (NSC)
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements are correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital-raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) . Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Clusters of brown Sargassum seaweed reported to be infested by flesh-eating bacteria were found awash in Florida recently.
About Seaweed:-
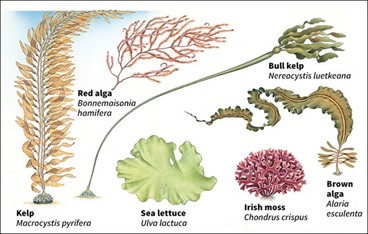
IMAGE SOURCE: blogspot.com
- They are primitive, marine non-flowering marine algae.
- They are without root, stem and leaves.
- They generally grow in shallow waters in the tidal zone.
- Some seaweeds are microscopic, such as the phytoplankton that live suspended in the water column.
- They contribute to about 50% of all photosynthesis in the world.
- Some are enormous, like the giant kelp that grow in abundant “forests” from their roots at the bottom.
- Kelp forests: formed by large seaweeds form dense underwater forests.
- They act as underwater nurseries for fish, snails and sea urchins.
Benefits of Seaweed:-
- Nutritional purpose:-
- Seaweed is a source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, and can be tasty.
- Medicinal Purpose:-
- Many seaweeds contain anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial agents.
- Certain seaweeds possess powerful cancer-fighting agents.
- Economical purpose:-
- Among their many uses in manufacturing, they are effective binding agents (emulsifiers) in such commercial goods as toothpaste and fruit jelly.
- They are also popular softeners (emollients) in organic cosmetics and skin-care products.
- Bioindicators:-.
- Seaweeds absorb the excess nutrients and balance out the ecosystem.
- Iron Sequestrator:-
- These aquatic organisms heavily rely on iron for photosynthesis.
- When the quantity of this mineral exceeds healthy levels and becomes dangerous to marine life, seaweeds trap it and prevent damage.
- Similarly, most heavy metals found in marine ecosystems are trapped and removed by seaweeds.
- Oxygen and Nutrient Supplier:-
- They release oxygen through every part of their bodies.
- They also supply organic nutrients to other marine life forms.
- Aquaculture: –
- At present, seaweed account for 30% of world aquaculture production.
- Industries:-
- They are used for the production of phytochemicals namely agar, carrageenan, and alginate.
- These phytochemicals are widely used as gelling, stabilizing, and thickening agents in food, confectionery, pharmaceutical
- They are used for the production of
- Seaweed has wide range of application in the fields of food, textile, cosmetic, pharmaceuticals, fodder, and fertilisers.
- Provide occupation for the coastal people.
- Provide continuous supply of raw material for seaweed-based industry.
- It is a major tool to treat coastal pollution in the sea & reduce CO2 in global warming.
MUST READ: Seaweeds
SOURCE:HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following kinds of organisms: (2021)
- Copepods
- Cyanobacteria
- Diatoms
- Foraminifera
Which of the above are primary producers in the food chains of oceans?
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Q.2) Consider the following animals (2022)
- Hedgehog
- Marmot
- Pangolin
To reduce the chance of being captured by predators, which of the above organisms rolls up/roll up and protects/protects its/their vulnerable parts?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3
Practice of Forum Shopping
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity and Governance) and GS 4 (Ethics – ethical concerns and dilemmas on govt institutions)
Context: Recently, the Chief Justice of India (CJI) DY Chandrachud condemned the practice of ‘forum shopping’.
About Forum shopping:
- When litigants or lawyers attempt to deliberately move their case to a particular judge or Court where they think the judgment could be more favourable, they are said to be “forum shopping.”
- This practice involves choosing a court that is likely to provide the most favourable outcome, rather than following the standard legal process.
- Lawyers think about which is the right forum to approach as part of their litigation strategy.
- For example, one could directly approach the Supreme Court via a public interest litigation case instead of the concerned High Court because the issue could get more eyeballs.
Advantages:
- It can permit offended parties to look for equity and remuneration in a court that is more thoughtful to their cases or interests.
- It has the potential to boost efficiency and quality of service among courts and judges by encouraging competition and new ideas.
Challenges posed by forum shopping:
- It creates uncertainty and confusion among litigants and lawyers about the proper jurisdiction and venue for their cases.
- It erodes public confidence and trust in the judiciary, as it creates an impression that justice is not based on merit but on manipulation.
- Wasting time and resources of the courts and the litigants by causing duplication, delay and confusion.
- Creating conflicting or inconsistent judgments on the same or similar issues, leading to legal uncertainty and chaos.
- Eroding the credibility and impartiality of the judiciary, as well as the trust and respect of the public and the legal profession.
- Encouraging forum shopping by other litigants or lawyers creates a vicious cycle of abuse and corruption.
Supreme Court’s View on Forum Shopping:
Dr. Khair-Un-Nisa and Ors vs. UT of Jammu and Kashmir and Ors 2023:
- The Jammu, Kashmir, and Ladakh High Court imposed costs worth one-lakh rupees on the petitioners for indulging in forum shopping by filing multiple petitions before different wings of the court, despite having the same cause of action.
Vijay Kumar Ghai vs. State of W.B. 2022:
- The SC termed forum shopping as a “disreputable practice by the courts” that “has no sanction and paramountcy in law”.
Dhanwantri Institute of Medical Science vs. the State of Rajasthan 2022:
- The Rajasthan High Court upheld an order imposing costs worth 10 lakh rupees on a party for engaging in forum shopping.
Kamini Jaiswal vs. Union of India 2017:
- The SC said that “unscrupulous elements” are always on the hunt to find a court or forum of their choice but are not permitted to do so by law.
Way Forward:
Thus, Forum shopping is a serious challenge that threatens the quality and legitimacy of justice delivery. It requires concerted efforts from all stakeholders to address it effectively and efficiently. By doing so, we can ensure that justice is not only done but also seen to be done.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Internal Security -Linkages of Organized Crime with Terrorism)
Context: The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) Chandigarh Zone recently detained an alleged drug trafficker, who is reportedly operating in Una district in Himachal Pradesh.
About Drug trafficking:
- Drug trafficking is a global illicit trade involving the cultivation, manufacture, distribution and sale of substances which are subject to drug prohibition laws.
- United Nation Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is continuously monitoring and researching global illicit drug markets in order to gain a more comprehensive understanding of their dynamics.
India and Drug Abuse:
- According to a report by the United Nation Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), India is one of the major hubs of illicit drug trade ranging from age-old cannabis to newer prescription drugs like tramadol, and designer drugs like methamphetamine.
- The money from the drug trade is used to finance terrorism, human trafficking, illegal businesses etc.
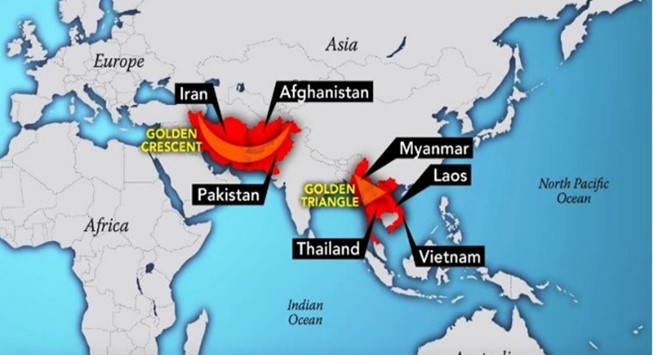
- India lies in the middle of two major illicit opium production regions in the world, the Golden Crescent in the west and the Golden Triangle in the east that makes it a viable hub of the illicit drug trade.
- Golden Triangle: It includes the regions of Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand and is Southeast Asia’s main opium-producing region and one of the oldest narcotics supply routes to Europe and North America.
- Golden Crescent: It includes Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan and is a principal global site for opium production and distribution.
- China Factor: These heroin and methamphetamine-producing areas have porous borders and are, reportedly, under the control of rebel groups, indirectly supported by the Chinese.
- Illicit arms are manufactured here and supplied to underground groups active in India.
Reasons behind Drug trafficking in India: There are several reasons behind drug trafficking in India, some of which are:
- Geographical location: India’s location between the “Golden Crescent” and “Golden Triangle” regions, which are major drug-producing areas, makes it vulnerable to drug trafficking.
- Drugs like heroin, opium, and hashish are produced in the Golden Crescent, which includes Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan, and are smuggled into India through the northwest border.
- Porous borders: India shares borders with several countries that are known for drug production and trafficking, and these borders are often poorly guarded and easily penetrated by smugglers.
- For instance, the North-East States that share borders with Bangladesh, Nepal, Myanmar, China, and Bhutan are the hot spots for drug smuggling.
- High demand: India has a large population, and there is a high demand for drugs, both for recreational and medicinal purposes.
- For example, drugs like marijuana and cocaine are in high demand in metropolitan cities like Mumbai and Delhi.
- Lack of awareness: There is a lack of awareness among people about the dangers of drug abuse, and many people do not know how to identify drug abuse or how to get help.
- For example, young people who are not educated about the risks of drug abuse are particularly vulnerable to falling prey to drug traffickers.
- Corruption: Corruption among law enforcement agencies and government officials allows drug traffickers to operate with impunity.
Challenges in tackling Drug Trafficking in India:
- Dark Net: Dark net markets are difficult to trace because of their anonymity and low risks.
- Studies reveal that 62% of the dark net is being used for illicit drug trafficking.
- The success rate in catching traffickers using the dark net has been very low the world over.
- Transactions in Cryptocurrency: Cryptocurrency payments and doorstep deliveries, through courier services, have made dark net transactions attractive.
- Traffickers have become Creative and Tech Savvy: The traffickers have adopted to new age technologies such as supplying drug and guns through drones in Punjab, which have posed new challenges before the security forces.
- Using more Safe and Anonymous methods: The drug traffickers have started relying more upon courier/parcel/post after the restrictions imposed on vehicular/ship/airline movement during Covid-19 pandemic.
- Nexus between Drugs Lords and NRIs: Recent investigations have revealed the connection of the drug cartels with NRIs based in Canada, Australia, Singapore, Hong Kong and several European countries along with local drug lords and gangsters in India, who have links with Khalistan terrorists and the ISI in Pakistan.
- Trafficking through Local Gangs: A new trend has emerged wherein organised gangs, which primarily used to carry out extortion activities in their local areas, are being used for drug trafficking, as they are ready-made logistics to carry out such activities.
Initiatives undertaken to regulate Drug trafficking in India:
- National Policy on Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS): It was introduced in 1985 to regulate drug trafficking and the use of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances in India.
- National Narcotics Coordination Portal: The multiplicity of stakeholders in Drug Law Enforcement has necessitated coordination between various agencies on real time basis.
- Integrated Rehabilitation Centres for Addicts (IRCAs): The MoSJE provides financial assistance to NGOs and voluntary organizations for the maintenance of Integrated Rehabilitation Centres for Addicts (IRCAs).
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR): The MoSJE launched the NAPDDR for 2018-2025.
- The Plan aims at reduction of adverse consequences of drug abuse through a multi-pronged strategy.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan/Drugs-Free India Campaign: It was flagged off on 15th August 2020 (Independence Day) for 272 districts across 32 State/Union Territories that have been identified as the most vulnerable in terms of usage of drugs in the country.
- It is operational with the involvement of more than 500 voluntary organizations across the country, which are assisted financially under the NAPDDR scheme.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following about seaweeds:
- They are Carbon Sequestrators.
- They form Kelp forests underwater.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following about National Statistical Office (NSO):
- It compiles and releases the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- It compiles and releases the Index of Industrial Production (IIP) every year.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following about River Hirmand/Helmand:
- It is the longest river in Iran.
- Lake Hamun is the largest freshwater lake in Afghanistan.
Which of the above is/are incorrect?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 3rd June 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 5th June – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) -a











