IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) busted the country’s biggest darknet Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) cartel.
About Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD):-

IMAGE SOURCE: southcoastrecoverycentre.co.za
- LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide) is a type of synthetic and mind-altering substance.
- This psychedelic belongs to a class of drugs called (Drug Addiction)
- Psychedelic: a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary mental states.
- Hallucinogens: a drug that causes hallucinations..
- It is a white or colorless crystalline powder.
- Oduor: It has no smell.
- Taste: it might taste bitter.
- But in this form, even the smallest dose can be strong and dangerous.
- Other names for LSD: Sugar cubes, White Lightning, Dose, Tripping, Blotter, Mellow Yellow, Dots, Windowpane, etc.
- It belongs to the same class of drugs, ergolines, that treats migraine and Parkinson’s disease.
- LSD affects the brain and central nervous system.
- It causes psychoactive effects that make one see colors, hear sounds, or lose the sense of time.
Effects of LSD:-
- Dilated pupils
- High body temperature
- High heart rate
- High blood pressure
- Lots of sweating
- Loss of appetite
- Sleeplessness
- Dry mouth
- Tremors (body shakes)
- Serious feelings of anxiousness
- Panic
- Confusion
- Violence
- Duration of effects: These effects are typically experienced within an hour or so of dosing and can last 12 to 15 hours.
About Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB):-
- Establishment: 1986.
- HQ: Delhi.
- Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs.
Background:-
- The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 which came into effect in 1985.
- It made an express provision for constituting a Central Authority to exercise the powers and functions of the Central Government under the Act. ( Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985)
- In the presence of this provision, the Government of India constituted the Narcotics Control Bureau on the 17th of March, 1986.
- Narcotics Control Bureau is the drug law enforcement and intelligence agency of India.
- It is responsible for fighting drug trafficking and the abuse of illegal substances.
Objectives of NCRB:-
- To function as a clearing house of information on crime and criminals operating at National and International levels.
- To assist the investigators, and others in linking crimes to their perpetrators.
- To store, coordinate and disseminate information on inter-state and international criminals from and to respective States, national investigating agencies, courts, and prosecutors in India without having to refer to the Police Station records.
- To collect and process crime statistics at the National level.
- To receive and supply data to penal and correctional agencies.
- To coordinate, guide and assist the functioning of the State Crime Records Bureau.
- To provide training facilities to personnel of the Crime Records Bureau.
- To evaluate, develop and modernize Crime Records Bureau.
Functions of NCB:-
- Coordination of actions by various offices, State Governments, and other authorities under the NDPS Act, Customs Act, Drugs and Cosmetics Act, and any other law for the time being in force in connection with the enforcement provisions of the NDPS Act, 1985.
- Implementation of the obligation in respect of countermeasures against illicit traffic under the various international conventions and protocols that are in force at present or which may be ratified or acceded to by India in the future.
- Assistance to concerned authorities in foreign countries and concerned international organizations to facilitate coordination and universal action for prevention and suppression of illicit traffic in these drugs and substances.
- Coordination of actions taken by the other concerned Ministries, Departments, and Organizations in respect of matters relating to drug abuse.
MUST READ: NIDAAN Portal – National Integrated Database on Arrested Narco-offenders
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) “Triclosan” considered harmful when exposed to high levels for a long time, is most likely present in which of the following? (2022)
- Food preservatives
- Fruit ripening substances
- reused plastic containers
- Toiletries
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital-raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Recently, the government said that nearly 2.46 lakh farmers have benefitted from the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM Scheme).
About (PM-KUSUM Scheme:-

IMAGE SOURCE: MyGov.in
- Launched: 2019.
- Ministry: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
Objectives of PM KUSUM:-
- To subsidize farmers to install solar irrigation pumps for cultivation.
- To ensure energy security for farmers in India,
- To honour India’s commitment to increase the share of installed capacity of electric power from non-fossil-fuel sources to 40% by 2030 as part of Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs).
- Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs): these are the intended reductions in greenhouse gas emissions under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Each farmer will receive a 60% subsidy to set up tube wells and pump sets.
- They will also get 30% of the total cost as a loan from the Government. ( PM KUSUM)
Benefits of PM KUSUM:-
For Discoms:-
- Electricity for agriculture is highly subsidized and is often termed as the main cause of the poor financial position of Discoms. ( State of DISCOMs)
- This scheme will support the financial health of discoms by reducing the burden of subsidy to the agriculture sector.
For States:-
- The scheme will promote decentralized solar power production, and reduce transmission losses.
- For state governments, this is a potential way to reduce their subsidy outlay towards irrigation.
- It will also help States meet the RPOs (renewable purchase obligation) targets.
For Farmers:-
- If farmers are able to sell surplus power, they will be incentivized to save power.
- This will mean the reasonable and efficient use of groundwater.
- It will also provide water security to farmers.
For Environment:-
- The expansion of the irrigation cover by providing decentralized solar-based irrigation will help in moving away from polluting diesel.
- This will also fill the void in solar power production in the intermediate range between rooftops and large parks.
MUST READ: Solar Energy in India
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organization that drives climate action by building large networks and running them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) The Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE) a UN mechanism to assist countries to transition towards greener and more inclusive economies, emerged (2018)
- The Earth Summit on Sustainable Development 2002, Johannesburg
- The United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development 2012, Rio de Janeiro
- The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change 2015, Paris
- The World Sustainable Development Summit 2016, New Delhi
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: A delegation from the Confederation of Indian Industries and Vivekananda International Foundation met the Governor of the Northern Province of Sri Lanka recently.
Background:-
- The visit of the delegation is directed at exploring investments across multiple sectors in Sri Lanka’s Northern Province.
About Confederation of Indian Industries (CII):-
- Establishment: 1895.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It is a non-government, not-for-profit, industry-led and industry-managed organization.
- Objectives: It works to create and sustain an environment conducive to the development of India, partnering with industry, Government, and civil society, through advisory and consultative processes. ( CII)
Functions of CII:-
- To identify and strengthen the industry’s role in the economic development of the country.
- To act as a catalyst in bringing about the growth and development of Indian Industry. (Cooperative Sector Reforms)
- To reinforce the industry’s commitment to society.
- To provide up-to-date information and data to industry and government
- To create awareness and support the industry’s efforts on quality, environment, energy management, and consumer protection.
- To identify and address the special needs of the small sector to make it more competitive.
- To promote cooperation with counterpart organizations.
- To work towards the globalization of Indian industry and integration into the world economy.
About Vivekananda International Foundation:-
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It is a think tank set up with the collaborative efforts of India’s leading security experts, diplomats, and philanthropists under the aegis of the Vivekananda Kendra.
- Objective: to become a center of excellence to kick start innovative ideas and thoughts that can lead to a stronger, secure, and prosperous India playing its destined role in global affairs.
MUST READ: Quality Council of India (QCI)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following heavy industries: (2023)
- Fertilizer plants
- Oil refineries
- Steel plants
Green hydrogen is expected to play a significant role in decarbonizing how many of the above industries?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
India accounts for 3·2% of the global export of goods.
Statement-II :
Many local companies and some foreign companies operating in India have taken advantage of India’s ‘Production-linked Incentive’ scheme.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: As per recent reports, the combined Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) increased by 8.2 percent in June this year as compared to the Index of June 2022.
Background:-
- The production of Steel, Coal, Cement, Refinery Products, Natural Gas, Fertilizers, and Electricity increased in June 2023 over the corresponding month of last year.
- Final growth rate of the Index of Eight Core Industries for March 2023 is revised to 2 percent from its provisional level of 3.6 percent.
- The cumulative growth rate of ICI during the quarter April to June 2023-24 is reported to be 8 percent (provisional) as compared to the corresponding period of last year.
About the Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI):-

IMAGE SOURCE: indiangovtscheme.com
- Published by: National Statistical Office (NSO).
- Time period: It is compiled and published
- Base Year for IIP is 2011-2012.
- Ministry: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. (Index of Industrial Production (IIP))
- ICI measures combined and individual performance of the production of eight core industries.
- These include Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilizers, Steel, Cement, and Electricity.
- These Eight Core Industries comprise 40.27 percent of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
- The eight core sector industries in decreasing order of their weightage: Refinery Products> Electricity> Steel> Coal> Crude Oil> Natural Gas> Cement> Fertilizers.
- It is a composite indicator that measures the growth rate of industry groups classified under:-
- Broad sectors: Mining, Manufacturing, and Electricity.
- Use-based sectors: Basic Goods, Capital Goods, and Intermediate Goods.
- Details of annual and monthly indices and growth rates are provided in Annex I & II respectively.
Significance of IIP:-
- It is used by government agencies including the Ministry of Finance, the Reserve Bank of India, etc., for policy-making purposes.
- IP is the only measure of the physical volume of production.
- It forms a crucial input for the compilation of the Gross Value Added (GVA) of the manufacturing sector in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) on a quarterly basis.
- IIP remains extremely relevant for the calculation of quarterly and advanced GDP estimates. ( Provisional GDP)
- It is also used extensively by financial intermediaries, policy analysts, and private companies for various analytical purposes.
- It provides an advanced indication of the production performance of industries of a ‘core’ nature prior to the IIP
MUST READ: Purchasing Manager’s Index
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following brings out the ‘Consumer Price Index Number for Industrial Workers’? (2017)
- The Reserve Bank of India
- The Department of Economic Affairs
- The Labour Bureau
- The Department of Personnel and Training
Q.2) In the ‘Index of Eight Core Industries’, which one of the following is given the highest weight? (2015)
- Coal production
- Electricity generation
- Fertilizer production
- Steel production
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, UNESCO has removed Australia’s Great Barrier Reef from its “in danger” list.
Background:-
- Off late, Australia’s Great Barrier was under “serious threat” from pollution, warming of oceans, and constant coral bleaching events. Therefore, the UNESCO committee put the reef on the danger list.
- However, UNESCO removed the Reef from its “in danger” list, due to the Australian government’s efforts and commitments towards keeping the reef clean.
About Great Barrier Reef:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Maps of the World
- Location: Coral Sea (North-East Coast), off the coast of Queensland, Australia.
- It is the world’s most coral reef ecosystem composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands.
- This reef structure is composed of and built by billions of tiny organisms, known as coral polyps, form the structure of coral reefs.
- Coral polyps: tiny, soft-bodied organisms and their base which is a hard, protective limestone skeleton called a calicle.
- These polyps have microscopic algae called zooxanthellae living within their tissues.
- The corals and algae have a mutualistic (symbiotic) relationship.
- Mutualism: a long-term relationship between individuals of different species where both individuals benefit.
- It is the largest aggregation of coral reefs in the world. ( Third mass bleaching of Great Barrier Reef recorded)
- It was selected as a World Heritage Site in 1981. (Great Barrier Reef recommended to be added to a list of “in danger” World Heritage Sites)
Advantages of Coral Reef:-
- Protect humanity from natural calamities.
- Provide revenue and employment through tourism and recreation.
- Provide habitats for fishes, starfish, and sea anemones.
Use of Coral Reef:-
- They are used in
- Coral blocks are used for buildings and road construction.
- The lime supplied by corals is used in cement industries.
Threats to Coral Reefs:-
- Anthropogenic activities: such as coastal development, destructive fishing methods, and pollution from domestic and industrial sewage.
- Due to increased sedimentation, over-exploitation, and recurring cyclones.
- Coral diseases: such as black band and white band due to infectious microorganisms introduced by the human population that lives in the coastal regions.
- Ocean Acidification.
- Overfishing and overharvesting of corals.
- Coral bleaching.
- Sunscreen chemicals.
- Many corals are threatened by the illegal harvesting of jewelry.
Coral Reef Areas in India:-
- Gulf of Mannar,
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands,
- Lakshadweep islands
- Gulf of Kutch.
MUST READ: New species of black corals
SOURCE: TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Some microorganisms can grow in environments with· temperatures above the boiling point of water.
- Some microorganisms can grow in environments with temperatures below the freezing point of water.
- Some microorganisms can grow highly acidic environments with a pH below 3.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Some species of turtles are herbivores
- Some species of fish are herbivores.
- Some species of marine mammals are herbivores
- Some species of snakes are viviparous
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3, and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Awards
Context: Recently, Prime Minister Modi was conferred Lokmanya Tilak National Award.
Background:-
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi was given the Lokmanya Tilak National Award for his outstanding contributions towards the progress of the country.
- He was given the award at a function in Pune this afternoon.
About Lokmanya Tilak National Award:-
- Instituted: 1983
- Instituted by: Tilak Smarak Mandir Trust.
- This award is given every year on 1st August.
- Significance: It is to mark the death anniversary of Lokmanya Tilak.
- It is awarded to persons who have made remarkable and extraordinary contributions, working for the progress and development of the nation. (UNational Lalit Kala Akademi awards)
About Bal Gangadhar Tilak:-
- Birth: July 23, 1856.
- Birthplace: Ratnagiri (now in Maharashtra state), India.
- Death: August 1, 1920, in Mumbai.
- He was a scholar, mathematician, philosopher, and ardent nationalist who helped lay the foundation for India’s independence by building his own defiance of British rule into a national movement.
- He was also known as Lokmanya Tilak.
- His famous declaration “Swaraj is my birthright, and I shall have it” served as an inspiration for future revolutionaries during India’s struggle for freedom.
- The British Government termed him the “Father of Indian Unrest”. (Sedition Law)
Important Institutions Started by Tilak:-
- Deccan Education Society (1884): He was the founder of the Deccan Education Society along with his associate Gopal Ganesh Agarkar and others.
- Fergusson College (1885): He was one of the founders of Fergusson College in Pune.
Political ventures of Tilak:-
- 1890: He joined the Indian National Congress (INC).
- Tilak protested against the oppressive nature of the British efforts and wrote provocative articles on it in his newspapers on the epidemic of the Plague in Pune and adjacent regions.
- His article inspired the Chapekar brothers and they carried out the assassination of Commissioner Rand and Lt. Ayerst on June 22.
- Because of this, Tilak was imprisoned for 18 months on Sedition charges for inciting murder. Sedition Law)
- Indian Home Rule League (1914): He founded the Indian Home Rule League.
- Lucknow Pact (1916): he concluded the Lucknow Pact with Mohammed Ali Jinnah, which provided for Hindu-Muslim unity in the nationalist struggle.
Newspapers by Tilak:-
- Weeklies: Kesari (Marathi) and Mahratta (English)
Books by Tilak:-
- Gita Rhasya
- Arctic Home of the Vedas.
MUST READ: Padma awards
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards: (2021)
- Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards are titled under Article 18(1) of the Constitution of India.
- Padma Awards, which were instituted in the year 1954, were suspended only once.
- The number of Bharat Ratna Awards is restricted to a maximum of five in a particular year.
Which of the above statements is not correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements in respect of the 44th Chess Olympiad, 2022: (2023)
- It was the first time that Chess Olympiad was held in India.
- The official mascot was named Thambi’.
- The trophy for the winning team in the open section is the Vera Menchik Cup.
- The trophy for the winning team in the women’s section is the Hamilton-Russell Cup.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: The Confederation of All India Traders (CAIT) has announced the creation of the National Digital Nagrik Forum.
About National Digital Nagrik Forum:-
- It is an online platform that aims to advance the rights of traders and consumers and shape policy to boost the digital trade economy.
- Objective: to raise awareness about digital regulations and help build the capacities of citizens to engage with innovation via expert sessions and instructional materials.
- It will conduct awareness camps, digital and physical dialogues, and training.
- It will reach out to stakeholders from the government, private sector, and civil society, including policymakers and other relevant stakeholders at the state level towards realizing its objectives.
Five Themes of National Digital Nagrik Forum:-
It will focus on five core themes.
- First: consumer protection and online safety with a core focus on efficient grievance redressal.
- Second: pitfalls of digital cartelization and how a level-playing field is necessary to discourage discriminatory and anti-competitive practices in the online world.
- Third: the potential of Indian digital technologies to not only transform retail and industrial trade but also boost employment and expand the investment footprint.
- Fourth: a first principles-based taxation policy that encourages certainty and productivity, especially for sectors with high growth potential, while preventing illegal activities such as tax evasion and money laundering.
- Fifth: the forum will study emerging technologies, such as blockchain and artificial intelligence, to assess their impact on retail trade and, at the same time, safeguard consumers’ interests.
About Confederation of All India Traders (CAIT):-
- Founded: 1990.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It is the apex body of the trading community in India.
- Objective: representing and protecting the interests of traders.
- It has over 8 crore members and over 40,000 affiliated trade associations across India.
Functions of CAIT:-
- To render the best possible assistance to Trading Community.
- To communicate with Administrators concerned to seek redress of legitimate grievances of Traders.
- To impart education to Traders to upgrade their performance to render the most satisfactory service to consumers by adhering to fair trading policy.
- To lend full cooperation to the Govt. in streamlining the existing system.
- organize Seminars, Conferences and lectures, etc.
- To lay down a code of conduct for Traders to pursue business activity.
- To adopt digitalization, computerization, adoption & acceptance of digital payments and other significant digital technology in the existing business format of domestic trade of India.
- To create an Indian E-Commerce Portal promoting Indian Goods. E-Commerce)
MUST READ: New-age digital commerce
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of finance, the term ‘beta’ refers to (2023)
- the process of simultaneous buying and selling of an asset from different platforms ·
- an investment strategy of a portfolio manager to balance risk versus reward
- a type of systemic risk that arises where perfect hedging is not possible
- a numeric value that measures the fluctuations. of stock to changes in the overall stock market.
Q.2) With reference to foreign-owned e-commerce firms operating in India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2022)
- They can sell their own goods in addition to offering their platforms as marketplaces.
- The degree to which they can own big sellers on their platforms is limited.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Preserving Tribal Culture
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The vision of inclusive growth and community-led development is not an idea but an actionable strategy for Odisha in its 5T (transparency, technology, teamwork, time-limit, leading to transformation)-driven development model.
Tribal population in India
- India comprises 8.6% tribal population, has access to an enormous indigenous knowledge, which through recognition, adoption, and mainstreaming has the potential to provide sustainable solutions.
- According to article 342 of the Indian Constitution, the President may with respect to any State or Union territory specify the tribes, tribal communities, parts of, or groups within tribes or tribal communities as Scheduled Tribes in relation to that State or Union territory.
Odisha’s Special Development Councils (SDCs) initiative
- In a significant move towards preserving, promoting, and popularising tribal culture while also continuing with the development process, the Odisha government launched the Special Development Councils (SDCs) initiative in 2017.
- This is an active effort to preserve the culture and heritage of 62 tribes in the State under one umbrella while keeping economic development on course in the regions.
- The scheme, which covered 9 tribal-dominated districts and 60 lakh tribal households in 117 blocks, has now been expanded to 23 districts covering more than 84 lakh tribal people.
About Tribal Cultures:
- Communal living: Many tribal communities in India have a strong emphasis on communal living and sharing resources.
- They live in close-knit communities and often make decisions collectively.
- Self-Sufficiency: Tribe is a synonym for a self-reliant community, a tribe is a relatively closed society and its openness is inversely related to the extent of its self-sufficient pursuits.
- Connection with nature: Tribals have a strong connection with nature, with traditional beliefs and practices that revolve around the forests and animals.
- Folk arts and crafts: Tribals are known for their unique art forms, including pottery, weaving, and jewellery making.
- Spiritual beliefs: Tribals often have their own unique spiritual beliefs, which may involve the worship of ancestors, nature spirits, or deities.
Tribal Lifestyle and Sustainable development:
- Respect for the natural environment: Tribal traditional practices, such as using natural materials for housing, food, and medicine, and living in harmony with the cycles of nature.
- Community-based decision-making: Collective decision-making considers the needs of the community as a whole and ensures that decisions are made in a sustainable and equitable manner.
- Promotion of biodiversity: Tribals have developed practices to protect and promote diversity, which includes traditional methods of agriculture, such as intercropping and seed saving, as well as the protection of sacred sites that are important for the preservation of biodiversity.
- Conservation of natural resources: Sustainable practices involve limiting the use of resources to ensure their long-term availability, such as rotational farming or allowing forests to regenerate before harvesting timber.
- Emphasis on intergenerational knowledge sharing: Passing down knowledge to the next generation includes traditional knowledge of the natural environment and sustainable practices for managing resources.
- Protection of water resources: Tribal communities rely on water resources and have developed practices that can help to ensure that water is available for future generations, and can reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Regenerative agriculture: tribal communities have been practicing regenerative agriculture for centuries, which involves practices like crop rotation, intercropping, and regenerating soils with organic matter.
- These practices help to sequester carbon in the soil, which can help to mitigate climate change.
- Use of renewable energy: They have traditionally used renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydropower, which can be expanded and modernized to provide clean energy for more people.
Challenges faced by tribals in performing their lifestyle
- Discrimination: Tribal communities often face discrimination and prejudice from the dominant society, including limited access to education, healthcare, and other basic services.
- Land rights: Tribal communities have been displaced from their traditional lands due to industrialization, and mining, which has resulted in the loss of cultural identity, and social and economic marginalization.
- Climate change and environmental degradation: Climate Change, such as changes in rainfall patterns, increased frequency of natural disasters, loss of biodiversity, deforestation, pollution, and loss of habitat, has negatively affected their traditional livelihoods and ways of life.
- Socioeconomic marginalization: Many tribal communities have limited access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities, which can result in poverty and social exclusion.
- Lack of political representation: Tribal communities often lack political representation and may not have a voice in decision-making processes that affect their lives.
- Cultural assimilation: Many tribal communities face pressure to assimilate into the dominant culture, which can lead to the loss of traditional knowledge, language, and cultural practices.
Government initiatives to conserve tribal culture:
- National Scheduled Tribes Finance and Development Corporation (NSTFDC), an apex Organization under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs in 2001 was brought into existence with the sole aim of economic upliftment of the Scheduled Tribes by way of extending concessional financial assistance to the target group under its various schemes.
- TRIFED’s Initiatives for Tribal Population: The Government plans to establish 50,000 Van Dhan Vikas Kendras, 3000 Haat Bazaars, etc.
- Central Sector Scheme: Institutional Support for Development & Marketing of Tribal Products / Produce.
- Pradhan Mantri Van Dhan Yojana: It is a market-linked tribal entrepreneurship development program for forming clusters of tribal Self Help Groups (SHGs) and strengthening them into Tribal Producer Companies.
- Scholarships for pre-matric, post-matric, and overseas education
- Support to National Scheduled Tribes Finance and Development Corporation
- Development of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs): The scheme covers activities like housing, land distribution, land development, agricultural development, animal husbandry, construction of link roads, etc.
- Vocational Training in Tribal Area: The aim of the Scheme is to develop the skills of the ST youth for a variety of jobs as well as self-employment and to improve their socio-economic condition by enhancing their income.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: The mechanism for Marketing of Minor Forest Produce (MFP) through (MSP) and Development of a Value Chain for MFP’ as a measure of social safety for MFP gatherers.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: The health ministry plans to revamp guidelines for approving biosimilar drugs to make the regulatory pathway more robust and synchronize it with the rapidly evolving global landscape.
About Biosimilar:
- A biosimilar is , it is a biologic that is “similar” to another biologic medicine (known as a reference product), Biosimilars are highly similar to the reference product in terms of safety, purity and potency, but may have minor differences in clinically inactive components.
- Biosimilars are not new drugs, but rather they are copies of biologic drugs that have been used to treat many diseases and conditions.
- Familiar biologic drugs include widely prescribed therapies like etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab and others.
Difference between biosimilars and generics:
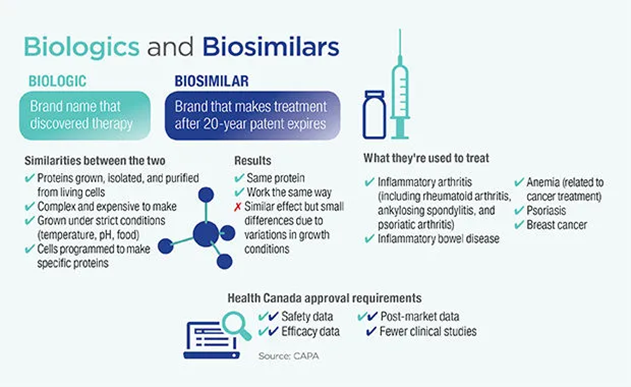
- Biosimilars involve developing equivalent of biological entity while generics involve developing equivalent of a chemical entity-the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient.
- In case of biosimilars, biological entities being some ward different (and not as it is of replica), every organism has to be engineered to produce the same therapeutic effect while in generics, the copies of API can be generated
- Bio-similars differ from generics – in complexity, in the manufacturing processes and in the data needed to demonstrate similarity for approval.
- The structure of Generic Simple and well-defined whereas for Bio-similar its Complex with potential structural variations.
- Regulatory procedure to get approval for biosimilars is complex as compared to that of a generic.
Prospects for biosimilars
- Market growth in biologics for cancer (monoclonal antibodies), diabetes (insulin) and many other autoimmune diseases has opened up new opportunities for biosimilars worldwide.
- Many Indian pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in the development of biosimilars.
- The first biosimilar version of trastuzumab emtansine not only prevents the growth of cancer cells (trastuzumab), but also delivers a cytotoxic agent to the cancer cell and helps destroy it.
- The market for biosimilars is expanding because they are cheaper than biologics, whose high cost puts them out of reach for many patients.
- Complex generic and similar biological medicines are designed to treat non-communicable diseases such as cancer, asthma and arthritis, and encouraging their manufacture can have a positive impact on development.
Challenges of biosimilars:
- The expensive and lengthy development process can take six to seven years.
- Temperature has a significant impact on the preservation of biosimilars due to their high sensitivity.
- Therefore, they must be distributed through a cold chain network.
- Biosimilars and generics differ significantly in production costs and investments in machinery, buildings and other assets.
The regulation and development of biosimilars in India includes:
- Department of Biotechnology (DBT)
- Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO)
- Indian council of Medical Research (ICMR)
- Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC)
- National Control Laboratory Biosafety Committee
Different laws and guidelines that Biosimilars fall under:
- Drugs and Committee Act (1940)
- Drugs and Cosmetics Rules (1945)
- Environment Protection Act (1986)
- Recombinant DNA Safety Guidelines (1990)
- Guidelines for preclinical and clinical data for rDNA vaccines, diagnostics and other biologicals (1999)
- CDSCO guidance for Industry (2008)
Way forward
Thus to ensure dishonest and unethical activities, a regulatory structure must be established and proper inspection must be implemented. India needs to invest in basic research and training to grow its biological research ecosystem.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Coral reef type | Description |
| 1.Fringing reefs | They are shaped circularly or elliptically and are surrounded by seas on all four sides. |
| 2.Atolls | They develop near the continent and remain close to the coastline. |
| 3.Barrier reefs | They usually run parallel to the coastline at some distance. |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide) is a Psychedelic.
Statement-II:
It belongs to the same class of drugs, ergolines, that treats migraine and Parkinson’s disease.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Australia’s Great Barrier Reef has been removed from UNESCO’s “in danger” list.
Statement-II:
It was selected as a World Heritage Site in 1981.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) What is the significance of culture-sensitive and culture-inclusive tribal development in India? Discuss (250 words)
Q.2) What are Biosimilar technology? Discuss its applications along with challenges. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 2nd August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 1st August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) -d











