IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) doctors have warned against using steroids for eye treatment.
Background:-
- As cases of Conjunctivitis (eye flu) are rising in North India including the national capital Delhi, the senior doctor in the All India Institute of Medical Sciences-AIIMS have warned against using steroids for eye treatment.
About Steroids:-
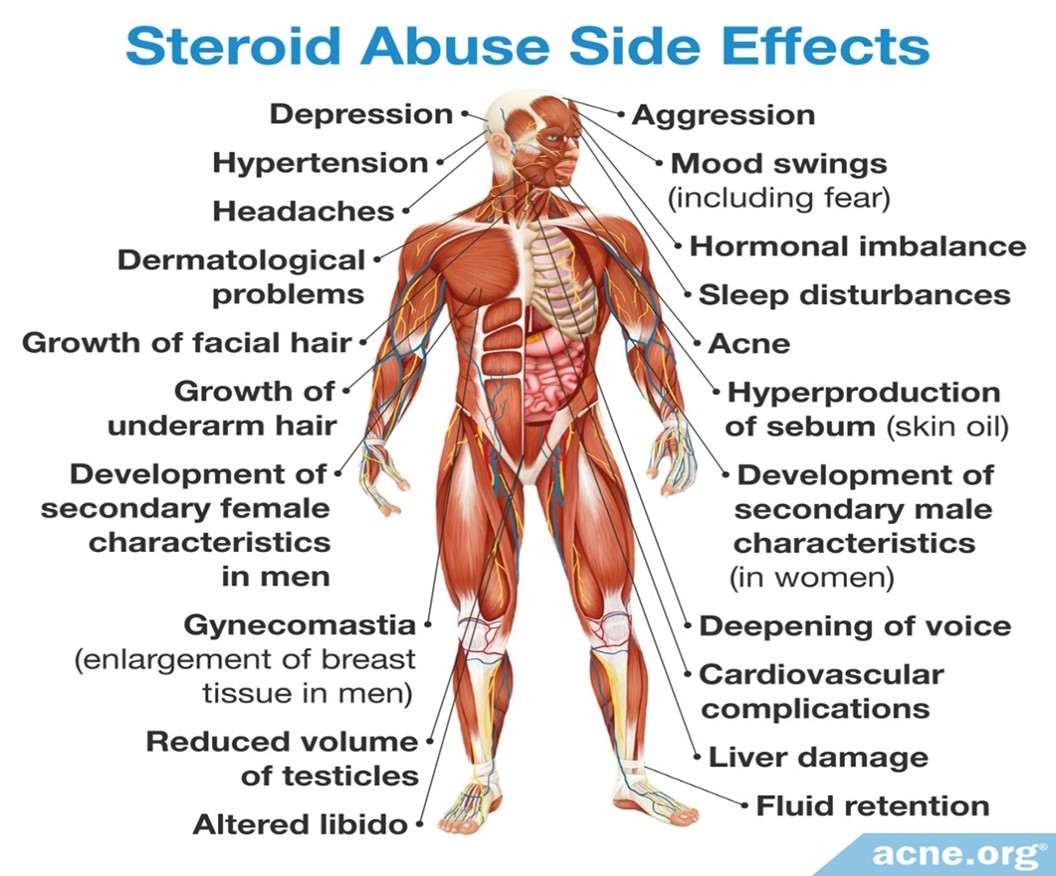
IMAGE SOURCE: acne.org
- Steroids are biologically active organic compounds.
- Steroids are a type of lipid molecule made up of 4 fused carbon rings.
- Different steroids vary slightly in their structure, but they all have 4 fused carbon rings.
- The most common steroid in our bodies is
- Hundreds of steroids can be found in animals, plants, and fungi.
- Steroid medicines are man-made and are similar to the natural hormones made in the body.
- Corticosteroids: the type of steroids used to treat disease.
- Anabolic steroids: used by some athletes and bodybuilders. (Anabolic Steroids)
The principal functions carried out by steroids include-
- It acts as an important component for the cell membrane where it alters the fluidity of the membrane.
- These also act as signaling molecules.
Side effects of Steroids:-
- Acne.
- High blood pressure.
- Difficulty in sleeping.
- Blurred or loss of vision.
- Weight gain. (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs))
- Indigestion (dyspepsia).
- Heartburn (acid reflux).
- Increased appetite, which may cause weight gain.
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia).
- Increased risk of infections, especially viral infections such as shingles or measles.
- Pre-diabetes or type 2 diabetes.
- Weakening of the bones (osteoporosis).
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
- Eye conditions, such as glaucoma and cataracts.
- Mental health problems, including:
- Changes in mood (mood swings) and behavior – eg, feeling irritable or anxious.
- Depression
MUST READ: Ibuprofen
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of probiotics: (2022)
- Probiotics are made of both bacteria and yeast.
- The organisms in probiotics are found in foods we ingest but they do not naturally occur in our gut.
- Probiotics help in the digestion of milk sugars.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
Q.2) Bisphenol A (BPA), a cause of concern, is a structural/key component in the manufacture of which of the following kinds of plastics? (2022)
- Low-density polyethylene
- Polycarbonate
- Polyethylene terephthalate
- Polyvinyl Chloride
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recent reports suggest that the National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC) delivered record performances in Fiscal Year 2023-2024 so far.
Background:-
- NMDC is paving the way towards becoming a 100 Million Tonnes (MT) mining company.
About National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC):-
- Establishment: 1958.
- Ministry: Ministry of Steel.
- HQ: Hyderabad.
- Vision: To emerge as a global Environment-friendly Mining Organization and as a quality Steel producer with a positive thrust on Social Development. . (Iron-Ore Policy 2021)
- It is India’s largest iron ore producer. ( Iron Ore)
- The company has been categorized by the Department of Public Enterprises as a “Navratna” Public Sector Enterprise in 2008.
Objectives of NMDC:-
Macro Objectives
- To expand the operations in the areas of Mining and Mineral Processing to meet the growing demands from domestic and international Markets.
- Achieve international standards in per capita productivity, value addition, and cost-effectiveness.
- To increase the iron ore production capacity to 67 MTPA by FY 2025.
- Setting up of Steel Plant at Nagarnar.
Micro Objectives
- Give thrust to the exploration and exploitation of iron ore and other strategic & critical minerals.
- To maintain environmental protection.
- To conserve mineral resources through scientific mining.
- To maintain a high level of customer satisfaction.
- To improve the quality of life of people in general and the socio-economic environment in and around the mines in particular.
MUST READ: Report
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
Switzerland is one of the leading exporters of gold in terms of value.
Statement-II:
Switzerland has the second-largest gold reserves in the world
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q.2) Consider the following minerals: (2020)
- Bentonite
- Chromite
- Kyanite
- Sillimanite
In India, which of the above is/are officially designated as major minerals?
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3, and 4 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: As per the recent reports of the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), a record six crore 77 lakh Income Tax Returns, have been filed for 2023-24.
Income Tax Return:-
- These are forms used to declare net tax liabilities, claim tax deductions, and report gross taxable income.
- Income Tax Return Forms are notified by CBDT.
About Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT):-
- Establishment: 1963.
- Ministry: Ministry of Finance.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Administered by: Department of Revenue.
- It is a statutory authority functioning under the Central Board of Revenue Act, of 1963.
- The Central Board of Revenue is the apex body of the Department of Revenue.
- It is charged with the administration of taxes.
- It came into existence as a result of the Central Board of Revenue Act, of 1924.
- It is India’s official financial action task force unit.
Historical Background of CBDT:-
- Initially the Board was in charge of both direct and indirect taxes. Increase in Direct Tax Collections)
- However, when the administration of taxes became too unwieldy for one Board to handle, the Board was split up into two, namely the Central Board of Direct Taxes and Central Board of Excise and Customs with effect from 1964.
Functions of CBDT:-
- Making Policies regarding the discharge of statutory functions of the Board and of the Union Govt. under the various laws relating to direct taxes. ( CBDT and Income Tax Return Forms)
- General Policy relating to:-
- Organization of the set-up and structure of the Income-tax Department.
- Methods and procedures of work of the Board.
- Measures for disposal of assessments, collection of taxes, prevention, and detection of tax evasion and tax avoidance.
- Recruitment, training, and all other matters relating to service conditions and career prospects of the personnel of the Income-tax Department.
- Laying down targets and fixing priorities for disposal of assessments and collection of taxes and other related matters.
- Write off of tax demands exceeding Rs. 25 lakhs in each case.
- Making Policy regarding grant of rewards and appreciation certificates.
- Any other matter which the Chairman or any Member of the Board, with the approval of the Chairman, may refer for joint consideration of the Board.
MUST READ: One nation, One ITR Form
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements are correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital-raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) In India, which one of the following is responsible for maintaining price stability by controlling inflation? (2022)
- Department of Consumer Affairs
- Expenditure Management Commission
- Financial Stability and Development Council
- Reserve Bank of India
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Environment
Context: Recently, it was reported that Assam’s Manas Tiger Reserve is 63% short of staff.
About Manas Tiger Reserve:-

IMAGE SOURCE: ejatlas.org
- Location: it spans across the district of Kokrajhar, Chirang, Buxa, and Udalguri in northwest Assam.
- Area: 12 sq. km.
- It is located in the Himalayan foothills in Assam.
- It is contiguous with the Royal Manas National Park in Bhutan.
- The name of the park originated from the Manas River.
- The Manas River flows through the west of the park.
- Manas is a major tributary of the Brahmaputra River.
- Significance: The Park is known for its rare and endangered endemic wildlife such as the Assam roofed turtle, hispid hare, golden langur, and pygmy hog. It is also famous for its population of wild water buffalo.
Historical Background:-
- Before 1928, Manas National Park was a reserve forest and called Manas R.F. and North Kamrup R.F.
- 1928: The park’s 360 sq. km area was designated as a wildlife sanctuary.
- Between 1951 and 1955, the forest area was increased to 391 km², and Manas Biosphere Reserve was established in the year 1973.
- 1973: it was declared among India’s First Tiger Reserves under Project Tiger.
- 1985: it was declared a World Heritage Site (Natural) by UNESCO for Outstanding Universal Conservation Value.
- 1989: It was declared a Biosphere Reserve.
- 1990: it was declared a National Park.
- 2003: it was declared an Elephant Reserve.
- 2006: Under Indian Rhino Vision 2020, Manas was re-introduced with the famous One Horned Rhinoceros.
- 2014: it is also recognized as a Tiger Source Site for Conservation. (UPSC CSE: Amrabad Tiger Reserve)
Flora:–
- The combination of Sub-Himalayan Bhabar Terai and the Himalayan subtropical broadleaf forests.
- There are four types of vegetation in Manas National Park: Sub-Himalayan Light Alluvial Semi-Evergreen forests (northern parts); East Himalayan mixed Moist and Dry Deciduous forests; Low Alluvial Savanna Woodland, and Assam Valley Semi-Evergreen Alluvial Grasslands. ( Manas National Park)
- Common tree species in Manas National Park: Anthocephalus Chinensis, Aphanamixis Polystachya, Syzygium Formosum, Syzygium Cumini, etc.
Fauna:-
- The park has rich wildlife where a large number of animals and birds co-exist.
- Animal Species in Manas National Park: Asian Elephants, Indian Rhinoceros, Gaurs, Asian Water Buffaloes, etc.
- Birds Species in Manas National Park: Bengal Florican, Giant Hornbills, Jungle Fowls, Bulbuls, Brahminy Ducks, etc.
MUST READ: Kaziranga National Park
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (2020)
- Corbett
- Ranthambore
- Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
- Sunderbans
Q.2) Which one of the following protected areas is well-known for the conservation of a sub-species of the Indian swamp deer (Barasingha) that thrives well on hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous? (2020)
- Kanha National Park
- Manas National Park
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Tal Chhaper Wildlife Sanctuary
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, Home Minister Amit Shah launched a digital portal of the Central Registrar of Cooperative Societies office.
Background:-
- The Ministry of Cooperation said that the main objectives of computerization of the Central Registrar’s Office are Completely paperless application, Automatic compliance with the Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act (MSCS Act) and Rules, Ease of Doing Business, Digital communication and Transparent processing.
About the Digital Portal of the Central Registrar of Cooperative Societies:-
- Launched:2023.
- Ministry: Ministry of Cooperation.
- The office of the Central Registrar is responsible for administering the Multi-State Cooperative Societies (MSCS) Act, 2002. ( Multi-State Cooperative Societies (Amendment) Bill, 2022)
- Significance: The Central Registrar’s Office is being computerized to ease all the activities of multi-state cooperatives and to create a digital ecosystem, including registration of new multi-state cooperatives.
- Co-operative society: a voluntary association of individuals who come together with the intention to work together and promote their economic interests.
Objectives of the Digital Portal of the Central Registrar of Cooperative Societies:-
- Completely paperless application and processing
- Automatic compliance with Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act (MSCS Act) and Rules through software
- Enhancing Ease of Doing Business
- Digital communication
- Transparent processing ( Cooperative Sector Reforms)
- Improved Analytics and MIS (Management Information Systems)
MUST READ: India’s Cooperative Sector
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- The Self-Help Group (SHG) programme was originally initiated by the State Bank of India by providing microcredit to the financially deprived.
- In an SHG, all members of a group take responsibility for a loan that an individual member takes.
- The Regional Rural Banks and Scheduled Commercial Banks support SHGs.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) With reference to Urban Cooperative Banks in India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, of 1949 through an Amendment in 1996
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Cabinet approved ₹1.39 lakh crore for the BharatNet project.
About the BharatNet project:-
- Launched:2011.
- Ministry: Ministry of Communications.
- Implemented by: Bharat Broadband Network Ltd. (BBNL).
- BBNL: a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) set up by the Government of India under the Companies Act, 1956 with an authorized capital of Rs 1000 crore.
- Initially, it was under the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology, which was bifurcated into the Ministry of Communications and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology in July 2016.
- Currently, it is being implemented by the Department of Telecommunication under the Ministry of Communications.
- BharatNet is one of the biggest rural telecom projects in the world.
- Objective: to facilitate the delivery of e-governance, e-health, e-education, e-banking, Internet, and other services to rural India.
- Historical Background:-
- Bharat Net Project was originally launched as the National Optical Fibre Network(NOFN).
- It was renamed as Bharat-Net in 2015.
- It seeks to provide connectivity to 2.5 lakh Gram Panchayats (GPs) through an optical fibre.
- Funding: The entire project is being funded by the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF), which was set up for improving telecom services in rural and remote areas of the country. ( Bharat Net Project)
Phases of the Project:-
First Phase:-
- To provide one lakh gram panchayats with broadband connectivity by laying underground Optic Fibre Cable (OFC) lines by December 2017.
Second Phase:-
- To Provide connectivity to all the gram panchayats in the country using an optimal mix of underground fibre, fibre over power lines, radio, and satellite media by March 2019.
Third Phase:-
- From 2019 to 2023, a state-of-the-art, future-proof network, including fibre between districts and blocks, with ring topology to provide redundancy would be created. ( India Matters)
MUST READ: E-PANCHAYAT FACILITY
SOURCE: BUISINESS LINE
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements (2023)
- Carbon fibres are used in the manufacture of components used in automobiles and aircraft.
- Carbon fibres once used cannot be recycled.
Which of the statements given above Is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements in relation to Janani Suraksha Yojana : (2023)
- It is a safe motherhood intervention of the State Health Departments.
- Its objective is to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality among poor pregnant women.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women.
- Its objective includes providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the President of India, Smt Droupadi Murmu inaugurated ‘Unmesha’ and ‘Utkarsh’ festivals.
Background:-
- The President of India, Smt Droupadi Murmu inaugurated ‘Unmesha’ – International Literature Festival and ‘Utkarsh’ – Festival of Folk and Tribal Performing Arts on August 3, 2023, at Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
About Unmesha festival:-
- It is India’s most inclusive and Asia’s largest literature festival in terms of the number of languages represented.
- ‘Unmesha 2023’ will be the second edition of ‘Unmesha’.
- The first event was held in Shimla in June 2022.
- More than 575 authors in 102 languages are expected to participate in over 75 events in ‘Unmesha 2023’.
- Writers from 13 countries will participate in the festival.
About UTKARSH festival:-
- It showcases the folk and tribal Performing Arts.
- It casts a spotlight on the treasure trove of India’s folk and tribal heritage, endowing these expressive art forms with a resplendent stage to captivate. National Tribal Dance Festival 2022)
- Significance: ‘Utkarsh’ serves as a vital launchpad for traditional artists and performers to unfurl their artistry, safeguarding the priceless heritage of myriad communities. (Significance of Tribal Culture in Sustainable Development)
- Amidst its vibrant canvas, ‘Utkarsh’ brings forth a vivid tableau of cultural diversity, nurturing an appreciation for indigenous arts and underscoring their intrinsic value in an increasingly interconnected world.
MUST READ: Asia’s Largest Tribal Festival commences: Medharam Jathara
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India, the terms ‘Halbi, Ho, and Kui’ pertain to (2021)
- dance forms of Northwest India
- musical instruments
- pre-historic cave paintings
- tribal languages
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2021)
- 21st February is declared to be International Mother Language Day by UNICEF.
- The demand that Bangla has to be one of the national languages was raised in the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Urbanisation and associated issues
Syllabus
- Mains – G S 1 (Society and Social Issues) and GS 2 (Governance)
Context: With the increasing pace of urbanisation along with the baggage of problems it comes.
About Urbanisation:
- Urbanisation is the process of transformation that occurs as a society evolves from predominantly rural to predominantly urban areas.
- It involves the increase in the proportion of a country’s population residing in urban areas, leading to the expansion and growth of cities and towns.
- Urbanisation is not just about the physical expansion of cities but also encompasses social, economic, and cultural transformations.
- It involves the migration of individuals from rural to urban areas in pursuit of employment opportunities, improved living standards, access to better education and healthcare facilities, and a more cosmopolitan lifestyle.
Important characteristics of the urban system
Population Density: Urban areas are characterised by high population density, with a large number of people residing in relatively small geographical areas.
- This density leads to the concentration of social, economic, and cultural activities, promoting interaction and exchange.
Diverse Economic Activities: Urban systems are centres of economic growth and diversification.
- They offer a wide range of employment opportunities across various sectors such as manufacturing, services, finance, technology, and creative industries.
- The presence of diverse economic activities attracts people seeking better job prospects.
Infrastructure and Services: Urban areas typically have better-developed infrastructure compared to rural areas.
- This includes transportation networks, communication systems, water supply, sanitation, electricity, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and recreational amenities.
- These amenities are crucial in attracting and sustaining urban populations.
Social Heterogeneity: Urban areas are characterised by social diversity and cultural heterogeneity.
- They serve as melting pots of different ethnicities, languages, religions, and lifestyles.
- This diversity fosters social interaction, multiculturalism, and the exchange of ideas, leading to vibrant urban communities.
Urban Planning and Governance: Effective urban planning and governance are essential for the functioning and development of urban systems.
- Urban planning involves the systematic allocation of land for various purposes, ensuring the provision of infrastructure and public services, and addressing issues like housing, transportation, and environmental sustainability.
Urbanization in India:
- The population residing in urban areas in India, according to the 1901 census, was 11.4%, increasing to 31.16% by the 2011 census, and is now currently 34% in 2017 according to The World Bank. .
- According to a survey by UN, in 2030 40.76% of country’s population is expected to reside in urban areas.
- Population and economic growth has fostered urbanization in the country and the number of urban towns and cities have drastically increased.
- This growth is expected to continue in the years to come and India has to step up its game in order to catch up with this kind of change. Investments have to be made in order to better serve the country.
Positive impacts of urbanisation
- Economic Growth and Opportunities: Urban areas serve as engines of economic growth. According to the World Bank, more than 80 per cent of global GDP is generated in the cities.
- The concentration of industries, businesses, and services in urban centers leads to increased productivity, innovation, and entrepreneurial activities.
- Improved Infrastructure and Services: Urban areas tend to have better-developed infrastructure and a wider range of services compared to rural areas.
- Urbanisation drives the expansion of transportation networks.
- Social and Cultural Exchange: Urbanisation fosters social interaction and cultural exchange due to the diversity of people from different backgrounds residing nearby.
- Urban centers become melting pots of diverse cultures, languages, traditions, and ideas.
- Education and Skill Development: Urban areas offer better access to educational institutions, including schools, colleges, and universities.
- This facilitates higher levels of education and skill development among urban populations.
Issues Associated to Urbanisation
- Excessive Population Pressure: On the one hand, the rural-urban migration accelerates the pace of urbanisation, on the other; it creates excessive population pressure on the existing public utilities.
- Consequently, the cities suffer from the problems of slums, crime, unemployment, urban poverty, pollution, congestion, ill health and several deviant social activities.
- Inadequate Housing: Among the numerous social problems of urbanisation, the problem of housing is the most distressing.
- A vast majority of urban population live under conditions of poor shelter and in highly congested spaces.
- In India, more than half of the urban households occupy a single room, with an average occupancy per room of 4.4 persons.
- Unplanned Development: The model of building a developed city comprises unplanned development, which only bolsters the dichotomy prevailing in urban cities between the rich and the poor.
- Pandemic-Induced Problems: The Covid-19 pandemic has exacerbated the misery of urban poor or slum dwellers.
- The sudden implementation of complete Covid lockdown severely affected the ability of slum dwellers to earn their living.
- Non-Inclusive Welfare Schemes: The benefits of welfare schemes for urban poor often reach only a small part of the intended beneficiaries.
- Most relief funds and benefits do not reach slum dwellers, mainly because these settlements are not officially recognised by the government.
India’s Initiatives for Urbanization:
- Smart Cities
- AMRUT Mission
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban
- Aspirational district programme
Way Forward:
Multi-stakeholder involvement, adequate financial resources, and institutional support will strengthen urban governance to reorient our strategy of urban planning and management. In the end, this will ensure desired green cover in cities for our current generations as well as for the future. New approaches to urban planning and effective governance are the need of the hour. Necessary actions should be taken to build sustainable, robust and inclusive infrastructure.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently, Bombay High Court stated that it is high time India considered reducing the age of consent for sex.
About age of consent:
- ‘Age of consent’ refers to the legally defined age at which an individual is considered capable of granting consent for sexual activities.
- The age of consent was 16 prior to the enactment of POCSO Act.
- The POCSO Act categorizes any sexual acts involving individuals under 18 as criminal offenses, irrespective of whether actual consent exists between the minors.
- This is based on the legal presumption that individuals below 18 are incapable of providing consent in the legal context.
The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act:
- It is the first comprehensive law in the country dealing specifically with sexual abuse of children, enacted in 2012 and is administered by the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- It was intended to protect children from sexual assault, sexual harassment and pornographic violations, as well as to establish Special Courts for such trials.
- In 2019, the Act was amended to strengthen the penalties for specified offences in order to deter abusers and promote a dignified upbringing.
Key provisions:
- Gender-neutral legislation: The Act defines a child as “any person” under the age of 18.
- Non reporting is a crime: Any person in charge of an institution (excluding children) who fails to report the commission of a sexual offence involving a subordinate faces punishment.
- No time limit for reporting abuse: A victim may report an offence at any time, even years after the abuse has occurred.
- Keeping victim’s identity confidential: The Act forbids the disclosure of the victim’s identity in any form of media unless authorised by the special courts established by the Act.
Issues with Age of Consent under the Act
- Instrument to Silence or Regulate a Consensual Sexual Relationship: The root cause of the problem at hand is that POCSO conflates exploitative sexual practice and general sexual expression by an adolescent and criminalises both.
- As a result, criminal law has become an instrument to silence or regulate a non-exploitative consensual sexual relationship involving a minor girl, which is voluntary.
- Desexualises Minor Girl: The legal aspects of teenage sexuality have undergone several changes since colonial times.
- The age of consent has increased from 10 to 12 to 14 to 16 and finally to 18 years by the 2013 amendment, in order to bring it in conformity with the then newly legislated POCSO Act.
- The law disregards the likelihood of a minor girl engaging in sexual activity voluntarily — it thus desexualises her.
- Ignores Social Reality: The law that criminalises adolescent sexuality either ignores social reality or pretends to do so. According to the NFHS-5, for instance, 39% women had their first sexual experience before turning 18.
- The same survey provides additional evidence of sexual engagement among unmarried adolescent girls by reporting contraception use by 45% of unmarried girls in the age group of 15-19 years.
- Burdens Already Overburdened Courts: The number of juveniles (especially those between the ages of 16 and 18) apprehended under the POCSO Act in the country has seen a staggering jump of 180% between 2017- 2021 according to the National Crime Records Bureau’s report, ‘Crime in India 2021’.
- Criminalising underage sexuality (25% of total POCSO cases) burdens the already-overburdened courts thereby clogging up the criminal justice machinery even more.
- Undermines the Victim’s Privacy: The cumulative victimisation of the “consenting” girl also deserves the lawmakers’ attention. POCSO, MTP (Medical Termination of Pregnancy) Act and the Child Marriage Act create a complex socio-legal web that deprives the minor girl of the rights to dignity, liberty, sexual and reproductive health, and undermines her privacy.
- This also feeds into a milieu of poor sexual awareness among young girls.
Recent judgements in this regard:
- In Vijayalakshmi vs State (2021) the Madras High Court stated that punishing an adolescent boy, who enters into a relationship with a minor girl by treating him as an offender, was never the objective of POCSO Act.
- Bombay HC’s recent recommendation:
- The court has pointed out that after the enactment of the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012, many adolescents are being prosecuted for consensual relationships with minor girls.
- The Court recommended that the Indian government consider reducing the age of consent of the prosecutrix from 18 to 16 years.
- The Delhi High Court released a 25-year-old accused on bail on the premise that the 15-year-old girl had eloped with him on her own.
- The Madhya Pradesh High Court quashed an FIR registered under POCSO and all criminal proceedings on the basis that the sexual relationship was consensual.
- The Court recommended that the Indian government consider reducing the age of consent of the female prosecutor from 18 to 16 years.
Suggestive measures: need of reforms in Law
- Social realities: The high rate of acquittals shows that the law is not in sync with the social realities of adolescent relationships.
- Blanket criminalisation: Consensual sexual acts involving older adolescents erodes their dignity, best interests, liberty, privacy, evolving autonomy, and development potential.
- Burden on courts: It also impacts the delivery of justice as these cases constitute a large burden on our courts.
- They divert attention from investigation and prosecution of actual cases of child sexual abuse and exploitation.
Way Forward:
The high rate of acquittals shows that the law is not in sync with social realities of adolescent relationships. While the marriage between some cases have influenced several High Courts and resulted in the quashing of romantic cases under the POCSO Act Sexual behavior is normative during adolescence, and not all relationships end in marriage.
There is thus a compelling need for law reform to revise the age of consent and prevent the criminalization of older adolescents engaging in factually consensual and non-exploitative acts.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Tiger Reserve | State |
| 1.Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam | Andhra Pradesh |
| 2.Pilibhit | Bihar |
| 3.Manas | Arunachal Pradesh |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
The Digital Portal of the Central Registrar of Cooperative Societies aims in enhancing the Ease of Doing Business.
Statement-II:
It can provide transparent processing.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
CBDT makes policy regarding the discharge of statutory functions of the Board and of the Union Govt. under the various laws relating to direct taxes.
Statement-II:
CBDT is in charge of only direct taxes.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) Discuss the causes of rapid urbanisation in India and also suggest measures to overcome issues arising out of rapid urbanisation. (250 words)
Q.2) “Age of consent has been used to weaponized POCSO Act against adolescents which was primarily meant to protect them.” In light of the statement critically analyze aims and objectives of the Act and suggest measures to avoid misuse of the Act (250 words).
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 7th August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 5th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) -b











