IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –ECONOMY
Context: Recently, NITI Aayog organised a workshop on the theme “Inclusive Trade for Prosperity”.
Background:-
- NITI Aayog organized a one-day workshop on the theme “Inclusive Trade for Prosperity”.
- Date: 6th November 2023.
- Venue: Hotel Taj Mahal, New Delhi.
- This workshop is part of a series of 10 feeder thematic workshops being held on varied themes discussed in the G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration (NDLD).
About NITI Aayog:-
- Establishment: 2015.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- NITI Aayog was established on 1st Jan 2015.
- Before NITI Aayog, there was a Planning Commission formed on 15 March 1950.
- The Planning Commission was non-constitutional.
- It serves as an advisory Think Tank.
- It focuses upon a ‘Bottom-Up’ approach to Planning.
- It does not possess mandate to impose policies.
Objectives NITI Aayog:-
- Shared vision and participation of both central and state governments for the national development of sectors.
- Cooperative federalism.
- Credible Planning
- Focusing on the weaker sections
- Making Strategies and long-term policies
- Innovation for creating knowledge.
- Technology up-gradation
Composition of NITI Aayog:-
- Chairperson: Prime Minister.
- Vice-Chairperson: To be appointed by the Prime Minister.
- Governing Council: Chief Ministers of all states and Lt. Governors of Union Territories.
- Regional Council: To address specific regional issues, Comprising Chief Ministers and Lt. Governors Chaired by the Prime Minister or his nominee.
- Adhoc Membership: 2 members in ex-officio capacity from leading Research institutions on a rotational basis.
- Ex-Officio membership: Maximum four from the Union Council of ministers to be nominated by the Prime minister.
- Chief Executive Officer: Appointed by the Prime Minister for a fixed tenure, in the rank of Secretary to the Government of India.
- Special Invitees: Experts and specialists with domain knowledge nominated by the Prime-minister.
Functions:-
- Policy Formulation
- Monitoring and Evaluation
- Inter-governmental Coordination
- Promoting Reforms
- Research and Knowledge Sharing
MUST READ: NITI AAYOG -TRIFED join hands for successful implementation
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following infrastructure sectors: (2023)
- Affordable housing
- Mass rapid transport
- Health care
- Renewable energy
On how many of the above does the UNOPS Sustainable Investments in Infrastructure and Innovation (S3i) initiative focus on its investments?
- Only one
- Only two ·
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements in relation to Janani Suraksha Yojana : (2023)
- It is a safe motherhood intervention of the State Health Departments.
- Its objective is to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality among poor pregnant women.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women.
Its objective includes providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims –DEFENSE
Context: Recently, the Crest unveiling ceremony of the Indian Navy’s Warship “SURAT”.
Background:-
- The Crest of Indian Navy’s latest, indigenous under-construction, guided missile destroyer, ‘Surat’, is scheduled to be unveiled by Shri Bhupendra Patel, the Chief Minister of Gujarat in the presence of Adm R Hari Kumar, the Chief of the Naval Staff, at a ceremony to be held in the city of Surat on 06 November 2023.
About SURAT:-
- Constructed by: Mazagon Docks Shipbuilders Ltd. Mumbai.
- Naming: The Destroyer has been named after Gujarat’s commercial capital- Surat, which has a rich maritime and ship-building history.
- INS Surat is the fourth and the last ship of the Project 15B Indian Navy Destroyers.
- These are called the Visakhapatnam class after the lead vessel INS Visakhapatnam.
- The Indian Naval Destroyers are named after Indian cities as per the naval tradition.
- It began with Project 15, under which three destroyers were built: INS Delhi in 1997, INS Mysore in 1999 and INS Mumbai in 2001.
- Project 15 was followed by the three-destroyer Project 15A, under which INS Kolkata was commissioned in 2014, INS Kochi in 2015 and INS Chennai in 2016.
- It was followed by the ‘Project 15B’ programme involves the construction of four next-generation stealth-guided missile destroyers, of which ‘Surat’ is the fourth and the last ship.
- Under project 15-B:-
- The first: INS Visakhapatnam.
- The second: INS Mormugao.
- The third: INS Imphal.
- The fourth: INS Surat.
- While INS Mormugao will be commissioned in 2022, INS Imphal will be commissioned in 2023 and INS Surat is likely to be commissioned in 2024, all at one-year intervals.
- INS Surat has been built using Block construction methodology that involves hull construction in two different locations and then joined together at one hub.
- It is a Guided-missile destroyer.
- This is the first capital warship to be named after the city of Gujarat.
Significance:-
- Construction of this warship testifies to the nation’s dedication to indigenous cutting-edge warship-building technology and commitment to strategic military advancements.
MUST READ: Dunagiri, a Project 17A Frigate
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (2023)
- Australia
- Canada
- Israel
- Japan
Q.2) With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-stage launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – ART AND CULTURE
Context: Recently, Shuttle Bus service began from Metro Stations to Pradhanmantri Sangrahalaya.
Background:-
- The visitors were experiencing issues with connectivity between metro stations and Sangrahalaya.
About Pradhanmantri Sangrahalaya:-
- Location: Teen Murti, New Delhi.
- The Pradhanmantri Sangrahalaya is a tribute to every Prime Minister of India since Independence.
- It is a narrative record of how each one has contributed to the development of our nation over the last 75 years.
- It is a history of collective effort and powerful evidence of the creative success of India’s democracy.
- The Teen Murti Estate, home to India’s first Prime Minister Shri Jawaharlal Nehru for 16 years, was the natural environment for Pradhanmantri Sangrahalaya, because this is a story of continuity. Nehru Memorial Museum & Library (NMML)
- The Sangrahalaya is a seamless blend which begins at the renovated and refurbished Nehru Museum building, now completely updated and technologically advanced displays on the life and contribution of Shri Jawaharlal Nehru.
- The new panorama includes a section which exhibits a large number of rare gifts received by him from all over.
- The saga of modern India starts with the freedom struggle and the making of a great Constitution.
- The Sangrahalaya goes on to tell the story of how our Prime Ministers navigated the nation through various challenges and ensured the all-round progress of the country.
Significance:-
- Our Prime Ministers came from every class and tier of society, it shows us the gates of democracy were equally open to all.
MUST READ: National Council of Science Museums (NCSM)
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The Prime Minister recently inaugurated the new Circuit House near Somnath Temple Veraval. Which of the following statements are correct regarding Somnath Temple? (2022)
- Somnath Temple is one of the Jyotirlinga shrines.
- A description of Somnath Temple was given by Al-Biruni.
- Pran Pratishtha of Somnath Temple (installation of the present-day temple) was done by President S. Radhakrishnan.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following statements is correct? (2021)
- Ajanta Caves lie in the gorge of the Waghora River.
- Sanchi Stupa lies in the gorge of the Chambal River.
- Pandu – lena cave shrines lie in the gorge of the Narmada River.
- Amaravati Stupa lies in the gorge of the Godavari River.
Syllabus
- Prelims –GOVERNANCE
Context: Recently, the Government banned some illegal betting platforms on Enforcement Directorate’s (ED) request.
Background:-
- In an order , the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology blocked 22 illegal betting apps and websites including Mahadev Book and Reddyannaprestopro.
About Enforcement Directorate (ED):-
- Establishment: 1956.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- The Enforcement Directorate is a multi-disciplinary organization founded in 1956.
- It is a law enforcement organization tasked with enforcing economic laws and combating economic crime in India, such as money laundering and foreign exchange irregularities.
- It works under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- The functions of the Directorate include the enforcement of the following Acts:-
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA) ( Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) 2002)
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA): A civil law under which ED conducts an investigation into suspected contraventions of foreign exchange laws and regulations. (Foreign Exchange Management Act)
- The Foreign Exchange Regulation Act 1973
- Sponsoring Organizations under the 1974 Foreign Exchange Conservation and Smuggling Activity Prevention Act
- The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018 (FEOA): A law whereby the Directorate is mandated to attach the properties of the fugitive economic offenders who have escaped from India warranting arrest and providing for the confiscation of their properties to the Central Government. (Fugitive Economic Offenders)
- Director of Enforcement:-
- Appointed by the central government on the recommendation of a committee chaired by the Central Vigilance Commissioner and members comprising of Vigilance Commissioners, Home Secretary, Secretary DOPT and Revenue Secretary.
- Tenure: up to 5 years.
- Recruitment of other officers:-
- Other officers may be recruited directly from other investigative agencies or indirectly.
- It is made up of representatives from the police, excise, customs, and income tax departments of the Indian Revenue Services (IRS), the Indian Police Services (IPS), and the Indian Administrative Services (IAS).
MUST READ: CBI and ED
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps the Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –POLITY
Context: Recently, Information Commissioner Heeralal Samariya was sworn-in as the new Chief Information Commissioner of the Central Information Commission.
Background:-
- President Droupadi Murmu administered the oath of office to him at Rashtrapati Bhavan. Mr. Samariya was currently serving as the Information Commissioner in the Central Information Commission.
About Central Information Commission (CIC):-
- Establishment:2005.
- The CIC was constituted in 2005 under the Right to Information Act, 2005.
- The RTI Act 2005 provides for the constitution of a Central Information Commission and State Information Commissions in each state.
- Jurisdiction: the Commission extends over all Central Public Authorities.
- The Right to Information (Amendment) Act, of 2019 amended the Right to Information Act, of 2005.
- The RTI Act, of 2005 specified the tenure, terms of service, and salaries of the Chief Information Commissioner (CIC) and Information Commissioners (ICs) at the central and state levels, in the parent law.
Structure:-
- The Central Information Commission shall consist of:
- The Chief Information Commissioner (CIC).
- Members: Such numbers of Central Information Commissioners (ICs), not exceeding ten, as may be deemed necessary.
- The members shall be persons of eminence in public life with wide knowledge and experience in law, science and technology, social service, management, journalism, mass media or administration and Governance.
- The CIC or IC shall not be an MP or MLA or hold any other office of profit connected with any political party carrying on any business or pursuing any profession.
- Appointment: The members of the commission are appointed by a committee consisting of the PM (as Chair), the Leader of Opposition (LoP) in Lok Sabha and a Union Cabinet Minister appointed by the Prime Minister.
- Tenure: The CIC and ICs (at the central and state level) will hold office for a term of three years.
- Resignation: The CIC or an IC may, at any time, by writing under his hand addressed to the President, resign from his office.
- Removal: The CIC or an IC may be removed from office only by order of the President on the grounds of proven misbehaviour or incapacity after the
- Supreme Court, on a reference made to it by the President, reports that he/she should be removed on the grounds mentioned.
- The President may also remove them from office if such a person is adjudged insolvent, convicted for certain offences etc.
- They are not eligible for reappointment.
Power and Functions:-
- To receive and inquire into a complaint from any person regarding information requested under the RTI act.
- It can order an inquiry into any matter if there are reasonable grounds (suo-moto power).
- While inquiring, the Commission has the powers of a civil court in respect of summoning, requiring documents, etc.
- Adjudication in the second appeal for giving information.
- Direction for record-keeping.
- Imposition of penalties and Monitoring and Reporting including preparation of an Annual
MUST READ: Its time to review the Right To Information (RTI) Act
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following organizations/ bodies in India: (2023)
- The National Commission for Backward Classes
- The National Human Rights Commission
- The National Law Commission
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
How many of the above are constitutional bodies?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- The Self-Help Group (SHG) programme was originally initiated by the State Bank of India by providing microcredit to the financially deprived.
- In an SHG, all members of a group take responsibility for a loan that an individual member takes.
- The Regional Rural Banks and Scheduled Commercial Banks support SHGs.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT ANDECOLOGY
Context: Recently, a new species of jumping spiders’ Pancorius sebastiani’ has been discovered.
Background:-
- It has been discovered from the Western Ghats.
About Pancorius sebastiani:-
- Naming: It has been named Pancorius sebastiani after the late spider taxonomist P.A.
- Distribution: southeast Asia.
- Its distribution was hitherto limited to the east and northeastern regions in India.
- The new species is the first to be reported from the south.
- The males and the females exhibit reddish brown carapace.
- They have yellowish abdomen with black patches and chevron-shaped markings posteromedially.
- It belongs to the jumping spider genus Pancorius Simon, and Salticidae family.
- Only two States, West Bengal and Tamil Nadu, have reported high numbers of Salticidae species, while the others including those harbouring biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats and northeastern India have relatively few numbers of species.
MUST READ: Six spider species discovered
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following makes a tool with a stick to scrape insects from a hole in a tree or a log of wood? (2023)
- Fishing cat
- Orangutan
- Otter
- Sloth bear
Q.2) Which of the following is not a bird? (2022)
- Golden Mahseer
- Indian Nightjar
- Spoonbill
- White Ibis
Syllabus
- Mains – GS III – Agriculture & Economy
Context: India’s agriculture exports have fallen 11.6% from April to September, due to various bans/restrictions on the shipments of various commodities from wheat and rice to sugar and global prices easing from their peaks scaled immediately after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
According to department of commerce data
- Exports of farm commodities, at $23.6 Billion in April-Sept 2023, were $26.7 for the same period in 2022.
- Imports fell too, from $19.3 Billion to $16.2 Billion, resulting in a marginal dip in the agricultural trade surplus.
- The years 2021-22 and 2022-23 also saw record imports of $32.4 Billion and $35.7 Billion respectively.
Impact of Global Prices
- UN Food and Agriculture Organization’s Food Price Index rose from an average of 96.5 points in 2019-20 to 139.5 points in 2022-23.
- India’s agricultural exports fell from $43.3 Billion in 2013-14 to $35.6 Billion in 2019-20.
- With world prices coming down, the value of both exports and imports of farm commodities are set to decline 2023-24.
- FAO has projected global ending cereal stocks from 2023-24 at an all-time high of 881.1 Million tonnes (mt) and the stocks-to-use ratio at 30.7%.
Issues with Indian Farm Exports
- Quality and Standards Compliance: Indian agricultural exports often struggle to meet international quality and safety standards. The lack of uniform and consistently enforced quality control measures can result in rejections and bans of Indian agricultural products in international markets.
- Infrastructure and Logistics: Inefficient transportation, storage, and distribution systems can lead to post-harvest losses and higher costs. This affects the overall competitiveness of Indian farm exports.
- Lack of Cold Chain Facilities: A significant portion of perishable agricultural produce is lost due to inadequate cold storage and transportation facilities. This restricts the export potential of items like fruits and vegetables.
- Pest and Disease Concerns: Some countries place phytosanitary restrictions on Indian agricultural products due to concerns about pests and diseases. Ensuring pest-free produce can be a challenge.
- Trade Barriers and Tariffs: Non-tariff trade barriers, as well as tariffs and import restrictions, can affect the market access for Indian agricultural exports in various countries.
- Price Volatility: Fluctuations in commodity prices, both in domestic and international markets, can affect the profitability of Indian farm exports.
- Small and Marginal Farmers: The average land holding of Indian farmer is 1.8 Acres. Hence it limit their capacity to adopt modern agricultural practices and access export markets. Aggregation and coordination are often needed for effective exports.

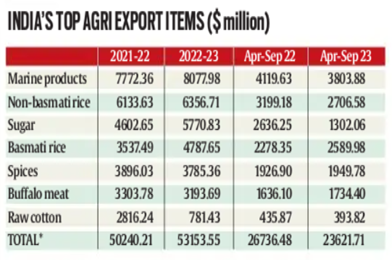
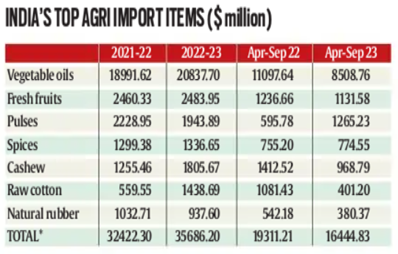
Conclusion
Addressing these issues requires a multi-faceted approach involving government policies, private sector participation, research and development, and investment in infrastructure and technology. Moreover, enhancing the quality and safety of agricultural products, as well as streamlining export procedures, can help improve the competitiveness of Indian farm exports in the global market.
Connect the Dots
- Analyze different government policies to enhance Indian exports.
Syllabus
- Mains – GS III – Internal Security
What is National Security Strategy (NSS)?
- A NSS document outlines the country’s security objectives, and the ways to achieve them.
- It defines traditional and non-traditional threats and opportunities while introducing accountability for agencies tasked with the implementation of various responsibilities.
- It means NSS would guide the military as well as critical Defence and security reforms, providing a holistic view of the overall National Security, the threats, and the roadmap to address them.
Need For NSS
- The NSS is poised to encompass a broad spectrum of contemporary challenges, including financial and economic security, food and energy security, information warfare, critical information infrastructure vulnerabilities, supply chain concerns, and environmental issues.
- Complex nature of various traditional and non-traditional threats, especially amid rising geopolitical uncertainties, there is a need for new NSS.
- National security cannot be confined to the use of the state’s coercive power to overcome domestic and external threats. For example, threats to domestic peace and stability may arise from economic and social grievances.
- A knee-jerk reaction may leave the grievances unaddressed while the use of coercive power exacerbates rather than ameliorates the situation. For instance, left-wing extremism in India is rooted in the persistent exploitation of tribal populations.
- Similarly, the vulnerability of our borders is linked to a large-scale smuggling and contraband trade. Such threats cannot be dealt with solely through enhanced military capabilities without addressing the drivers of illegal trade.
- For a modern state operating in an increasingly globalized world, the line between what is domestic and what is external is becoming increasingly blurred. For example, terrorism is a threat to domestic security but may have external links. Thus, a combination of domestic and external interventions may be necessary.
- It is only within a comprehensive NSS that such complex inter-relationships between domestic and external dimensions can be analysed and coordinated policy responses formulated.
Past Attempts and Hurdles
- Failed Attempts: India has previously made three attempts to develop a national security strategy, all without fruition.
- Political Hesitation: Some speculate that hesitation at the political level, driven by concerns about accountability in defence management, may have impeded the strategy’s release.
- Varied Views: There have been differing views within the strategic community regarding the absence of a national security strategy, ranging from a lack of cohesive government efforts to intentional non-disclosure of national security objectives.
Global Precedents
- Established Nations with NSS: Developed nations with robust military and security infrastructures maintain National Security Strategies, updated periodically. The United States, the United Kingdom, and Russia have published their NSS.
- China’s Comprehensive National Security: China has a closely integrated Comprehensive National Security strategy, tightly linked to its governance structure.
- Pakistan’s National Security Policy: Pakistan recently unveiled a National Security Policy for 2022-2026, outlining its national security objectives and priorities.
Conclusion
National security strategies are critical for guiding a nation’s security apparatus and ensuring that resources are effectively allocated to protect the country’s interests. They serve as a blueprint for government agencies, military forces, and other stakeholders to work together in pursuit of national security goals.
Connect the Dots
How the technological innovation in Defence sector helping us to combat traditional and non-traditional challenges?
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Navy Warships | Type |
| INS Sindhuvijay | Frigates |
| INS Mysore | Submarines |
| INS Vikran | Aircraft Carrier |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I :
Pradhanmantri Sangrahalaya is located in New Delhi.
Statement-II :
It is a tribute to only the first Prime Minister of India, Shri Jawaharlal Nehru.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) With reference to the NITI Aayog, consider the following statements:
- It possesses a mandate to impose policies.
- Its Headquarters are in Mumbai.
- It focuses upon a ‘Bottom-Up’ approach to Planning.
How many of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- and 3 only
- 2 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 6th November 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 4th November – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – d











