IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, IN SPACe, the commercial arm of the Indian Space Research Organisation, ISRO has called for an Expression of Interest from Indian private Industries to manufacture a Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV).
Background:-
- The Chairman of INSPACe, Dr. Pawan Goenka has outlined the objective of involving private players in the manufacturing of Small launchers by saying that this will pave the way for India to become a global hub for small satellite launches.
About Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV):-
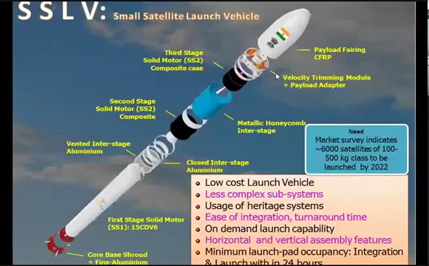
IMAGE SOURCE: Bharat Rakshak
- SSLV is an indigenously developed mini rocket launcher. (UPSC CSE: ISRO to undertake maiden flight of SSLV)
- It is the smallest vehicle at ISRO with a 110-ton mass.
- It is specially designed to carry smaller commercial satellites into the low-earth orbit (LEO) from 200-2,000 km above the Earth’s surface.
- Low-earth orbit (LEO): an orbit that is relatively close to Earth’s surface.
- It is normally at an altitude of less than 1000 km but could be as low as 160 km above Earth.
- It is a three-stage Launch Vehicle configured with three Solid Propulsion Stages and a liquid propulsion-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) as a terminal stage.
- Payload capacity: up to 500 kg.
- It has the capacity to deliver:-
- 600 kg to Low Earth Orbit (500 km) or
- 300 kg to Sun-synchronous Orbit (500 km)
Advantages of SSLV:-
- It is a low-cost launch vehicle.
- It has a Low turn-around time.
- It is flexible in accommodating multiple satellites.
- It has minimal launch infrastructure requirements, etc.
- It is intended to cater to a market for the launch of small satellites into low earth orbits with a quick turn-around time.
- It will take only 72 hours to integrate, unlike the 70 days taken now for a launch vehicle.
- Only six people will be required to do the job, instead of 60 people.
- It will shift the burden of commercial launches from PSLV.
- PSLV: is the third generation launch vehicle of India and the first Indian launch vehicle to be equipped with liquid stages.
- The SSLV is likely to cost a fourth of the current PSLV. (UPSC CSE: PSLV-C54 launch)
IN-SPACe :
- Establishment: 2020.
- HQ: Ahmedabad, Gujrat.
- Objective: promotion, encouragement and regulation of space activities of both government and private entities.
- It is an autonomous agency in the Department of Space. (UPSC CSE: IN-SPACe)
- It also facilitates the usage of ISRO facilities by private entities.
- Composition: It comprises technical experts for space activities along with safety experts, academic experts and legal and strategic experts from other departments.
- It also comprises members from the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO) and the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) of the Government of India.
Functions of IN-SPACe:-
- To develop a space start-up ecosystem in India.
- To boost the participation of students in the Indian space sector and develop future space force frontiers.
- To create international opportunities for Indian space companies.
- To make India the spaceport and ground station hub for selected countries/regions.
- To develop space tourism and to spread awareness to the public about space technology and its benefits and role in the everyday life of individuals
- To develop IN-SPACe talent and knowledgebase.
MUST READ: Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (2023)
- Australia
- Canada
- Israel
- Japan
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Ballistic missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flights, while cruise missiles are rocket-powered only in the initial phase of flight.
- Agni-V is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile, while BrahMos is a solid-fuelled intercontinental ballistic missile.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Home Minister Amit Shah will address two days G20 Conference on Crime and Security in the Age of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Background:-
- Two days G20 Conference on Crime and Security in the Age of NFTs, AI, and Metaverse will be organized in Gurugram, Haryana on the 13th and 14th of July. (UPSC CSE: India and G20 Presidency)
- The conference will bring together over 900 participants from G20 countries, 9 special invitee countries, international bodies, technology leaders, and domain experts from the country and across the world.
About Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs):-
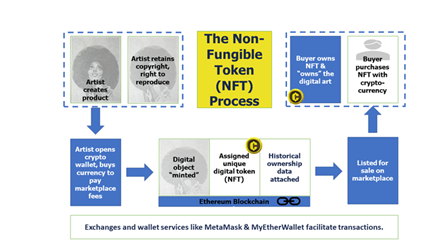
IMAGE SOURCE: datasciencecentral.com
- NFTs are assets in the digital world that can be bought and sold like any other piece of property, but which have no tangible form of their own. (UPSC CSE: Non Fungible Tokens (NFTs))
- Anything that can be converted into a digital form can be a Non-Fungible Token (NFT).
- It includes drawings, photos, videos, GIFs, music, in-game items, selfies etc.
- Even a tweet can be turned into an NFT, which can then be traded online using cryptocurrency.
- NFT transactions are recorded on blockchains.
Historical Background of NFTs:
- 2015: Terra Nulius was the first NFT on Ethereum Blockchain.
- 2017: Then came Curio Cards, CryptoPunks and CryptoCats .
- 2021: NFTS slowly moved into public awareness, expanding into mainstream adoption in early 2021.
Characteristic Features of NFTs:-
- Blockchain backed: NFTs are different from other digital forms in that they are backed by Blockchain technology. (UPSC CSE: Blockchain Technology and Voting)
- Exclusive ownership: NFTs can have only one owner at a time.
- Digital Storage: NFT owners can also digitally sign their artwork and store specific information in their NFTs metadata.
- Confidentiality: This will be only viewable to the individual who bought the NFT.
Conditions to buy NFTs:-
- Anyone who holds a cryptocurrency wallet can buy an NFT. (UPSC CSE: Cryptocurrency)
- That is the only prerequisite to purchasing an NFT.
- One does not need any KYC documents to purchase an art.
Risks associated with NFTs:-
- Risk of Fraud: In the recent past, several incidents of NFT Frauds have been reported.
- This includes the emergence of fake marketplaces, unverified sellers often impersonating real artists and selling copies of their artworks for half price.
- Environmental Risks: In order to validate transactions, crypto mining is done, which requires high-powered computers that run at a very high capacity, affecting the environment ultimately.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- It describes the action of machines accomplishing tasks that have historically required human intelligence. (UPSC CSE: A new global standard for AI ethics)
- It includes technologies like machine learning, pattern recognition, big data, neural networks, self-algorithms etc.
- India and AI
- According to a Canada-based company’s report, Global AI Report 2019, India stood at the ninth position in terms of the number of AI specialists working in the field.
- The US, China and the UK topped the list.
Benefits of AI:-
- In Policing: With the help of AI, one can predict the pattern of crime, and analyze a lot of CCTV footage, which is available across the country to identify suspects.
- In Agriculture: It can help sense one how much water the crop needs among many other works.
- Solving complex issues like efficient utilization of available resources.
- Analyzing the Data: AI technology helps in analyzing data
Disadvantages of AI:-
- Security: if somebody compromises a smart system, for instance, an autonomous car, the consequences can be disastrous, particularly given the ever-increasing cyber security threat.
- Lethal Autonomous Weapons: In the military, the autonomy in decision-making can be dangerous.
- Technological unemployment: by the introduction of new technologies the jobs will be replaced by intelligent machines or systems.
MUST READ: Binance
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Central Bank digital currencies, consider the following statements : (2023)
- It is possible to make payments in a digital currency without using the US dollar or SWIFT system.
- A digital currency can be distributed with a condition programmed into it such as a timeframe for spending it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), consider the following statements: (2022)
- They enable the digital representation of physical assets.
- They are unique cryptographic tokens that exist on a blockchain.
- They can be traded or exchanged at equivalency and therefore can be used as a medium transactions. of commercial
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Food Cooperation of India (FCI) started an e-auction of rice to control retail prices.
Background:-
- Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution Ministry have said that the decision to sell rice through e-auction under the Open Market Sale Scheme (OMSS) from the buffer stock to bulk consumers has been taken in the public interest.
About the Open Market Scheme:
- It refers to the selling of food grains by the Government at predetermined prices in the open market from time to time.
- Objective: to enhance the supply of grains, especially during the lean season and thereby to moderate the general open market prices, especially in the deficit regions.
- Ministry: Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
- Mechanism:-
- Under the OMSS, the FCI from time to time sells surplus food grains from the central pool, especially wheat and rice in the open market to traders, bulk consumers, retail chains, etc., at predetermined prices.
- The FCI does this through e-auctions where open market bidders can buy specified quantities.
- The FCI conducts this weekly auction using NCDEX (National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange Limited).
- NCDEX: a commodity exchange platform in India that provides a platform for trading in various agricultural and other commodities.
- The State Governments/ Union Territory Administrations are also allowed to participate in the e-auction if they require wheat and rice outside Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS ).
The present form of OMSS comprises three schemes as under-
- Sale of wheat to bulk consumers/private traders through e-auction.
- Sale of wheat to bulk consumers/private traders through e-auction by dedicated movement.
- Sale of Raw Rice Grade ‘A’ to bulk consumers/private traders through e-auction.
About Food Cooperation of India (FCI):-
- Established: 1965.
- FCI is a statutory body under the Food Corporations Act of 1964.
- Ministry: Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It has five Zonal Offices, twenty-five Regional Offices and 170 District Offices under its control.
Objectives of FCI:-
- Effective price support operations for safeguarding the interests of the farmers.
- Distribution of food grains throughout the country for the public distribution system.
- Maintaining satisfactory levels of operational and buffer stocks of food grains to ensure National Food Security.
Functions of FCI:-
- It has the primary duty to undertake the purchase, store, transport, distribute and sell food grains and other foodstuffs. (UPSC CSE: Procurement Reforms)
- To provide farmers with remunerative prices.
- To make food grains available at reasonable prices, particularly to vulnerable sections of society.
- To maintain buffer stocks as a measure of Food Security.
- To intervene in the market for price stabilization.
MUST READ: The Basis of MSP
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- The Government of India provides Minimum Support Price for niger( Guizotia aoyssinica) seeds.
- Niger is cultivated as a Kharif crop.
- Some tribal people in India use niger seed oil for cooking.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Which one of the following countries have been suffering from decades of civil strife and food shortages and was in the news in the recent past for its very severe famine? (2023)
- Angola
- Costa Rica
- Ecuador
- Somalia
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, a seven-year-old student from Kollam, Kerala tested positive for Brucellosis.
About Brucellosis:-
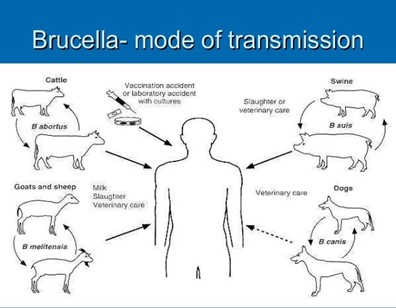
IMAGE SOURCE: SlideShare
- It is a bacterial infection that spreads from animals to people. (UPSC CSE: New Brucellosis Vaccine by ICAR)
- Brucellosis is a Zoonotic Disease.
- Zoonotic Diseases: It is a disease that passes into the human population from an animal source directly or through an intermediary species.
- It is also known as Malta fever or Mediterranean fever.
- Caused by: various Brucella species, which mainly infect cattle, swine, goats, sheep and dogs.
- Brucella melitensis is the most prevalent species causing human brucellosis.
- Spread: Brucellosis is found globally and is a reportable disease in most countries.
- Vulnerability: It affects people of all ages and both sexes.
- However, Person-to-person transmission is rare.
- Transmission:
- People are infected by eating raw or unpasteurized dairy products.
- Air transmission: the bacteria that cause brucellosis can spread through the air or through direct contact with infected animals.
- Symptoms:-
- Fever, weakness, malaise and weight loss.
- Treatment:-
- The infection can usually be treated with antibiotics.
- However, treatment takes several weeks to months, and the infection can recur.
- Preventions:-
- Avoiding unpasteurized dairy products.
- Taking safety precautions such as wearing rubber gloves, gowns or aprons, when handling animals or working in a laboratory.
- Other preventive measures include cooking meat properly, vaccinating domestic animals, etc.
MUST READ: Monkeypox/mpox
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) ‘Wolbachia method’ is sometimes talked about with reference to which one of the following? (2023).
- Controlling the viral diseases spread by mosquitoes.
- Converting crop residues into packing material.
- Producing biodegradable plastics.
- Producing biochar from thermochemical conversion of biomass.
Q.2) ‘Aerial metagenomics’ best refers to which one of the following situations? (2023)
- Collecting DNA samples from the air in a habitat in one go.
- Understanding the genetic makeup of avian species of a habitat.
- Using air-borne devices to collect blood samples from moving animals.
- Sending drones to inaccessible areas to collect plant and animal samples from land surfaces and water bodies.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, Tamil Nadu Forest Department stepped up vigil around Mukurthi National Park in Nilgiris to curb poaching.
Background:-
- Following the arrest of a gang of poachers from North India in the Nilgiris forest division a few months ago, the T.N. Forest Department has initiated a number of steps to bridge the lapses in surveillance in densely forested regions of the district.
About Mukurthi National Park:-
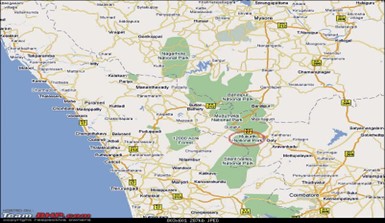
IMAGE SOURCE: Team-BHP.com
- Location: South East of the Nilgiri plateau, Tamil Nadu.
- It is located on the high altitudes of the Nilgiris, consisting of temperate shola forests.
- It has been created to protect the Nilgiri Tahr which was the state animal of Tamil Nadu, with the Mukurthi peak and its surroundings being the pivotal point.
- Rivers:-
- The Mukurthi National Park hillsides are the source of the Pykara River.
- The other important rivers originating from surrounding areas are Kabini, Chaliyar and Bhavani. (UPSC CSE: Manas National Park)
- Mukurthi National Park peaks act as the main source of water for not only the Nilgiris but other regions in the plains.
- The Mukurthi National Park area is a Hotspot and a core area in the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve Reserve. (UPSC CSE: Anamalai Tiger Reserve)
- Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve: the first Biosphere Reserve created in India the in the year 1986.
- Vegetation: Sholas and grasslands.
- The area is primarily grasslands interspersed with numerous isolated, compact, sharply defined montane wet temperate mixed forests locally termed as ‘Sholas’.
- Fauna: Nilgiri Tahr (state animal of Tamilnadu), sambar, barking deer, Nilgiri marten, otter, jungle Cat, jackal etc.
MUST READ: Kaziranga National Park
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements : (2023)
- In India, the Biodiversity Management Committees are key to the realization of the objectives
of the Nagoya Protocol.
- The Biodiversity Management Committees have important functions in determining access and benefit sharing, including the power to levy collection fees on the access of biological resources within its jurisdiction.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Recently, there was a proposal to translocate some of the lions from their natural habitat in Gujarat to which one of the following sites? (2017)
- Corbett National Park
- Kuno Palpur Wildlife Sanctuary
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Sariska National Park
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, live cultures of Candida auris have been found in hospitalised stray dogs in Delhi.
About Candida auris:-
- It is a multi-drug resistant fungus that is capable of causing invasive infections in the human body. (UPSC CSE: White fungus)
- First identified: in Japan, in 2009
- Global Spread: The fungus has been reported in more than 40 countries, including the United States, United Kingdom, South Africa, and Australia.
- Candida auris has been tagged as an “urgent” and “critical” threat by WHO.
Transmission:-
- It can spread indirectly from patient to patient in healthcare settings such as hospitals or nursing homes.
- It remains on people’s skin and objects such as hospital furniture and equipment like glucometers, temperature probes, blood pressure cuffs, ultrasound machines and nursing carts etc. for quite a long time.
Vulnerability:-
- Candida Auris mainly affects patients who already have many medical problems or have had frequent hospital stays or live in nursing homes.
- It is more likely to affect patients who suffer from conditions such as blood cancer or diabetes, have received a lot of antibiotics or have devices like tubes going into their bodies.
Symptoms:-
- Its symptoms include fever and chills that do not go away after treatment with antibiotics.
Treatment:-
- Antifungal drugs called echinocandins are used to treat this infection.
- It is resistant to multiple classes of antifungal drugs.(UPSC CSE: Shortage of anti-fungal injection, Amphotericin B)
- This makes treatment challenging and often requires the use of combination therapies.
MUST READ: Mucormycosis
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent the COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Serum Institute of India produced a COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using an mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using a vector based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen-based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body? (2022)
- They protect the environmental allergens. body
- They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
- They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
- They protect the body from diseases caused by pathogens.
Electric Vehicle Future
Syllabus
- Mains –GS 3 (Environment)
Context: India’s electric mobility plan is largely focussed on battery electric vehicles (BEVs) replacing internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, with Li-ion seen as the most viable battery option for now.
About BEVs:
- The Electric Vehicles (EVs) that qualify for a clear upfront tax incentive are the ones referred to as BEVs.
- Battery Electric Vehicles or EVs are fully electric vehicles with rechargeable batteries and no gasoline engine.
- All energy to run the vehicle comes from the battery pack, which is recharged from the grid.
- BEVs are zero emissions vehicles, as they do not generate any harmful tailpipe emissions or air pollution hazards caused by traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
India and Electric Vehicle:
- India is the fourth highest emitter of carbon dioxide globally and at the recently concluded COP26, it has pledged to reduce its carbon emissions to net-zero by the year 2070.
- India aims to achieve EV sales accounting for 30% of private cars, 70% of commercial vehicles, and 80% of 2 and three-wheelers by the year 2030.
- For this reason, India is aggressively promoting the adoption of EVs in the country by offering various incentives at both Central and State level, to buyers and manufacturers.
- India is among a handful of countries that support the global EV30@30 campaign, which aims for at least 30% new vehicle sales to be electric by 2030.
- India’s advocacy of five elements for climate change — “Panchamrit” — at the COP26 in Glasgow is a commitment to the same.
- Various ideas were espoused by India at the Glasgow summit, such as, renewable energy catering to 50% of India’s energy needs, reducing carbon emission by 1 billion tonnes by 2030 and achieving net zero by 2070.
- The government of India remodeled Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME II) scheme.
- The recently launched Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) for the supplier side.
- The recently launched PLI scheme for Auto and Automotive Components for manufacturers of electric vehicles.
Advantages of Electric Vehicles in India:
- Low cost of ownership: It is a proven fact by many researches that EVs offer way lower cost of ownership in their lifecycle compared to fossil fuel powered vehicles.
- At times, the cost of ownership for an EV is as lower as 27% than a fossil fuel vehicle.
- The incessant rise of petrol and diesel costs are increasing the cost of ownership further for the conventional vehicles.
- Easier to maintenance: An internal combustion engine usually contains more than 2,000 moving parts.
- An electric motor onboard an EV on the other hand contain around 20 moving parts.
- The only major components in an EV are the battery and the electric motor.
- This makes the EVs much easier for maintenance, reducing the cost of ownership significantly.
- State EV policies: Several state governments across India have already announced their respective EV policies.
- Some of them promote the supply side, while some promote the demand side.
- There are EV policies that promote both the supply and demand side through incentives, discounts and other benefits.
- Cleaner environment: The direct and obvious advantage of adopting electric mobility is the cleaner environment.
- Electric vehicles do not emit pollutants into the air like their ICE counterparts.
- The EVs are silent as well unlike their ICE counterparts.
- This means EVs ensure a cleaner and quieter environment.
Challenges associated with electric vehicles in India:
- High initial cost: The upfront cost of EVs is still higher than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, making it difficult for many consumers to afford them.
- Limited charging infrastructure: The lack of charging infrastructure makes it difficult for EV owners to travel long distances.
- Battery technology: The current battery technology still has some limitations, such as limited driving range and long charging time.
- Limited domestic manufacturing capabilities: India currently lacks the domestic manufacturing capabilities for electric vehicle components and batteries, making it dependent on imports.
- Lack of awareness: There is still a lack of awareness about the benefits of EVs among the public in India.
- Limited Government initiatives: The Indian Government has set ambitious goals for the adoption of electric vehicles, but the lack of concrete action plans and initiatives has been a hindrance.
- Lack of standardization: The lack of standardization in charging infrastructure and lack of uniformity in regulations across states and union territories is a challenge.
- Power Grid infrastructure: India’s power grid infrastructure is not fully developed and is not capable of handling the high-power demand of EV charging stations.
Government initiatives to promote EV adoption:
- The Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME)scheme II, which provides incentives for EV manufacturers and buyers. These incentives include subsidies, tax rebates, preferential financing, and exemptions from road tax and registration fees.
- The National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP), which sets out the target to achieve 6-7 million sales of hybrid and electric vehicles year on year from 2020 onwards by providing fiscal incentives.
- The National Mission on Transformative Mobility and Battery Storage, which seeks to create a comprehensive ecosystem for the adoption of EVs and support the establishment of giga-scale battery manufacturing plants in India.
- The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, which provides incentives for the manufacturing of electric vehicles and components.
- The Vehicle Scrappage Policy, which provides incentives for the scrapping of old vehicles and the purchase of new electric vehicles.
- The Go Electric campaign aims to create awareness on the benefits of EVs and EV charging infrastructure.
- India is among a handful of countries that support the global EV30@30 campaign, which aims for at least 30% new vehicle sales to be electric by 2030.
For the good or bad, India is establishing itself as a global leader in EV manufacturing. Electric vehicles are expected to accommodate higher renewable energy penetration while strengthening and stabilizing grid operation.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: Hailing its ambitious space programme, India is currently home to about 140-registered space-tech start-ups, “stands to transform the planet’s connection to the final frontier” and can emerge as a “counterweight” to China.
India’s Space Economy
- Today, while ISRO’s budget is approximately $1.6 billion, India’s space economy is over $9.6 billion.
- Broadband, OTT and 5G promise a double-digit annual growth in satellite-based services.
- With an enabling environment, the Indian space industry could grow to $60 billion by 2030, directly creating more than two lakh jobs.
About Indian Space Policy:
- In April 2023, the Union Cabinet approved the Indian Space Policy 2023.
- The Policy seeks to institutionalize the private sector participation in the space sector and give a larger participation to research, academia, startups, and industry. It also delineated the roles and responsibilities of ISRO, space sector PSU NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) and Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe).
Major highlights of the policy:
- The policy creates four distinct, but related entities, that will facilitate greater private sector participation in activities that have usually been the traditional domain of the ISRO.
- Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (InSPACe): It will be a single window clearance and authorisation agency for space launches, establishing launch pads, buying and selling satellites, and disseminating high-resolution data among other things.
- It will also share technologies, products, processes and best practices with NGEs (non-government entities and this will include private companies) and government companies.
- New Space India Limited (NSIL): It will be responsible for commercializing space technologies and platforms created through public expenditure, as well as, manufacturing, leasing, or procuring space components, technologies, platforms and other assets from the private or public sector.
- Department of Space: It will provide overall policy guidelines and be the nodal department for implementing space technologies and, among other things, co-ordinate international cooperation and coordination in the area of global space governance and programmes in consultation with the Ministry of External Affairs.
- It will also create an appropriate mechanism to resolve disputes arising out of space activity.
Advantages of the Indian Space Policy 2023:
- Provides clarity: The Indian Space Policy 2023 establishes a single regulatory body, IN-SPACe, to streamline the process and provide clarity to all involved parties.
- Fostering innovation: The Indian Space Policy 2023 encourages private sector participation, which brings new ideas, innovation, and competition into the Indian space sector.
- This could lead to the development of more advanced technologies and efficient processes, driving the overall growth of the sector.
- Economic growth and job creation: As the private sector and startups gain more share in the space sector, it is expected to lead to economic growth and job creation.
- The policy could spur investments, create high-tech jobs, and contribute significantly to the Indian economy.
- Accessible and affordable space technology: With increased competition, space technology and services could become more accessible and affordable, benefiting various sectors like communication, navigation, earth observation, and more.
- Encouraging entrepreneurship: The policy creates an encouraging environment for space startups, fostering entrepreneurship and innovation in the country.
- It provides a clear path for entrepreneurs to enter the space sector, contributing to the startup ecosystem’s growth.
- Streamlining regulations: By creating a single-window clearance system, the policy streamlines the regulatory process for space activities.
- This makes it easier for businesses to navigate the regulatory landscape and encourages more entities to participate in space activities.
Challenges associated with the Indian Space Policy 2023:
- Lack of Timeframe: The policy lacks a specific timeframe for implementation and the transition of ISRO’s practices, as well as the establishment of the regulatory framework by IN-SPACe.
- This makes it difficult to assess the progress and implementation of the policy.
- Absence of Clear Rules and Regulations: The policy framework requires clear and detailed rules and regulations in several areas, including foreign direct investment (FDI) and licensing, government procurement to support new space start-ups, liability provisions in case of violations, and an appellate framework for dispute settlement.
- Ambiguity in IN-SPACe’s Position and Authority: Currently, IN-SPACe’s position is ambiguous as it functions under the purview of the Department of Space.
- The Secretary (Space) is also Chairman of ISRO, the government entity to be regulated by IN-SPACe.
- Legislative Authority: The establishment of a regulatory body like IN-SPACe requires legislative authority to ensure its effectiveness and legitimacy.
- The absence of a dedicated legislation could hinder its ability to enforce regulations and provide a robust regulatory framework for the space industry.
Way Forward:
The introduction of India’s new space policy is a significant milestone in fostering a commercial space ecosystem, but there are still important questions to be addressed to fully realize the potential benefits of private sector participation.
Source: India Today
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Brucellosis is a Zoonotic Disease.
Statement-II:
The infection can be treated with antibiotics.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-11 is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q2) Consider the following pairs:
Organizations Headquarters
- Indian Space Research Organisation: Hyderabad
- Food Corporation of India: New Delhi
- IN-SPACe: Bhubneshwar
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- None
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Candida auris has been tagged as an “urgent” and “critical” threat by WHO.
Statement-II:
It is resistant to multiple classes of antifungal drugs.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains practice questions
Q.1) Discuss the salient features of the Indian Space Policy-2023 and its implications for the development of the Indian space sector. (250 words)
Q.2) To ensure a positive growth rate towards achieving India’s Net Zero Emissions by 2070, a transportation revolution is required in India which will lead to better “walkability”, public transportation. In this regard, discuss the significance and challenges associated with electric vehicle in India? (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 12th July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 11th July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – d
Q.3) -a














