IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
JB Ekka Committee to be formed
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy
In news
- A one-man committee under Principal Secretary Dr. JB Ekka will be formed for equal wages of small tea workers of Assam.
Key takeaways
- Also, the Assam government has announced the increase in wage of tea garden workers from Rs 167 to Rs 217 per day.
- The tea garden managements pay the wages which is fixed by the government.
- The tea tribe community of Assam also faces exploitation, economic backwardness, poor health conditions and low literacy rates.
- In the Union Budget 2020-21, Rs 1,000 crore was announced for the welfare of tea workers in Assam and West Bengal.
Related articles:
- Need of developing backward and forward linkages to improve plantation products’ exports.
- Highway projects in Assam
RBI releases the Annual Report of the Ombudsman Schemes
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy
In news
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released the Annual Report of the Ombudsman Schemes for 2019-20 recently.
- RBI has 3 Ombudsmen- Banking, Non-Banking Finance Company (i.e. NBFC) and digital transactions.
- A common man can approach these Ombudsmen for their grievances.
- These Schemes are being merged and integrated into a single scheme which will be rolled out from June 2021.
- There was an increase of around 65% in the receipt of complaints.
- 92% of them have been resolved.
Related articles:
Agreements signed between India and Maldives
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – International Relations
In news
- India and Maldives signed agreements on wide range of domains.
- These included fish processing, public broadcasting, sustainable urban development, road infrastructure and housing.
Key takeaways
- The broadcasting agreement is for cooperation between Prasar Bharati and official State Media of Maldives.
- It intends to facilitate collaboration and capacity building in the field of public broadcasting.
- Over one lakh additional doses of COVID vaccine were also handed over to Maldives.
- India has signed a 50 million dollar Line of Credit agreement in defence sector with the Maldives which will facilitate capability building in the maritime domain.
- The UTF Harbour Project agreement was also signed with Maldives.
- The project agreement will strengthen Maldivian Coast Guard capability and facilitate regional Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief efforts.
- India also extended a new line of credit of US dollar 40 million for the development of new sports infrastructure in the Maldives.
Related articles:
New Lead (Pb) free material discovered
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Sci & Tech; Achievements of Indians
In news
- Scientists have found a new Lead (Pb) free material.
- Identified by: Scientists at Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR), Bengaluru.
- It is called Cadmium (Cd) doped Silver Antimony Telluride (AgSbTe2).
Key takeaways
- It can efficiently convert waste heat to power our small home equipment and automobiles.
- Most efficient thermoelectric materials developed so far use Lead (Pb) as a major constituent element, restricting their use for mass-market applications.
- This work is supported by Swarna-Jayanti fellowship.
Do you know?
- The Swarna Jayanti Fellowships scheme was launched by the Indian Government to commemorate India’s 50th Independence.
- It provides special assistance and support to a selected number of young scientists with a proven track record to enable them to pursue basic research in frontier areas of science and technology.
- The award consists of a Fellowship of Rs. 25000 per month along with the salary drawn from the parent Institute and a Research Grant of Rs. 5 lakh per annum by Department of Science and Technology (DST) for a period of 5 years.
Smartcode Platform launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – Policy and governance
In news
- SmartCode Platform was recently launched.
- Ministry: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
Key takeaways
- SmartCode is a platform that enables all ecosystem stakeholders to contribute to a repository of open-source code for various solutions and applications for urban governance.
- It is designed to address the challenges that urban local bodies (ULBs) face in the development and deployment of digital applications.
- It shall enable cities to take advantage of existing codes and customising them to suit local needs, rather than having to develop new solutions from scratch.
- The source code will be free to use without any licensing or subscription fees
Miscellaneous
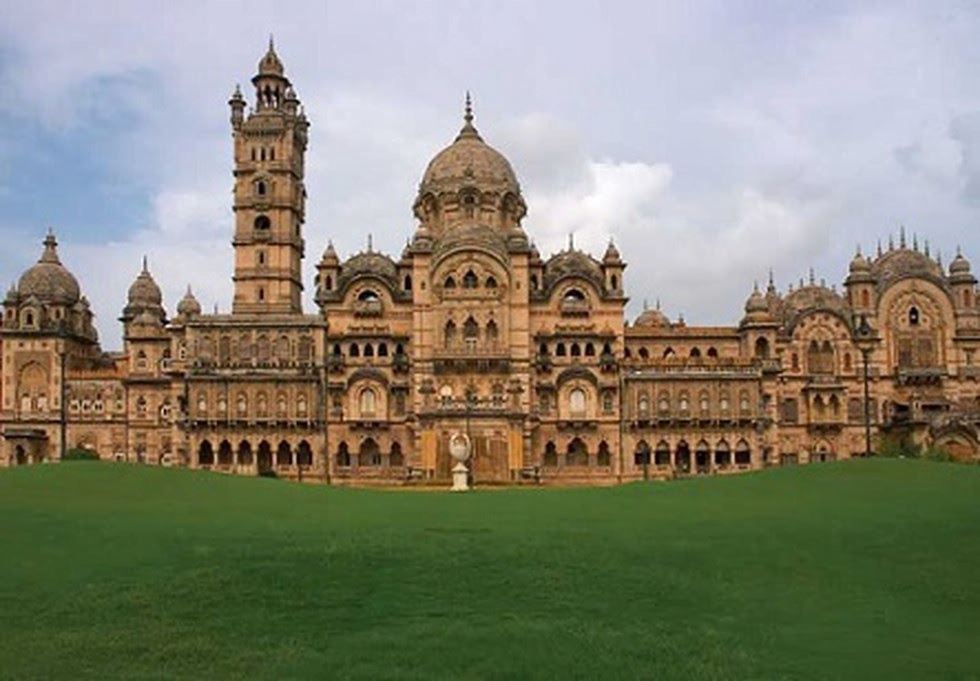
Laxmi Vilas Palace

-
The Lakshmi Vilas Palace is located in Vadodara, Gujarat.
- It was constructed by the Gaekwad family, a prominent Maratha family, who ruled the Baroda State.
- It was built by Maharaja Sayajirao Gaekwad III in 1890.
- Major Charles Mant was credited to be the main architect of the palace.
- It is styled on the Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture.
(Mains Focus)
ENVIRONMENT/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Environmental Conservation
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
Carbon Watch App: To assess Carbon Footprint
Context: Chandigarh became the first state or Union Territory in India to launch Carbon Watch, a mobile application to assess the carbon footprint of an individual.
What is Carbon Footprint?
- Carbon footprint is the amount of greenhouse gases-especially carbon dioxide-released into the atmosphere by a particular human activity.
- It is expressed as a weight of CO2 emissions produced in tonnes.
- It can be a broad measure or be applied to the actions of an individual, a family, an event, an organization, or even an entire nation.
- Carbon footprint includes direct emissions, such as from driving a car, as well as whatever emissions are required to consume any goods and services (indirect)
- Carbon footprint is different from ecological footprint. While the carbon footprint measures the emission of gases that contribute to global warming, the ecological footprint focuses on measuring the use of bio-productive space.
About the app
- The application that can be downloaded on mobile focuses on individual’s actions and calculates the carbon footprint based on four parameters: Water, Energy, Waste Generation and Transport (Vehicular movement)
- The application will also provide information such as the national and world average of the emission, and the individual’s level of emission generation.
- The motive behind this application is making people Climate-Smart Citizens while enabling them capable of accessing their carbon footprint, along with providing them with steps to reduce it
- The mobile application will suggest methods to reduce the carbon footprints as per the information furnished by the individuals.
- It also sensitizes people about their lifestyle emissions, their impact and possible countermeasures to mitigate the same.
Effects of Higher Carbon Footprint
- Increase in Carbon dioxide concentration in atmosphere causes Global Warming i.e Greenhouse gas effect
- Climate Change
- Melting of Polar Caps
- Depletion of resources: Due to changed Carbon concentration in biosphere
- Increasing Incidents of Severe Weather
- Changes in food supply
Methods of Reducing Carbon Footprint
- Water: Adopting better agronomic practices (like drip irrigation), shifting dietary basket from water guzzling cereal crops to water conserving millets (also Health benefits), recycling of water in industries, smart water metering at households
- Energy: Using renewable energy (shift from carbon intensive coal), smart metering, Energy sector Reforms particularly in DISCOMs, Using energy efficient appliances
- Waste: Adopting the 4 R’s- Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle.
- Transportation: Using Public Transport, bicycles, car pooling
- Market mechanism like Carbon Trading: Individuals and companies can also offset some of their carbon dioxide emissions by purchasing carbon credits, the money from which can go into projects such as planting trees or investing in renewable energy.
- International Collaboration: Implementation of the Climate change conventions like the Paris Agreement and Indian initiatives for the same must be fast forwarded.
Connecting the dots:
- The benefits of Carbon Tax
SOCIETY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-1: Urbanization, their problems and their remedies.
- GS-2: Mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections
Draft National Policy On Migrant Workers
Context: Spurred by the exodus of 10 million migrants (as per government estimates) from big cities during the Covid-19 lockdown, NITI Aayog, along with a working subgroup of officials and members of civil society, has prepared a draft national migrant labour policy.
Key Features of Draft Policy
- Rights Based Approach: The policy rejects a handout approach, opting instead for a rights-based framework The draft describes two approaches to policy design: one focussed on cash transfers, special quotas, and reservations and the other which enhances the agency and capability of the community and thereby remove aspects that come in the way of an individual’s own natural ability to thrive
- Acknowledgement: Migration should be acknowledged as an integral part of development and government policies should not hinder but seek to facilitate internal migration.
- Policy should have Long Term Goal: The goal according to draft policy should not be to provide temporary or permanent economic or social aids that is rather limited approach, but goal should be on a more permanent basis
- Legislation: The NITI Aayog’s policy draft mentions that the Ministry of Labour and Employment should amend The Inter State Migrant Workers Act, 1979 for “effective utilisation to protect migrants”.
- Need for Effective Coordination: It identifies the Ministry of Labour and Employment as the nodal Ministry for coordination between various agencies/ department and implementation of policies related to Migrants.
- Institutional Mechanism through Special Unit: The draft suggests to create a special unit under Labour Ministry to help converge the activities of other Ministries. This unit would manage migration resource centres in high migration zones, a national labour Helpline, links of worker households to government schemes, and inter-state migration management bodies.
- Inter-State Coordination: On the inter-state migration management bodies, it says that labour departments of source and destination states along major migration corridors, should work together through the migrant worker cells. Labour officers from source states can be deputed to destinations – e.g., Bihar’s experiment to have a joint labour commissioner at Bihar Bhavan in New Delhi.
- Enhanced Role of Local Bodies: Policies should “promote the role of panchayats to aid migrant workers” and integrate urban and rural policies to improve the conditions of migration. Panchayats should maintain a database of migrant workers, issue identity cards and pass books, and provide “migration management and governance” through training, placement, and social-security benefit assurance
- Ways to stem migration: Even as it underlines the key role of migration in development, the draft recommends steps to stem migration. The draft asks source states to raise minimum wages to “bring major shift in local livelihood of tribal that may result in stemming migration to some extent”.
- Importance of Data: The draft calls for a central database to help employers “fill the gap between demand and supply” and ensure “maximum benefit of social welfare schemes”. It asks the Ministries and the Census office to be consistent with the definitions of migrants and subpopulations, capture seasonal and circular migrants, and incorporate migrant-specific variables in existing surveys.
- Education for Migrant Children: The Ministry of Education should take measures under the Right to Education Act to mainstream migrant children’s education, to map migrant children, and to provide local-language teachers in migrant destinations.
- Grievance Redressal: The National Legal Services authority (NALSA) and Ministry of Labour should set up grievance handling cells and fast track legal responses for trafficking, minimum wage violations, and workplace abuses and accidents for migrant workers.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following Ministry launched Smartcode Platform?
- Ministry of Science and technology
- Ministry of Electronics and IT
- Ministry of Housing and urban Affairs
- Ministry of MSME
Q.2 What is the objective of Smartcode platform?
- To enable citizens to register complaints directly through the platform.
- TO enable citizens to learn coding virtually
- To enable Urban local bodies to monitor criminal activities
- To enable Urban local bodies to use existing codes and customise them to suit local needs.
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Swarna Jayanti Fellowships scheme:
- It is launched by Ministry of Education.
- It provides special assistance to a selected number of scientists to enable them to pursue basic research in areas of science and technology.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4 Consider the following difference between Banks & NBFCs:
- Banks are the government authorized financial intermediary aiming at providing banking services. Whereas NBFC provides banking services without carrying a bank license.
- NBFC is incorporated under the Companies Act whereas a bank is registered under Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Must Read
On Political Crisis in Myanmar:
On changing fiscal policy framework:
About rising fuel prices:











