IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Global Cybersecurity Index: ITU
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Cybersecurity
In news
- Recently, India has ranked tenth (10th) in Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2020 by ITU (International Telecommunication Union) by moving up 37 places.
- Top countries: USA (1st), UK and Saudi Arabia (2nd), Estonia (3rd)
- Performance is based on five parameters of cybersecurity – Legal measures, technical measures, organisational measures, capacity development, and cooperation
About India’s performance
- India scored a total of 97.5 points
- India secured the fourth position in the Asia Pacific region.
- India is emerging as a global IT superpower
- There has been substantial overall improvement and strengthening of the cybersecurity domain.
About International Telecommunication Union
- It is the United Nations specialized agency for information and communication technologies – ICTs.
- Founded in 1865
- Objective: To facilitate international connectivity in communications networks.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Functions:
- It allocates global radio spectrum and satellite orbits
- Develops the technical standards that ensure networks and technologies seamlessly interconnect
- Strives to improve access to ICTs to underserved communities worldwide.
Efforts to Improve Cyber Security in India
- National Cyber Security Strategy 2020: It is being formulated to improve cyber awareness and cybersecurity through more stringent audits.
- Draft Personal Data Protection Bill, 2018 (based on the recommendation of Justice BN Srikrishna Committee) to secure citizens’ data.
- The scheme to set up I4C (Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre) was approved in October 2018, to deal with all types of cybercrimes in a comprehensive and coordinated manner.
- National Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) functions as the nodal agency for coordination of all cyber security efforts, emergency responses, and crisis management.
- Protection and resilience of critical information infrastructure with the set up of National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC).
Viability Gap Funding for BharatNet Project
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Internet connectivity; Infrastructure
In news
- Recently, the Union Cabinet approved a Viability Gap Funding support of up to Rs. 19,041 crore for the implementation of the BharatNet project through Public-Private Partnership model.
- The project will be extended to all inhabited villages beyond the gram panchayats in 16 States — Kerala, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Assam, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh,
About BharatNet project
- It is the world’s largest rural broadband connectivity programme using Optical fibre.
- Implemented by: Bharat Broadband Network Ltd. (BBNL).
- BBNL is a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) set up by the Government of India under the Companies Act, 1956 with an authorized capital of Rs 1000 crore.
- It shall provide on demand, affordable broadband connectivity of 2 Mbps to 20 Mbps for all households and on demand capacity to all institutions.
- Ministry: Department of Telecommunication, Ministry of Communications.
- National Optical Fibre Network (NOFN) which was launched in October 2011 was renamed as Bharat Net Project in 2015.
- Funding:
- Universal service Obligation Fund (USOF) set up for improving telecom services in rural and remote areas of the country.
- Objective:
- To facilitate the delivery of e-governance, e-health, e-education, e-banking, Internet and other services to rural India.
Phases of the Project
- First Phase:
- Provide one lakh gram panchayats with broadband connectivity by laying underground Optic Fibre Cable (OFC) lines by December 2017.
- Second Phase:
- Provide connectivity to all the gram panchayats in the country using an optimal mix of underground fibre, fibre over power lines, radio and satellite media by March 2019.
- Third Phase:
- From 2019 to 2023, a state-of-the-art, future-proof network, including fibre between districts and blocks, with ring topology to provide redundancy would be created.
Do you know?
- Public-Private Partnership (PPP) involves collaboration between a government agency and a private-sector company that can be used to finance, build, and operate projects. The PPP Model in this critical infrastructure of Telecom is a novel initiative.
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF) means a grant one-time or deferred, provided to support infrastructure projects that are economically justified but fall short of financial viability.
Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Discoms; Infrastructure
In news
- Recently, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved a Reforms-based and Results-linked, Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme worth Rs. 3.03 trillion.
- The Centre’s share will be Rs. 97,631 crore.
- Aim: To improve the operational efficiencies and financial sustainability of discoms (excluding Private Sector DISCOMs).
About the revamped scheme
- It will provide conditional financial assistance to strengthen the supply infrastructure of discoms (power distribution companies).
- The financial assistance will be based on meeting pre-qualifying criteria and upon achievement of basic minimum benchmarks.
- All the existing power sector reforms schemes such as Integrated Power Development Scheme, Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana, and Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana will be merged into this umbrella program.
- The scheme will be available till 2025-26.
- Nodal Agencies: Rural Electrification Corporation and Power Finance Corporation.
- Special Category States/UTs: Sikkim, J & K, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, and Lakshadweep
- Objectives:
- Reduction of AT&C losses (operational losses due to inefficient power system) to 12-15% by 2024-25.
- Reduction of cost-revenue gap to zero by 2024-25.
- Developing Institutional Capabilities for Modern DISCOMs.
Components of the scheme
- Consumer Meters and System Meters:
- A compulsory smart metering ecosystem across the distribution sector
- Approximately 10 crore prepaid Smart Meters to be installed by December, 2023 in the first phase.
- Feeder Segregation:
- Funding for feeder segregation for unsegregated feeders, which would enable solarization under the PM-KUSUM Scheme.
- Modernization of Distribution system in Urban Areas
- Rural and Urban area System strengthening
G20 Foreign Ministers’ Meeting
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – International relations
In news
- Recently, Italy hosted the G-20 foreign ministers’ meeting to discuss the fight against Covid-19 and how to speed up the recovery of the global economy and boost sustainable development in Africa.
About the Meeting
- It criticized China and Russia for engaging in vaccine diplomacy.
- Vaccine diplomacy is the branch of global health diplomacy in which a nation uses the development or delivery of vaccines to strengthen ties with other nations.
- Promoting a science-based holistic One Health approach.
- ‘One Health’ is an approach to designing and implementing programmes, policies, in which multiple sectors communicate and work together to achieve better public health outcomes.
- It also emphasised that Increased climate variability and extreme weather events impact agriculture output and are among the forces driving the rise in global hunger.
- On Africa:
- The Covid-19 pandemic, conflict, drought, economic woes, and extreme weather are reversing years of progress.
- In the whole of Africa, 250 million people were experiencing hunger, which is nearly 20% of the population (as of 2019).
India’s Stand in the meeting
- Flagged the issue of “vaccine equity”
- It entails both affordability of vaccines and access opportunities for populations across the world, irrespective of geography and geopolitics.
- Economy needs decentralised globalisation, including in manufacturing, food and health.
- Resilient supply chains must develop in parallel.
App chendavia gaining popularity among the students of kalbeliya dance
Part of: GS Prelims and GS I – Culture
In news
- Recently, due to Covid-19-Pandemic an app called chendavia is gaining popularity among the students of kalbeliya dance.
About kalbeliya dance
- Kalbeliya dances are an expression of the Kalbeliya community’s traditional way of life.
- It was included in the UNESCO list of Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) in 2010.
- UNESCO’s List of ICH is made up of those intangible heritage elements that help demonstrate diversity of cultural heritage and raise awareness about its importance.
- It was established in 2008
- The dance form consists of swirling and graceful movements
- The movements associated with the Kalbelia also make it one of the most sensuous forms of folk dance in India.
- It is generally performed for any joyous celebration.
- Another unique aspect is that it is only performed by women while the men play the instruments and provide the music.
About the Kalbeliya Tribe
- Kalbeliya tribe people were once professional snake handlers.
- Today they are seen in their former occupation in music and dance
- They live a nomadic life and belong to the scheduled tribes.
- The largest number of the population of Kalbeliyas is in Pali district, then Ajmer, Chittorgarh and Udaipur district (Rajasthan).
Other Traditional Folk Dances of Rajasthan
- Gair
- Kachchhi Ghodi
- Ghoomar
- Bhavai, etc.
Miscellaneous
Guindy National Park: Tamil Nadu
- The Guindy National Park provides a number of ecosystem services to the people of Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- Ecosystem services are the direct and indirect contributions of ecosystems to human well-being.
- It is India’s eighth-smallest national park and one of the very few national parks located inside a city.
- It is located in the heart of Chennai’s metropolitan area.
- It is one of the last remnants of the tropical dry evergreen forests of the Coromandel Coast.
- In 1978 the small area, popularly known as Guindy Deer Park, was declared as a national park.
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
Rural Economy as Saviour
Context: Decline in GDP began even before COVID-19 Pandemic which has made economic recovery challenging
- The pandemic & its mishandling has only worsened an already fragile economic situation.
- Agriculture was the only major sector (other than electricity, gas, water supply and utility services) which reported an increase in Gross Value Added (GVA) in 2020-21.
- It not only provided jobs to returning migrants but also sustained the economy in the rural areas.
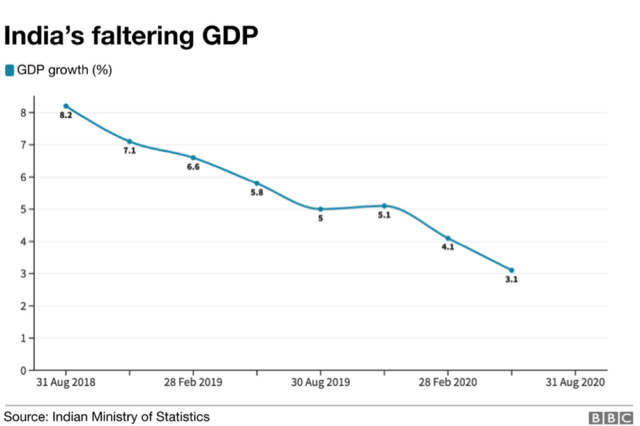
It is difficult for rural sector to play saviour again because of the following reasons:
1. Disproportionate impact on rural areas:
The second wave affected rural areas disproportionately, both in terms of
- Health – Huge expenditure on private healthcare
- Livelihoods- Loss of earning members
2. Possible Debt Trap: As a result, rural areas can witness a sharp rise in indebtedness from non-institutional sources
3. Incommensurate response from the Government:
- For the country as a whole, despite an increase in employment demand in NREGS, the person-days generated in May 2021 was only 65% when compared to May 2020.
- While the free food-grain scheme has been extended this year as well, it does not include pulses as was provided.
- Similarly, there has not been any cash transfer to vulnerable groups, unlike last year
4. Inflation Threat
- Rising inflation further threatens to reduce the purchasing power of the rural economy struggling with declining incomes and job losses
- The rise in input prices for diesel and fertilizers further adds to the misery
- Rural non-farm sector already struggling from low demand has now seen its profit margins getting impacted due to the increase in the cost of raw material.
Way Ahead
- Recognition by government about the importance of rural sector in economic recovery and proactive intervention.
- Speeding up vaccination in rural areas
- Greater fiscal support for rural areas (increased MGNREGA, PDS allocation)
- Protection from the rising inflation in input prices through subsidies
Connecting the dots:
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic:
- GS-2: India and its neighborhood- relations.
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
India-Africa: Challenges & Way Ahead
Context: India’s Africa policy needs a critical review, despite New Delhi’s new initiatives to assist Africa through prompt despatch of medicines and later vaccines.
Issues with Indo-Africa relationship
- India-Africa trade declined in 2020-21
-
- Bilateral trade valued at $55.9 billion in 2020-21, fell by $10.8 billion compared to 2019-20, and $15.5 billion compared to the peak year of 2014-15.
- India’s investments in Africa too saw a decrease from $3.2 billion in 2019-20 to $2.9 billion in 2020-21.
-
- Total investments over 25 years, from April 1996 to March 2021, are now just $70.7 billion, which is about one-third of China’s investment in Africa.
- Global Competition
-
- Africa experienced a sharpened international competition, known as ‘the third scramble’, in the first two decades of the 21st century.
- A dozen nations from the Americas, Europe and Asia have striven to assist Africa in resolving the continent’s political & social challenges and, in turn, to benefit from Africa’s markets, minerals, hydrocarbons and oceanic resources.
- Setback in India’s “Vax Diplomacy”
-
- China successfully used the pandemic to expand its footprint by increasing the outflow of its vaccines to African Continent.
- India’s vaccine supply to Africa suffered setback due to increased domestic demand in the wake of second wave of COVID-19 and the shortage of vaccine raw materials from the U.S.
- India wanted to consolidate its position in its subcontinent and hence Africa did not attain priority in Vax Diplomacy
Way Ahead
- The third India-Africa Forum Summit was held in 2015. The fourth summit, pending since last year, should be held as soon as possible, even if in a virtual format.
- Fresh financial resources for grants and concessional loans to Africa must be allocated, as previous allocations stand almost fully exhausted.
- India & Africa must develop and deepen collaborations in health, space and digital technologies.
- To overcome the China challenge in Africa, India should adopt partnership based approach with its international allies (like EU, US & Japan)
Connecting the dots:
- Pandemic in Africa and opportunity for India
- Asia-Africa growth Corridor
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Where is Guindy National Park located?
- Tamil Nadu
- Kerala
- Telangana
- Andhra Pradesh
Q.2 Kalbelia Dance is a folk dance of which of the following state?
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Gujarat
- Haryana
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding BharatNet project:
- It is the world’s largest rural broadband connectivity programme using Optical fibre.
- It is implemented by Bharat Broadband Network Ltd. (BBNL).
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 1st July 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | C |
Must Read
On Insolvency & Bankruptcy:
On Indian and Religion:
On Dowry & measures to overcome this social menace:











