IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
CoWIN Platform
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – International relations; Health and GS-III – Technology
In news: The Indian Prime Minister recently addressed the CoWin Global Conclave where India offered the CoWIN platform as a digital public good to the world to combat COVID19.
What is CoWIN?
- CoWIN (Covid Vaccine Intelligence Work) is the Indian government’s web portal to register for COVID-19 vaccination. It displays slots of COVID-19 vaccine available in the nearby areas and can be booked on the website.
-
- It is a secure and trustworthy proof helped people establish when, where and by whom they had been vaccinated.
- In totality, CoWIN is a cloud-based IT solution for planning, implementation, monitoring, and evaluation of Covid-19 vaccination in India.
- This allows the system to monitor the utilisation, wastage, coverage of Covid-19 vaccination at national, state, district and sub-district level.
- CoWIN system tracks on a real time basis the vaccination drive in India.
- The portal also provides vaccination certificates in digital format
- CoWIN is essentially an extension of eVIN (Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network).
Do you know?
- CoWIN has become the fastest tech platform in the world to amass over 200 million registrations in a record four months, and then 300 million registrations in a mere five months.
What are highlights of the recent PM address?
- The decision to make CoWIN platform open source and offer it as a digital public good was guided by the approach of ‘One Earth, One Health’.
- It is also a part of CoWIN Global Outreach Programme
- The software is customizable as per the local requirements of the interested countries.
- More than 50 countries including Nigeria, Canada and Mexico have shown interest in CoWIN platform
Source: TH
AYUSH sector
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Health
In News: The Minister of AYUSH launched Important Portals in the Ayush sector.
What are the launched portals?
- E-Medha (electronic Medical Heritage Accession) Portal
- Online public access catalog for more than 12000 Indian medical heritage books through NIC’s e-granthalaya platform.
- AMAR (Ayush Manuscripts Advanced Repository) Portal
- It has digitized information on rare and hard to find Manuscripts and catalogues of Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, Sowa Rigpa in libraries or in individual collections across India or in other parts of the world.
- SHAI (Showcase of Ayurveda Historical Imprints) Portals
- This portal showcases inscriptions, Archeo-botanical Information, Sculptures, Philological sources and advanced Archeo Genetic studies.
- This portal will be of tremendous use in understanding of Indian Knowledge system with a focus on indigenous health care practices.
- CCRAS-Research Management Information System (RMIS)
- A collaborative effort of Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and Central Council for Research in Ayurvedic Sciences(CCRAS), this portal will be a one stop solution for Research and Development in Ayurveda based studies.
Source: PIB
National Mission for Clean Ganga
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions
In news
- A policy document from the National Mission for Clean Ganga has instructed Cities situated on river banks to incorporate river conservation plans when they prepare their Master Plans.
- The recommendations are currently for towns that are on the main stem of the Ganga. There are 97 towns encompassing five States — Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal.
Some of the norms emphasised in the policy document are
- Clarifying land ownership issue, restrictions on the Floor Area Ratio, increasing green cover in the vicinity of the river by creating green buffers, removing concrete structures and employing green infrastructure.
- Facilitating the use of state-of-the-art technologies for river management – Satellite-based monitoring of water quality; Big data for river-health monitoring and Drones & AI for riverine biodiversity & floodplain mapping.
What is the National Mission for Clean Ganga(NMCG)?
- The National Ganga Council, also known as the National Council for Rejuvenation, Protection, and Management of River Ganga was set up in 2016. It replaced the National River Ganga Basin Authority (NRGBA).
- NGRBA was constituted under the provisions of the Environment (Protection) Act (EPA),1986.
- The National Ganga Council, chaired by Prime Minister, has been given overall responsibility for the superintendence of pollution prevention and rejuvenation of River Ganga Basin, including Ganga and its tributaries.
- National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) is the implementation arm of national Ganga Council.
- NMCG is registered as a society in 2011 under the Societies Registration Act 1860.
- The aims and objectives of NMCG are:
- To ensure effective control of pollution and rejuvenation of the river Ganga by adopting a river basin approach to promote inter-sectoral coordination for comprehensive planning and management.
- To maintain minimum ecological flows in the river Ganga with the aim of ensuring water quality and environmentally sustainable development.
Source: TH
UDISE+ 2019-20 Report
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Education
In news
- Recently, the Union Education Minister released the Report on United Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) 2019-20 for School Education in India.
What are the key findings of the Report (2019-20)?
| Total Student Strength Pre-primary to Higher secondary |
|
| Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) | GER at all levels of school education has improved in 2019 20 compared to 2018-19
Earlier = 2018-19 data |
| Teacher Strength |
|
| Pupil Teacher Ratio (PTR) | PTR has improved at all levels of school education.
Earlier = 2012-13 data |
| Enrolment of girls |
GER of girls in 2019-20 at
(from 2018-19). |
| Inclusivity |
|
| Infrastructural Facilities |
|
What are Some Important Government Initiatives for promoting Education?
- New National Education Policy (NEP), 2020.
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan.
- Mid Day Meal Scheme.
- Right To Education (RTE) Act, 2009.
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao.
Source: PIB
Fly Ash
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions and GS III – Conservation
In news
- National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) Limited has invited Expression of Interest (EOI) for sale of fly ash, in its endeavour to achieve 100% utilization of fly ash, from the designated plants of the Middle East and other regions.
What is Fly Ash?
- Fly Ash is a byproduct from burning of coal in the thermal power generation.
- It is called fly ash because it is transported from the combustion chamber by exhaust gases.
- Composition: silicon dioxide (SiO2), aluminium oxide (Al2O3), ferric oxide (Fe2O3) and calcium oxide (CaO).
- Uses: In concrete and cement products, road base, metal recovery, and mineral filler among others.
- Harmful Effects:
- Toxic air pollutants which can trigger heart disease, cancer, respiratory diseases and stroke.
- When combined with water they cause leaching of heavy metals in ground water.
- Affects the root development system of trees.
What is Fly Ash Utilisation Policy?
- To promote the use of Fly Ash bricks in building construction, NTPC has set up Fly Ash brick manufacturing Plants at its Coal based Thermal Power Plants.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban) has focused on new construction technologies such as using fly ash bricks that are innovative, and environmentally friendly.
- Maharashtra was the first state to adopt the Fly Ash utilization policy.
- A web portal for monitoring of fly ash generation and utilization and a mobile based application titled “ASHTRACK” has been launched by the Government.
- GST rates on fly ash and its products have been reduced to 5%.
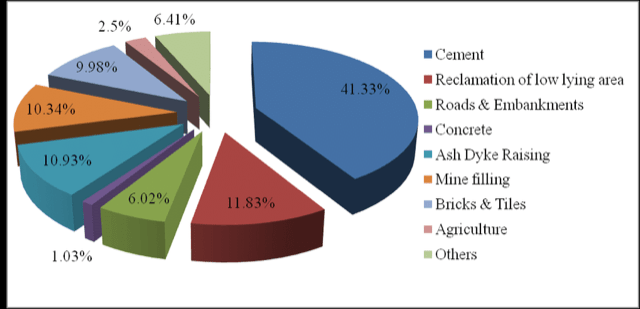
Pic courtesy: Researchgate
Source: PIB
Purchasing Managers Index (PMI)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS III – Economy
In News: Survey-based June PMI for services sector shows second successive contraction at 41.2
What is PMI?
- It is a survey-based measure that asks the respondents about changes in their perception about key business variables as compared with the previous month.
- It is calculated separately for the manufacturing and services sectors and then a composite index is constructed.
- The PMI is a number from 0 to 100.
-
- PMI above 50 represents an expansion when compared to the previous month;
- PMI under 50 represents a contraction, and
- A reading at 50 indicates no change.
- f PMI of the previous month is higher than the PMI of the current month (as is the case mentioned above), it represents that the economy is contracting.
- The PMI is usually released at the start of every month. It is, therefore, considered a good leading indicator of economic activity.
- Also, since the official data on industrial output, manufacturing and GDP growth comes much later, PMI helps to make informed decisions at an earlier stage.
- PMI provides information about current and future business conditions to company decision-makers, analysts, and investors.
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ ECONOMY
Topic:
- GS-2: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Crafting a unique partnership with Africa
Context: Critical to its foreign policy matrix, New Delhi’s engagement with the African continent has been multifaceted.
India should prioritise and channel resources into augmenting its partnership with Africa in agriculture sector because:
- Unexplored Potential: 65% of the world’s uncultivated arable land is in African continent that provides huge potential for India to collaborate in Agricultural sector through supply of machinery, acquisition of farmlands, institutional & Individual capacity building etc.
- Centrality to global food security: As Nations across the world faces dangers of declining agricultural productivity in the wake of Climate Change, Africa’s underdeveloped agriculture sector is a ray of hope for global food security.
- Business prospects: Indian farmers have purchased over 6,00,000 hectares of land for commercial farming in Africa, which has scope for further investment. Also, Africa provides golden opportunity for Indian entrepreneurs in agri-tech sector (the sector enjoyed a 110% growth between 2016 and 2018)
- Countering China: India’s engagement in Africa’s agriculture sector provides credible alternatives to the increasing involvement of Chinese stakeholders in the sector.
Analysing Chinese engagement
- Biggest Economic Partner: China is among Africa’s largest trading partners. It is also Africa’s single biggest creditor. Its corporations dominate the region’s infrastructure market and are now entering the agri-infra sector.
- Primary Drivers for China’s engagement with Africa: Access to Africa’s natural resources, its untapped markets and support for ‘One China Policy’ are primary drivers of Chinese engagement with the region.
- Relocation Site for Chinese Firms: Chinese-built industrial parks and economic zones in Africa are attracting low-cost, labour-intensive manufacturing units that are relocating from China (as labour costs are increasing in China impacts the competitiveness of Chinese goods)
- Learning Experience: Chinese operations in Africa are important to accumulate global experience in management, risk and capital investments.
- Building Brand China: Chinese are willing to overlook short-term profits in order to build ‘brand China’, but they want to dominate the market in the long term, which includes pushing Chinese standards in host countries.
- Alternate to traditional western powers: Beijing’s model, if successful in Africa, could be heralded as a replica for the larger global south. This will catapult China as leader of Global South weaning thee countries away from their dependence on USA.
- Evolving Engagement in Africa’s agricultural landscape: Chinese firms are introducing agri-tech (drones), setting up Technology Demonstration centres (TDC), collaboration with locals on developing new crop varieties, skill training, ecological parks etc
What mistakes Chinese are committing in Africa which India should avoid repeating it?
- Growing, insular Chinese diaspora in Africa
- Lopsided trade
- Looming debt
- Competition with local businesses
- Chinese and African experts working in Agricultural TDCs are operating in silos leading to ineffective outcomes
- Technology taught in China is not available locally.
- Inability to implement lessons learnt due to the absence of supporting resources.
- Aggravating socio-cultural stresses due to larger commercial farms being run by Mandarin-speaking managers and the presence of small-scale Chinese farmers in local markets.
Way Ahead for India
- While India’s Africa strategy exists independently, it is important to be cognisant of China’s increasing footprint in the region.
- Prominent African voices have emphasised that their own agency is often overlooked in global discourse on the subject. India’s engagement should not lead to dilution of African agency.
- India’s stand that the development partnership has to be in line with African priorities should be continued & should be showcased as an alternative to Chinese Model (Chinese priorities overtake Africa’s priorities)
Connecting the dots:
- Pandemic in Africa and opportunity for India
- India-Africa Relationship
- Asia-Africa growth Corridor
ECONOMY/ INTERNATIONAL/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
OPEC’s output pact proposal
Definition: The latest round of meetings among the OPEC+ group of oil-exporting countries has stalled as the UAE has pushed back proposals making an increase in crude oil supply conditional on an extension to an output agreement.
What is the background?
- Low Oil Prices in wake of Pandemic-induced global slowdown: The price of Brent crude hit an 18-year low of under $20 per barrel in April 2020 as economic activity around the world crashed as countries dealt with the pandemic.
- Production Cut to boost Prices: As a result, OPEC+ group of countries had, in April 2020, entered into a two-year agreement, which entailed steep cuts in crude production (reduction in supply leads to increase in prices)
- Subsequently in November 2020, the price of Brent crude started climbing and has, now, risen to $76.5 per barrel —buoyed by the steady rollout of vaccination programmes around the world.
- Continuance with Production Cut: OPEC+, however, maintained lower levels of production despite crude oil prices reaching pre-Covid levels, with Saudi Arabia, notably, announcing a further cut in production of 1 million barrels per day for the February-to-April 2021, which helped boost rising prices even further
- Criticism on rising Oil Prices: The OPEC+ group ran into sharp criticism from developing economies, including India, for deliberately maintaining low supply levels to raise prices. This was in turn slowing down the economic recovery of countries post the pandemic.
- Gradual Increase in Oil Production: Amidst the growing criticism, OPEC+, in April 2021, agreed to gradually increase crude production as prices reached $64.5 per barrel.
What is the issue?
- UAE agreed that there was a need to increase crude oil production from August, but did not agree to a condition by the OPEC Joint Ministerial Monitoring Committee (JMMC) that the two-year production agreement be extended by six months.
- The UAE’s key objection to the existing agreement is the reference output used to calculate the total production apportioned (allotted) to each oil-exporting country.
- The UAE noted that the baseline production level reference used in the current agreement was not reflective of the UAE’s production capacity and, therefore, led to the UAE being apportioned a lower share of total production of crude oil.
How will this impact India?
- If the UAE and other OPEC+ nations do not reach an agreement to increase production in August, expected relief in the form of lower crude oil prices could be delayed.
- India is currently facing record-high prices of petrol and diesel (near to Rs 100/ltr). If oil prices do not come down, petrol/diesel prices will further increase which in turn will lead to inflation hampering economic recovery (as purchasing capacity lowers)
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements about National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG)
- It acts as implementation arm of National Council for Rejuvenation, Protection and Management of River Ganga
- National Ganga Council is under the chairmanship of Prime Minister of India
Select the correct statements
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding new portals launched by Ministry of Ayush:
- E-Medha Portal is an Online public access catalog for more than 12000 Indian medical heritage books through NIC’s e-granthalaya platform.
- AMAR Portal has digitized information on rare and hard to find Manuscripts and catalogues of Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha, Sowa Rigpa in libraries or in individual collections across India or in other parts of the world.
Select the correct statements
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Which of the following is not a Harmful Effect of Fly Ash:
- Toxic air pollutants
- Leaching of heavy metals
- Affects the root development system of trees
- None of the above
ANSWERS FOR 5th July 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
On All India Judicial Services:
On Nationalism in India and China:
On Zoonotic diseases:














