IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
In News: The government notified new norms for overseas investments by Indians.
- The Overseas Investment Rules and Regulations, notified under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), will be administered by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and shall subsume all existing norms pertaining to overseas investments as well as acquisition and transfer of immovable property outside India.
- New norms are aimed at making it easier for domestic corporates to invest abroad, while making it tougher for loan defaulters and others being probed by investigative agencies and regulators to shift funds out of the country.
- No Indian resident shall be allowed to make investments into foreign entities that are engaged in real estate activity, gambling in any form, and dealing with financial products linked to the Indian rupee without the central bank’s specific approval.
- To make it difficult for bank defaulters and fraudsters to acquire assets abroad, often as a precursor to leaving the country, the new rules mandate they secure a No Objection Certificate (NOC) from their lender, or concerned regulators and investigative agencies before making any ‘financial commitment’.
- This NOC shall be mandatory for any person who has a bank account classified as a non-performing asset, or is labelled a wilful defaulter by any bank, or is under the investigation by a financial service regulator, the Enforcement Directorate (ED) or the Central Board of Investigation (CBI).
- The rules, framed in consultation with the central bank, provide that if lender banks or the concerned regulatory body or investigative agency fail to furnish the NOC within 60 days of receiving an application, it may be presumed that they have no objection to the proposed transaction.
- Any resident in India acquiring equity capital in a foreign entity or overseas direct investment (ODI), will have to submit an Annual Performance Report (APR) for each foreign entity, every year by December 31.
- No such reporting shall be required where a person resident in India is holding less than 10% of the equity capital without control in the foreign entity and there is no other financial commitment other than equity capital or a foreign entity is under liquidation.
- Any resident individual can make ODI by way of investment in equity capital or overseas portfolio investment (OPI) subject to the overall ceiling under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) of the Reserve Bank. Currently, the LRS permits $2,50,000 outward investment by an individual in a year.
- An Indian entity can make OPI not exceeding 50% of its net worth as on the date of its last audited balance sheet.
In view of the evolving needs of businesses in India, in an increasingly integrated global market, there is a need of Indian corporates to be part of the global value chain.
The revised regulatory framework for overseas investment provides for simplification of the existing framework for overseas investment and has been aligned with the current business and economic dynamics.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Retail investors through demat account can invest in ‘Treasury Bills’ and ‘Government of India Debt Bonds’ in primary market.
- The ‘Negotiated Dealing System-Order Matching’ is a government securities trading platform of the Reserve Bank of India.
- The ‘Central Depository Services Ltd.’ is jointly promoted by the Reserve Bank of India and the Bombay Stock Exchange.
Which of the statements given below is/are correct?
- 1 Only
- 1 and 2
- 3 Only
- 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
In News: India-China dispute casts gloom over space project.
- Tension between India and China since May 2020 is worrying Indian astrophysicists involved in an ambitious project to install an India-made spectroscope aboard the developing Chinese space station, Tiangong.
- Scientists at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru, were among nine groups selected from 42 applicants in 2019 as part of a United Nations-led initiative that invites research teams from all over the world to compete for an opportunity to design payloads that will be shuttled to Tiangong aboard rockets of the Chinese Manned Space Agency.
- The project, called Spectrographic Investigation of Nebular Gas (SING), also involves collaboration with the Institute of Astronomy, Russian Academy of Sciences, and has been designed and developed by research students at the IIA.

- The SING project would be the first space-collaboration involving India and China, and primarily deals with sending and positioning a spectrograph, an instrument that splits light into constituent frequencies and wavelengths, to study ultraviolet radiation.
- This will help analyse the make-up and sources of interstellar gas in the region that swept by the space station as it orbits around the earth.
- The Chinese T-shaped Tiangong space station, when complete, is expected to be around 20% as massive as the International Space Station, or about 460 tonnes on Earth.
- The space station consists of three modules, two of which have already been launched in April 2021 and July this year, respectively.
- The third is expected to be launched this October. It will be only the second such station after the International Space Station in orbit.
India and China have been collaborators in the past on research projects such as the Giant Metre Wave Radio Telescope, a Pune-based observatory that’s employed by astrophysicists across the world to study radiation at metre-scale resolutions to observe and analyse stars and galaxies.
Must Read: China’s space station
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million kilometres long, with lasers shining between the craft”. The experiment in question refers to (2020)
- Voyager
- New Horizons
- LISA Pathfinder
- Evolved LISA
Syllabus
- Prelims – Defence – Current Affairs
In News: Recently, Vertical Launch Short Range Surface to Air Missile (VL-SRSAM) was successfully flight-tested by Defence Research & Development Organization (DRDO) and the Indian Navy from an Indian Naval Ship at Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur off the coast of Odisha.
- It is a quick reaction surface-to-air-missile indigenously designed and developed by DRDO for the Indian Navy, is meant for neutralizing various aerial threats at close ranges, including sea-skimming targets.
- Sea skimming is a technique many anti-ship missiles and some fighter or strike aircraft use to avoid radar and infrared detection.
- The missile has been designed to strike high-speed airborne targets at the range of 40 to 50 km and at an altitude of around 15 km.
- Its design is based on Astra missile which is a Beyond Visual Range Air to Air missile.

Features:
- Cruciform wings: They are four small wings arranged like a cross on four sides and give the projective a stable aerodynamic posture.
- Thrust Vectoring: It is the ability to change the direction of the thrust from its engine, control the angular velocity and the attitude of the missile.
- VL-SRSAM is a canisterised system, which means it is stored and operated from specially designed compartments. In the canister, the inside environment is controlled thus making its transport and storage easier and improving the shelf life of weapons.
Source: Pib.Gov
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to the Agni-IV Missile, which of the following statement(s) is/are correct? (2014)
- It is a surface-to-surface missile.
- It is fuelled by liquid propellant only.
- It can deliver a one-tonne nuclear warhead about 7500 km away.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science – Current Affairs
In News: The James Webb Space Telescope, NASA’s latest and most powerful telescope, has captured new images of our solar system’s largest planet, Jupiter, presenting it in a never-before-seen light.

Unprecedented view
- While most of us are familiar with the yellow and reddish-brown gas giant,the telescope’s Near-Infrared Camera, with its specialized infrared filters, has shown Jupiter encompassed in blue, green, white, yellow, and orange hues.
- Since infrared light is not visible to the human eye, the images were artificially colored to match those on the visible spectrum, so that the planet’s distinctive features could stand out.
- The brightness here indicates high altitude — so the Great Red Spot has high-altitude hazes, as does the equatorial regio.
- The numerous bright white ‘spots’ and ‘streaks’ are likely very high-altitude cloud tops of condensed convective storms.
The Webb Telescope
- NASA’s $10 billion James Webb Telescope was developed with the assistance of the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency.
- It was launched to space in December2021 and is currently observing from Lagrange point 2, approximately 1.5 million km beyond Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs – legislations and schemes
- Mains – GS 1 (Society – Social Justice)
In News: Study says sex ratio at birth fell from 111 boys per 100 girls in 2011 to 108 boys per 100 girls in 2019-21
- The latest study by Pew Research Center has pointed out that “son bias” is on a decline in India and the average annual number of baby girls “missing” in India fell from about 480,000 (4.8 lakh) in 2010 to 410,000 (4.1 lakh) in 2019.
- The “missing” here refers to how many more female births would have occurred during this time if there were no female-selective abortions.
- Among the major religions, the biggest reduction in sex selection seems to be among the groups that previously had the greatest gender imbalances, particularly among Sikhs.
- World over, boys modestly outnumber girls at birth, at a ratio of approximately 105 male babies for every 100 female babies.
- That was the ratio in India in the 1950s and 1960s, before prenatal sex tests became available across the country.
- India legalised abortion in 1971 but the trend of sex selection started picking up in the 1980s due to the introduction of ultrasound technology.
- In the 1970s, India’s sex ratio was at par with the global average of 105-100, but this widened to 108 boys per 100 girls in the early 1980s, and reached 110 boys per 100 girls in the 1990s.
- From a large imbalance of about 111 boys per 100 girls in India’s 2011 census, the sex ratio at birth appears to have normalised slightly over the last decade, narrowing to about 109 in the 2015-16 wave of the National Family Health Survey and to 108 boys in the latest wave of the NFHS, conducted from 2019-21.
- The Pew Research Center report points out that between 2000-2019, nine crore female births went “missing” because of female-selective abortions.
- The report has also analysed religion-wise sex selection, pointing out that the gap was the highest for Sikhs.
- The study points out that while the Sikhs make up less than 2% of the Indian population, they accounted for an estimated 5%, or approximately 440,000 (4.4 lakh), of the nine crore baby girls who went “missing” in India between 2000 and 2019.
- The share of “missing” girls among Hindus is also above their respective population share. “Hindus make up 80% of India’s population but accounted for an estimated 87%, or approximately eight crores of the females “missing” due to sex-elective abortions.
- The share of female births “missing” among Muslims and Christians during this period is lower than each group’s share of the Indian population.
Measures taken by Government to fight sex selective abortions
Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques Act
- The act was enacted in 1994 in response to the decline in Sex ratio in India, which deteriorated from 972 in 1901 to 927 in 1991.
- The main purpose of the act is ban the use of sex selection techniques before or after conception and prevent the misuse of prenatal diagnostic technique for sex selective abortion.
Salient features of the act:
- It regulates the use of pre-natal diagnostic techniques, like ultrasound and amniocentesis by allowing them their use only to detect few cases.
- No laboratory or centre or clinic will conduct any test including ultrasonography for the purpose of determining the sex of the foetus.
- No person, including the one who is conducting the procedure as per the law, will communicate the sex of the foetus to the pregnant woman or her relatives by words, signs or any other method.
- Advertisement for pre-natal and pre-conception sex determination facilities will attract fine of Rs 10000 and imprisonment upto 3 years.
- The Act mandates compulsory registration of all diagnostic laboratories, all genetic counselling centres, genetic laboratories, genetic clinics and ultrasound clinics.
- The Act was amended to bring the technique of pre conception sex selection and ultrasound technique within the ambit of the act.
- The 2003 amendment to the act led to establishment of the central supervisory board and state level supervisory board was constituted.
Other measure taken by government to improve condition of females:
‘Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao’ campaign
The objectives of this initiative are to prevent of gender biased sex selective elimination, and to ensure survival and protection of the girl child. The strategies involved in this scheme are:
- Implement a sustained Social Mobilization and Communication Campaign to create equal value for the girl child & promote her education.
- Place the issue of decline in CSR/SRB in public discourse, improvement of which would be a indicator for good governance.
- Focus on Gender Critical Districts and Cities low on CSR for intensive & integrated action.
- Mobilize & Train Panchayati Raj Institutions/Urban local bodies/ Grassroot workers as catalysts for social change, in partnership with local community/women’s/youth groups.
Legislations for creating a safe and secure environment for females.
- POCSO Act (Prevention of Children from Sexual offences)
- Sexual Harassment at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act
- Changes in the Criminal Law on the recommendations of Justice Verma Committee
Enhanced Focus on Health & Education of Child
- Provision of better nutrition through ICDS and MDM.
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram
- Scholarship schemes like Pragati
- Special girl’s school like Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalayas
Political Empowerment
- Reservation of seats for women in Panchayats and Urban Local bodies are provided to enhance the decision making powers of women which leads to increased awareness among women about their rights especially reproductive rights.
Must Read: Child Malnutrition
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana is aimed at (2016)
- bringing the small entrepreneurs into formal financial system
- providing loans to poor farmers for cultivating particular crops
- providing pensions to old and destitute persons
- funding the voluntary organizations involved in the promotion of skill development and employment generation
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance); GS 3 (Cyber security)
Context: Role of Law Enforcement Agencies in roll-out of 5G technology.
With a shaky cyber security foundation, the impact on crime and criminals could be serious
- Prime Minister recently announced that 5G deployment in India will commence sooner than expected.
- The long-awaited upgrade from 4G to 5G will allow ultra-fast Internet speeds and seamless connectivity across the country compared to 4G.
- The implications of the 5G roll-out could be significant, particularly for law enforcement in India.
Ensuring security
- On the one hand, the 5G roll-out is set to enhance efficiency, productivity, and security by helping the police access critical information in real-time and nab criminals.
- 5G has high bandwidth and low latency, so its adoption would ensure the best performance of police devices such as body cams, facial recognition technology, automatic number-plate recognition, drones, and CCTVs.
- The increased storage capacity promised by 5G will allow the police to streamline their investigation methods.
- 5G will also allow rapid and secure communication within the organisation as well as between civilians and emergency responders.
- With 5G, the police can remotely access and analyse crime data and information from other infrastructure such as traffic lights.
Challenges in adopting 5G
Infrastructure and technology
- The government and telecommmunication companies must first ensure that law enforcement agencies have the necessary infrastructure to take full advantage of all that 5G can offer.
- Most police systems are outdated and may not be compatible with 5G.
- To bridge this technology gap, the police must invest in modern tools, software and infrastructure. They require funds to do this.
Cyber security concerns
- Deploying 5G with a shaky cyber security foundation is like erecting a structure on soft sand.
- As the previous networks were hardware-based, India could practise cyber hygiene.
- But 5G is a software-defined digital routing.
- This makes it susceptible to cyber threats such as botnet attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) overloads.
- Besides, as 5G lacks end-to-end encryption, hackers can plot their attacks more precisely and perpetrate cybercrimes by hacking into systems or disseminating illegal content.
- The bandwidth expansion due to 5G will enable criminals to embezzle data bases easily. With time, as 5G connects with additional devices, the frequency of attacks could increase.
Increase in crimes and criminals
- The impact that the roll-out of 5G in India could have on crime and criminals is pretty obvious and should be taken seriously.
- Criminals could use 5G to conceal their activities or mask their location.
- They could use 5G to locate their victims quickly and track their movements and coordinate onslaughts through real-time communication with each other.
- There could be a lower probability of criminals getting caught when they commit identity theft or credit card fraud or steal information from computers, smartphones and tablets.
- 5G may also make it easier for criminals to perpetrate cyber bullying.
- They could also hack into Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices and remotely commit crimes.
- Security patching of all IoT devices may eventually become necessary.
- Terrorists, too, could benefit from 5G as the high speed would allow them to execute attacks more rapidly and precisely.
Way forward
Authorities will have to adopt measures to hinder crimes facilitated by 5G technology.
- First, the police will need to be trained so that they recognise new 5G-enabled crimes.
- Second, training programmes focusing on such crimes must be developed. This includes identifying potential scenarios for new types of crimes and their prevention.
- Third, the government and telecom companies could set up a 5G crime monitoring task force to monitor and identify new crimes and develop countermeasures.
- Fourth, it is imperative to create regulations that make it a crime for people to use 5G technology to commit crimes.
- Such a regulation could help prevent criminals from using stolen or counterfeit equipment since telecom companies will be able to track the location of the equipment and shut it down remotely.
- Fifth, regulations may also require telecom companies to allow police officers access to their equipment to track the location of victims and perpetrators of 5G-facilitated crimes for countermeasures.
- These countermeasures may not only safeguard critical infrastructure but also defend private citizens from cyber-attacks using 5G technology.
- Finally, law enforcement agencies will have to evolve strategies to identify victims of 5G-facilitated crimes, locate them and take action against the perpetrators of such crimes.
The 5G roll-out will be a game-changer for law enforcement agencies. It will enable the police fight crime effectively. At the same time, criminal use of 5G is inevitable. In this context, the recent recommendation of the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India to the government to develop a national road map for India to implement 5G in the best possible manner should encompass law enforcement requirements.
Must Read: 5G Technology + 5G Auctions
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
- Mains – GS2 (International Relations)
Context: After months of what appeared to be a “go-slow”, the Union government has revved up its interest in using Iran’s Chabahar port to connect to Afghanistan, Europe, Russia and Central Asia for trade.
Importance of Chabahar port for India:
- It will also boost India’s access to Iran, the key gateway to the International North-South Transport Corridor that has sea, rail and road routes between India, Russia, Iran, Europe, and Central Asia.
- It also helps India counter Chinese presence in the Arabian Sea which China is trying to ensure by helping Pakistan develop the Gwadar port.
- Trade benefits: With Chabahar port becoming functional, there will be a significant boost in the import of iron ore, sugar, and rice to India. The import cost of oil to India will also see a considerable decline considering recent global energy crisis due to Russia- Ukraine conflict.
- From a diplomatic perspective, Chabahar port could be used as a point from where humanitarian operations could be coordinated.
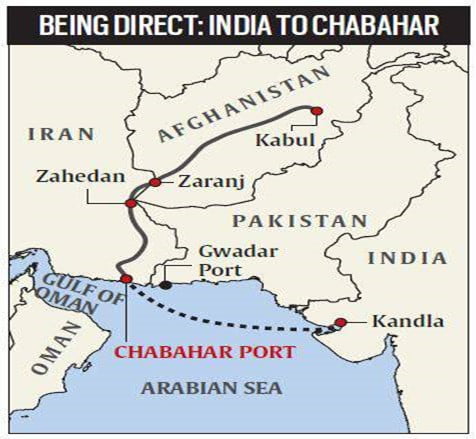
Delay in the Chabahar port project:
- Iran’s relationship with western countries, especially the United States: In years when western sanctions against Iran increased, the Chabahar project has been put on the back-burner, while in the years when nuclear talks that resulted in the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) in 2015 came into being, the Chabahar port has been easier to work on.
- In 2018, the S. Trump administration put paid to India’s plans by walking out of the JCPOA and slapping new sanctions on dealing with Iran. This led to the Union Government “zeroing out” all its oil imports from Iran, earlier a major supplier to India, causing a strain in ties.
- The Union Government also snapped ties with Afghanistan after the Taliban takeover in August 2021, which put an end to the humanitarian aid of wheat and pulses that was being sent to Kabul via Chabahar. When India restarted wheat aid to Afghanistan this year, it negotiated with Pakistan to use the land route instead.
Way Forward
- With the government now reopening the Indian Embassy in Kabul, and establishing ties with the Taliban government, it is possible that the Chabahar route will once again be employed
- Completion of Chabahar port project will give a boost to Indian strategic interest and objectives in the region.
Must Read: Chabahar Port
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography (Map)
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance); GS 3 (Environment)
In News: The week-long ongoing protests against the construction of the Adani Group’s Vizhinjam International Transhipment Deepwater Multipurpose Seaport in Kerala’s capital Thiruvananthapuram intensified, with fisherfolk laying siege to the port from the sea and land.
- The fishing community has said the protests will continue until all their demands are met.
- The Chief Minister of Kerala told that the government was ready for talks, and wanted to resolve the concerns faced by the fishing community — however, it could not agree to halting the project.
Fisherfolk’s demands
- The biggest demand of the protesters is that the project should be stopped and a proper environmental impact study should be carried out.
The community has also put forward six other demands:
- rehabilitation of families who lost their homes to sea erosion,
- effective steps to mitigate coastal erosion,
- financial assistance to fisherfolk on days weather warnings are issued,
- compensation to families of those who lose their lives in fishing accidents,
- subsidised kerosene, and
- a mechanism to dredge the Muthalappozhi fishing harbour in Anchuthengu in Thiruvananthapuram district.
The government has conceded all demands except providing a kerosene subsidy, and halting the construction of the port.
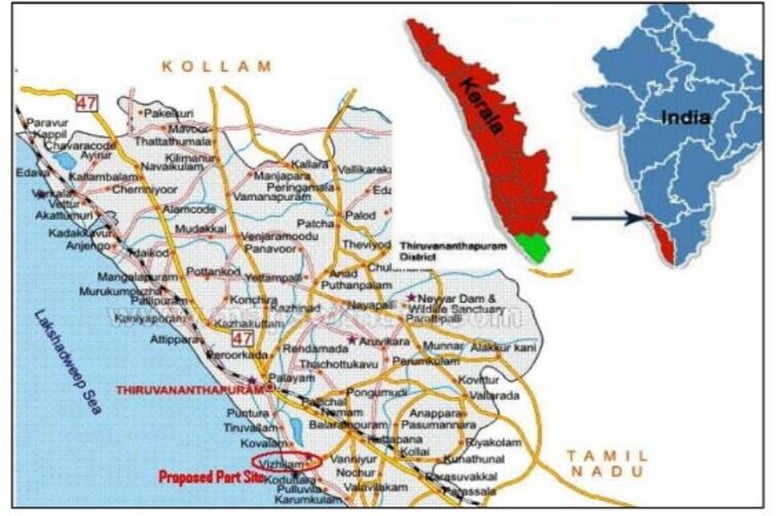
Delays; contested studies
- As per the initial agreement, the project was supposed to be operational by 2019. The Adani Group cited several reasons for the delay, from the 2017 Ockhi cyclone to the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Fisherfolk were also provoked by the central government’s annual shoreline studies that concluded work on the port did not lead to increased coastal erosion, even though the impact was clearly visible.
- In 2019, the National Institute of Ocean Technology, Chennai, said in its Annual Shoreline Monitoring report that erosion spots such as Valliyathura, Shangumugham, and Punthura had remained unchanged since the construction of the port began in 2015.
- The 2021 edition of the study noted erosion at Pulluvila (500 m), Mullur (290 m), Kochuveli (250 m), Punthura (150 m), Cheriyathura (120 m), Shangumugham (100m), and Valliyathura (50m), but concluded that the port activity had less impact than high wave activities and cyclones in the Arabian Sea.
Question of viability
- The Rs 7,525 crore port being built under a Public Private Partnership (PPP) model with Adani Ports Private Limited, in December 2015.
- The port will have 30 berths, and will be able to handle giant “megamax” container ships.
- It is said to be ultramodern port, located close to major international shipping routes, will boost India’s economy.
- The port is expected to compete with Colombo, Singapore, and Dubai for a share of trans-shipment traffic.
- The report of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India, tabled in the Kerala assembly in 2017, had said the conditions of the concession agreement were not favourable to the state government.
- Out of a total project cost of Rs 7,525 crore, the Adani Group needs to invest only Rs 2,454 crore. The rest of the cost would be borne by the state and the central governments, the CAG report stated.
- The CAG had said that the standard concession period for PPP projects was 30 years, but the Vizhinjam project concessionaire had been given an extra 10 years, which would allow it to reap an additional revenue of Rs 29,127 cr
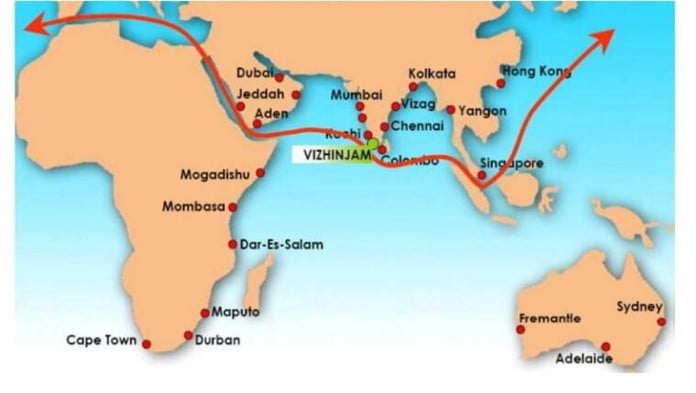
According to locals, the project would put the government in a “debt trap”, and could meet a fate similar to that of the Vallarpadam Terminal in Kochi, which has failed to make a profit more than a decade after it was opened.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography – Rivers
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment – Climate Change)
Context: Europe is experiencing the great drought.
- Some of Europe’s biggest rivers — Rhine, Po, Loire, Danube — which are usually formidable waterways, are unable to support even mid-sized boats.
- As water levels have fallen, remains of sunken ships and ominously named hunger stones — rocks engraved by previous generations during earlier periods of extraordinary dryness — have come out of erstwhile depths.
- The drought has been billed as the worst in 500 years.
- It is being said that never has a European summer been so dry since 1540, when a year-long drought killed tens of thousands of people.
- The dry spell this year follows a record-breaking heatwave that saw temperatures in many countries rise to historic highs.

The impact has been debilitating.
- Water transport has suffered badly, and is having cascading effects.
- Power production has been hit, leading to electricity shortages and a further increase in energy prices already pushed high by the war in Ukraine.
- Food is sharply more expensive in many countries, and drinking water is being rationed in some regions.
Worst in 500 years
- Earlier European droughts — such as those in 2003, 2010, and 2018 — too were compared to the 1540 event.
- Much like now, the 2018 drought was described as the “worst in 500 years”.
- But a senior scientist at the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre said this year could turn out to be worse than 2018, though data were still being analysed.
- The “worst in 500 years” description may be still not settled, but the impacts of this event are expected to be far worse than anything experienced in the recent past.
- Europe has been facing large scale climatic anomalies for over six months — precipitation has been far less than usual, while temperatures have soared to unprecedented levels.
- And this has come on top of the massive energy and food-supply implications of the Ukraine war.

Waterways and power
- Apart from agriculture and drinking water supplies, the most visible impact has been the disruption in Europe’s waterways.
- Europe depends heavily on its rivers to move cargo in an economical manner, including coal to power plants.
- With water levels down to less than a metre in some stretches, most large ships have been rendered unusable.
- Supply disruptions in coal has hit power generation.
- Lack of adequate water has affected the operation of nuclear power plants, which use large amounts of water as coolant.
- The result has been a shortage of electricity and an unprecedented rise in energy prices.
Drought in China, US too
- Many parts of China too are headed towards a serious drought, being described as the worst in 60 years.
- The country’s longest river, Yangtze, which caters to about a third of the Chinese population, is seeing water levels drop to record lows, according to a report in the South China Morning Post.
- Two of the country’s biggest freshwater lakes, Poyang and Dongting, have touched their lowest levels since 1951, the report said.
- The water scarcity is leading to problems similar to those in Europe. Power shortages in some areas have begun to force factories to shut, adding to the strain on global supply chains.
- Over 40% of the area in the United States too is under drought conditions currently, affecting about 130 million people, according to the US government.
Must Read: Drought in UP and Jharkhand
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains: GS 3 (Science and Technology)
What is the issue?
- India has failed to propagate scientific literacy not only among the public, but also among scientists themselves.
- While politicians, writers, artists, actors, and other celebrities have been given their due, science and scientists seem to have been largely ignored.
- The general apathy towards science, and the lack of scientific temper among the public and politicians, is a poor commentary on the Indian sensibility.
What is the status of scientific advancement in India?
- A solid foundation for modern science was built by scientists in the 1950s and 1960s, facilitated by the then Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru.
- India has made significant scientific advances in fields such as molecular biology, agricultural/pharmaceutical science, solid-state chemistry, space, nuclear science, and information technology.
What is the case of scientific literacy in India?
- Parliament underscored our commitment to propagate scientific temper by including it as a duty in Article 51A of the Constitution through the 42nd Amendment.
- Article 51A says, “It shall be the duty of every citizen of India to develop the scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform.”
- Lack of scientific temper– Although India has made some significant scientific advances in research fields, it has failed to propagate scientific literacy in India.
- Scientific temper has not really percolated into society paving the way for retrogressive religion-based politics at the expense of constitutionally guaranteed secular values.
- The bulk of scientists in the country were themselves not committed to scientific temper which calls for rationality, reason, and lack of belief in dogma and superstition.
- India had not produced any Nobel Prize winner in science since 1930 largely because of the lack of a scientific environment in the country, of which scientific temper would be an important component.
- Pseudoscience- Pseudoscience is everywhere, whether in denying the science of climate change or the evolution theory.
- There is official backing of the theory that cow excreta has therapeutic properties despite no scientific validation of this.
- Official circulars quote ancient texts to support the curative properties of cow urine for ailments.
- Disinformation weakens human rights and many elements of democracy.
- Dissemination of fake news is faster and reaches millions of consumers in seconds thanks to Information Technology.
What is the need of the hour?
- It is the job of the science academies to chip in and inspire the country to attain greater science literacy among the public.
- There is a need to develop a knack for critical thinking using the time-tested and highly successful methodologies followed in science.
- Revamping of National Science, Technology, and Innovation Policy.on
- Increasing fund allocation to R&D Institutes.
- Collaboration between various stakeholders – academic institutes, research organisation and industries.
Source: The Hindu
Baba’s Explainer – Rohingya & ICC
Syllabus
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
There are approximately 6.6 million refugees across the world today. Amongst them, the Rohingya community from Myanmar is one of the most vulnerable and endangered. Over 900,000 Rohingya people have already been displaced from Myanmar while many remain within the nation as internally displaced person.
Read Complete Details on Rohingya & ICC
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) In which one of the following groups are all the four countries part of International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC)?
- Turkey, India, Russia, and Yemen
- India, Ukraine, Belarus, and Egypt
- Russia, Iran, Pakistan, and India
- India, Russia, Azerbaijan, and Kazakhstan
Q.2) The Great Red Spot-on Jupiter is a
- High Pressure region that rotates clockwise
- Low Pressure region that rotates clockwise
- High Pressure Region that rotates anti-clockwise
- Low Pressure region that rotates anti-clockwise
Q.3) With reference to space technology, consider the following statements.
- Spectrographic Investigation of Nebular Gas (SING)deals with the study infrared radiation.
- The SING project would be the first space-collaboration involving India and China
Which of the statement/s given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’24th August 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 23rd August 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – c











