IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
In News:
- The Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO) arrested the mastermind, named Dortse (board member of Jillian India Ltd) who incorporated multiple shell companies linked to China and provided dummy directors on their boards to run the fraudulent businesses.
- Pursuing this serious financial crime, Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) conducted simultaneous search-and-seizure operations at Bangalore and Hyderabad offices.
What are shell companies?
- A shell company is a corporation without active business operations or actual assets. They exist only on paper and has no office and no employees, but may have a bank account or passive investments, etc.
- They can be used for legitimate reasons such as for obtaining different forms of financing, conducting a hostile takeover or issuing Initial Public Offerings.
- These types of corporations are not all necessarily illegal, but they are sometimes used illegitimately such as for tax evasion, tax avoidance, money laundering or anonymity.
- Indian laws to deal with shell companies
- Benami Transaction (Prohibition) Amendment Act 2016
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act 2002
- The Companies Act, 2013.
Tax evasion vs. Tax avoidance
- Tax avoidance is a legal strategy to minimize the amount of income tax owed by an individual or a business by taking advantage of the loop holes and ambiguities in the legal provisions.
- Tax evasion is a serious financial crime that uses illegal methods to evade tax liability. It may result in hefty fines and penalties.
- Examples of tax avoidance like claiming deductions under chapter VIA of the Income Tax Act 1961 such as donations under section 80G
- Examples of tax evasion are underreporting income, window dressing of accounts, falsifying deductions, hiding money, etc.
Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO)
- As per the Companies Act 2013, SFIO is a multi-disciplinary organization under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, consisting of experts in the field of accountancy, forensic auditing, banking, law, information technology, taxation, etc. for detecting and prosecuting or recommending for prosecution white-collar crimes/frauds.
- The SFIO conducts investigations on receipt of a report of the Registrar or on intimation of a special resolution passed by a company, request from any department of the Central Government or a State Government or in the public interest.
- SFIO is headed by a Director as Head of Department in the rank of Joint Secretary to the Government of India.
- The Headquarter of SFIO is in New Delhi, with five Regional Offices in Mumbai, New Delhi, Chennai, Hyderabad & Kolkata.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to the “Tea Board” in India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Tea Board is a statutory body.
- It is a regulatory body attached to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The Tea Board’s Head Office is situated in Bengaluru.
- The Board has overseas offices at Dubai and Moscow.
Which of the statements given above are correct ?
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Technology
In News: Death of a 12-year-old girl in Kerala from rabies, despite having multiple inoculations of the rabies vaccine.
- From 2016-18, around 300 laboratory-confirmed rabies deaths were reported in India. The WHO says India is endemic for rabies and accounts for 36% of the world’s deaths.
- As per available information, Rabies causes 18,000-20,000 deaths every year.
- About 30-60% of reported rabies cases and deaths in India occur in children under the age of 15 years, as bites that occur in children often go unrecognised and unreported, it notes.
About Rabies
- Rabies is a disease that is caused by a family of viruses called the lyssaviruses and found in a range of mammals.
- The virus targets the central nervous system and is nearly 100% fatal to the host animal if it succeeds in infecting it.
- It is most likely to spread to people from the bite of an infected dog or a cat as they are the most common pets.
Significance of Rabies vaccine
- The vaccine is made up of an inactivated virus that is expected to induce the body into producing antibodies that can neutralise the live virus in case of infection.
- There is no single-shot rabies vaccine or one that offers permanent immunity.
- Administering a vaccine, even after being bitten by a rabid animal, is effective because the virus is slow-moving and it can be several weeks before the disease manifests into a fatal encephalitis.
- A shot of rabies immunoglobulin (rabies-antibodies against the virus derived either from people or horses) followed by a four-week course of anti-rabies vaccine, is nearly guaranteed to prevent rabies.
- There are mainly two ways of administering the rabies vaccine – firstly, post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) which is given to persons who have been exposed via a bite to an animal suspected to be infected. The vaccines are administered either into the muscles, or into the skin.
- Secondly, Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) which is given ahead of time to persons who have a high risk of being infected, such as veterinarians.
- The advantage of a PrEP is that if bitten, one doesn’t need an immunoglobulin injection, and two subsequent shots of the vaccine will suffice for full protection, unlike the four-course prescription in the case of PEP.
- However, the WHO doesn’t recommend PrEP as a general preventive.
Rabies vaccines in India
- There are at least six rabies vaccines approved for India and all contain inactivated virus made of duck, chicken or human cell cultures.
- They are marked as safe, efficacious and with long immunity.
- They are available for free in government dispensaries .
Concerns
- Hospitals running out of vaccines
- Knowledge about vaccines and treatment is still inadequate in India.
- No centralised database of vaccine availability is maintained.
- Requirement of multiple shots of vaccine as well as immunoglobin makes sticking to the schedule challenging.
Way forward
- India has committed to eliminate the disease by 2030 which requires vaccination of dogs who are deemed responsible for 99% of all rabies infections in people
- Hence, the government in its 2021 plan, called the ‘National Action for Plan — Rabies Elimination’, aims to vaccinate at least 70% of all dogs in a defined geographical area annually for three consecutive years.
- With this, a degree of herd immunity is expected leading to eventual elimination within eight years. Rather than inoculate all dogs, the plan is to identify ‘rabies hotspots’ in the country and target them.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) What is the importance of using \ Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines in India? (2020)
- These vaccines are effective against pneumonia as well as meningitis and sepsis.
- Dependence on antibiotics that are not effective against drug-resistant bacteria can be reduced.
- These vaccines have no side effects and cause no allergic reactions.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
In News: The Kushiyara river water agreement signed between India and Bangladesh on September 6 2022 is the first major water sharing accord between the two friendly neighbours since the Ganga water treaty in 1996.
- The India-Bangladesh joint river commission met in New Delhi last month after 12 years and agreed on several vital initiatives.
- Kushiyara river is a distributary of the Barak River which originates in the uplands of Assam and flows through it, and then on to Bangladesh.
- Barak River rises in Manipur and is part of Surma-Meghna River System.
- The agreement is aimed to benefit the southern areas of Assam in India and the Sylhet region in Bangladesh.
- Bangladesh will be able to withdraw 153 cusecs (cubic feet per second) of water from the Kushiyara out of the approximately 2,500 cusecs of water that is there in the river during the winter season.
- The water of Kushiyara will be channelled through the Rahimpur Canal project in Sylhet.
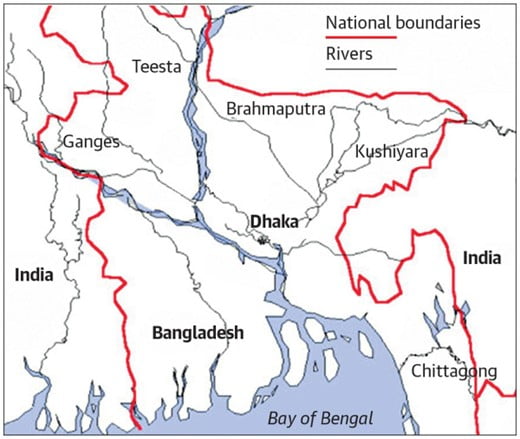
Geographical insight:
- Bangladesh and India share a 4,096-kilometre-long (2,545 mi) international border, which is the longest land boundary that India shares with any of its neighbours.
- The countries share over 50 rivers such as the main branch of the Ganges known as the Padma River
- Hence, water management remains a contentious issue between the two countries.
Significance
- Help in addressing the major issue of changing nature of the river which unleashes floods in Bangladesh during the monsoon and goes dry during the winter when demand of water goes up because of a crop cycle in Sylhet.
- Benefit to approximately 10,000 hectares of land and millions of people from the water that will flow through a network of canals in Sylhet benefiting the farmers involved in Boro rice – the rice cultivated during the dry season of December to February and harvested in early summer.
- To ensure steady supply of water for irrigation of agriculture fields and orchards of the subdivisions of Sylhet.
- Greater cooperation in flood control
- Strengthening mutual cooperation in combating pollution of common river
- Regular sharing of water-stock data
- Extension of the Ganga treaty beyond its expiry date of 2026
Concerns expressed:
- India objection to the to the Rahimpur Canal of Sylhet which was built to help the farmers access Kushiyara’s water – and claimed that the dyke and other infrastructure interfered in border security.
- Similar pact for Teesta River – which is a tributary of the Brahmaputra, originates in the Teesta Kangse glacier and flows through the state of Sikkim and West Bengal before entering Bangladesh; has been in the works for around a decade and is currently disputed.
- Impact of climate change on South Asian rivers that can affect communities and trigger migration.
- Bangladesh has cited low water flow in its rivers during the winter months as a matter of concern as it affects its agriculture sector
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements (2017)
- The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim
- River Ranjeet originates in Sikkim and it is a tributary of river Teesta.
- River Teesta flows into Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science & Tech (Defence)
In News: Third stealth frigate of Project 17A Taragiri launched in Mumbai by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd. (MDL) with an estimated cost of Project being around ₹25,700 crore.
Features:
- Indigenously designed Taragiri will have a state-of-the-art weapon, sensors, an advanced action information system, an integrated platform management system, world class modular living spaces, a sophisticated power distribution system and a host of other advanced features.

- It will be fitted with a supersonic surface-to-surface missile system and the ship’s air defence capability is designed to counter the threat of the enemy aircraft and the anti-ship cruise missiles would revolve around the vertical launch and long-range surface to air missile system
- The vessel is being launched with an approximate launch weight of 3,510 tonnes and is designed by the Indian Navy’s in-house design organisation — the Bureau of Naval Design
- The ship, 149.02 metre long and 17.8 metre wide, is propelled by a CODOG combination of two gas turbines and two main diesel engines which are designed to achieve a speed of over 28 knots at a displacement of approximately 6,670 tonnes.
Structure:
- The ship has been built using integrated construction methodology which involves hull blocks construction in different geographical locations and integration/erection on slipway at MDL.
- The keel (the timber or steel structure along the base of a ship to increase support & stability) of Taragiri was laid on September 10, 2020, and the ship is expected to be delivered by August 2025.
- The steel used in the hull construction of P17A frigates is an indigenously developed DMR 249A which is a low carbon micro alloy grade steel manufactured by the SAIL.
Background
- The second ship of P17A class Udaygiri was launched on May 17 this year and is expected to start the sea trials during the second half of 2024. The keel of the fourth and the final ship was laid on June 28.
Must Read: Project 17A Frigate
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims: Current Affairs
Context: Army chief General Manoj Pande visited the Ladakh sector to review Exercise Parvat Prahar.
- The exercise comes as India and China are undertaking disengagement from Patrolling Point-15 in eastern Ladakh.
Key details:
- The exercise was held in the Ladakh plateau at an altitude of 14,000 feet.
- This exercise used newly inducted all-terrain vehicles transported by Chinook heavy lift helicopters and K9-Vajra howitzers.
- The exercise featured a display of operational capabilities by artillery guns and other key weapon systems.
- Simultaneously on the western front, Exercise Gagan Strike culminated with a fire power display of attack helicopters supporting deep operations by Strike Corps.
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Siachen Glacier is situated to the (2020)
- East of Aksai Chin
- East of Leh
- North of Gilgit
- North of Nubra Valley
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
In News: The Union Minister of Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and Textiles launched the US Startup SETU.
- It would connect start-ups in India to US-based investors and start-up ecosystem leaders with mentorship and assistance in various areas including funding, market access and commercialization.
Key details:
- SETU is designed to break the geographical barriers between mentors based in US that are willing to invest in entrepreneurship and sunrise start-ups in India.
- The interaction will be supported through the mentorship portal under the Startup India initiative the Mentorship, Advisory, Assistance, Resilience, and Growth program (MAARG), which is a single-stop solution finder for start-ups in India.
- MAARG is inviting applications from Mentors across the world. Till date, more than 200 mentors have been on-board on MAARG across the globe.
- The applications have come from distinguished individuals representing the industry and the Startup ecosystem.
- The core functions of MAARG are to improve ease of access, use Artificial Intelligence for Matchmaking, schedule meetings virtually, host masterclasses, provide a custom dashboard for relevant information, analytics, features, etc., host cohort-based programs that will allow Startup ecosystem enablers to be become a part of the program and enable outcome driven activities.
Source: Pib.Gov
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
In News: India has for now opted to stay out of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework’s (IPEF) trade pillar. The IPEF has four pillars with the member nations given flexibility to choose which pillars they want to be part of.
Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF)
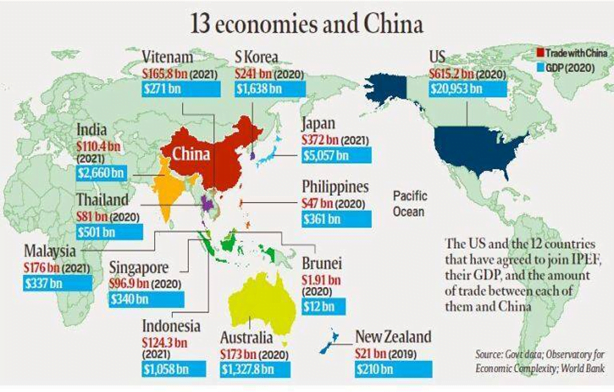
- According to an insight paper on IPEF put out by the US Congressional Research Service, the IPEF is not a traditional trade agreement. Rather, it would include different modules (four pillars) covering:
- fair and resilient trade,
- supply chain resilience,
- infrastructure and decarbonization, and
- tax and anticorruption.
- Countries would have to sign up to all of the components within a module, but do not have to participate in all modules.
India and IPEF:
- India decided to join three pillars of IPEF
- India has joined the supply chain, decarbonisation and infrastructure, and anti-tax and corruption pillars of the IPEF. However, it has decided to remain out of the trade pillar.
Reasons for India not joining the trade pillar:
- So far, official reason has not been given. However, trade experts say India may have some genuine concerns regarding certain aspects of the trade pillar that perhaps go beyond WTO obligations.
Must Read: Indo-Pacific Economic Framework
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) ‘Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (COMCASA)’, recently seen in news relates to: (2022)
- USA
- European Union
- SAARC
- ASEAN
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Society); GS 2 (Governance)
In News: New adoption rules create confusion over implementation as they require transfer of adoption papers from courts to District Magistrates.
Background:
- The parliament passed the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Amendment Bill 2021 and it came into effect on September 1 2021.
- The objective was to prevent court-related delays during adoptions because of a large no. of pending cases by transfer of adoption papers from courts to District Magistrates. This was to ensure speedy disposal of cases and enhance accountability.
Adoption and its Procedures
- Adoption means the process through which the adopted child is permanently separated from his biological parents and becomes the lawful child of the adoptive parents with all the rights, privileges. and responsibilities that are attached to a biological child.
- A child can be adopted if
- an orphan, abandoned or surrendered (OAS) child has been declared legally free for adoption as per the provisions of the JJ (C&PC) Act 2015
- a child of a relative (a relative means the child’s paternal uncle or aunt, a maternal uncle or aunt or paternal and maternal grandparents)
- a child or children of spouse from earlier marriage surrendered by the biological parent(s) for adoption by the step-parent
- Adoptions in India are governed by two laws: The Hindu Adoption and Maintenance Act, 1956 (HAMA) and the Juvenile Justice Act 2015 (JJA). Both laws have separate eligibility criteria for adoptive parents
- Those applying under JJA, have to registers for adoption by filing application on Central Adoption Resources Authority (CARA) portal > An assessment through home study report is done > The parent(s) is then referred a child and subsequently allowed to take a child in pre- adoption foster care > Formal adoption order from the court gives a legal status to the adoption.
- Under HAMA, a “dattaka hom” ceremony or an adoption deed or court order is sufficient to obtain irrevocable adoption rights.
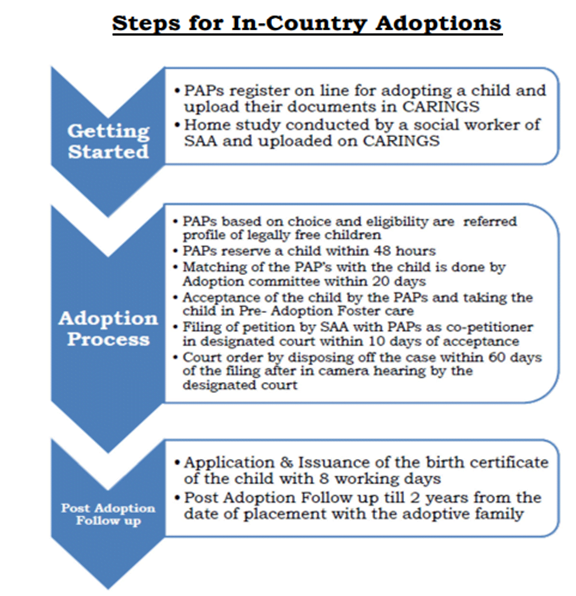
Challenges:
- Lack of awareness among the parents, the judges and the DMs regarding the process creating confusion and delay. Delay in the transfer process to be amplified due to requirement of a fresh petition.
- Such a delay in the above-mentioned process implies problems in school admissions due to absence of birth certificate of the child or inability to claim health insurance, etc.
- There are no rules for monitoring adoptions and verifying sourcing of children and determining whether parents are fit to adopt, under HAMA.
- Under CARA, there are only 2188 children in its registry while there are more than 31,000 prospective parents. This leads to long wait which further allows human traffickers to take advantage of loopholes – this issue was further verified by a Parliamentary Panel “Review of Guardianship and Adoption Laws”
- The question of whether an order passed by DM will pass muster when an adopted child’s entitlements on succession & inheritance are contested before a court
- Nearly 3500 adoptions are completed every year while 1000 pending cases in limbo across the country
CARA
- It is a specialised adoption agency and a statutory body of the Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- It functions as the nodal body for adoption of Indian children and is mandated to monitor and regulate in-country and inter-country adoptions.
- CARA is designated as the Central Authority to deal with inter-country adoptions in accordance with the provisions of the Hague Convention on Inter-country Adoption, 1993, ratified by Government of India in 2003.
- CARA primarily deals with adoption of orphan, abandoned and surrendered children through its associated /recognised adoption agencies.
Parliamentary Panel “Review of Guardianship and Adoption Laws”
- In India, there are only 2,430 children available for adoption while the number of parents desiring to bring home a child is growing rapidly.
- There were 27,939 prospective parents registered with the Child Adoption Resource Authority (CARA) as of December 2021, up from nearly 18,000 in 2017.
- The waiting time for adoption has increased to three years from one year in the past five years.
Must Read: Review of Guardianship and Adoption Laws
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Recent context:
- Recently, India-Japan 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue held in Tokyo under which India’s Defence Minister and External Affairs Minister to meet their Japanese counterparts.
- The meeting took place against the backdrop of heightened tensions across the Taiwan Strait during which China lobbed five missiles in Japan’s exclusive economic zone which was described by Japan as “a serious problem that affects our national security and the safety of our citizens”.
Major areas of discussion during the Ministerial meeting:
- The Ministers reaffirmed their commitment Rules-based global order that respects sovereignty and territorial integrity of nations:
- Indian side expressed its support to work towards enhanced security and defence cooperation with Japan on the line of Japan’s commitment to reinforce Japan’s defence capabilities .
- Both nations agree to launch the Joint Service Staff talks between the Japan Joint Staff and the Indian Integrated Defence Staff.
- building on existing bilateral and multilateral exercises including “Dharma Guardian” (ground forces), “JIMEX” and “Malabar” (navies), and, an earlier decision to conduct the inaugural India-Japan fighter exercise between the two air forces.
- India welcomes the Japan’s participation in multilateral exercise MILAN and the operationalization of the Agreement Concerning Reciprocal Provision of Supplies and Services (ACSA) between the Self-Defense Forces of Japan and the Indian Armed Forces in the exercise.
- So, MILAN 2022 will have the first-ever participation from all the Quad nations, as well as France and South Korea.
- Japan is expected to provide thrust to cooperation in defence equipment and technology, covering areas such as Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGV) and Robotics and manufacturing of drones where Japan has considerable strengths.
- Recently, Japan’s largest drone manufacturer, ACSL, has already established a joint venture in India with Delhi-based Arc Ventures.
- Both the nation committed to a common strategic goal of achieving a free and open Indo-Pacific, that is inclusive and resilient, based on the rule of law and free from coercion.
- The Ministers also reiterated their strong support for ASEAN’s unity and centrality and their full support for the “ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP)” which upholds the principles such as the rule of law, openness, freedom, transparency, and inclusiveness.
Way forward:
Both nations are marking the 70th anniversary of the establishment of bilateral relations this year which is instrumental in re-energising ties and also attributable to the long-term vision shared by the leaders on both sides such as ensuring cooperate for peace, stability and prosperity of Indo-Pacific and work together for a rules-based and inclusive world order.
India’s emergence as the fifth-largest as well as the fastest-growing economy in the world will definitely ensure a further quantum leap in strategic ties with Japan.
Must Read: 70 years of establishment of diplomatic relations between India and Japan
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Geography) and GS 3 (Disaster Management)
Context: Why cloudburst forecast in India still remains elusive
Forecasting of cloudbursts:
- While satellites are extensively useful in detecting large-scale monsoon weather systems, the resolution of the precipitation radars of these satellites can be much smaller than the area of individual cloudburst events, and hence they go undetected.
- The IMD’s forecasts, and in general, the weather prediction scenario, have advanced such that widespread extreme rains can be predicted two-three days in advance.
- Cyclones can be predicted about one week in advance. However, cloudburst forecasts still remain elusive.
- Multiple doppler weather radars can be used to monitor moving cloud droplets and help to provide nowcasts (forecasts for the next three hours).
- This can be a quick measure for providing warnings, but radars are an expensive affair, and installing them across the country may not be practically feasible.
- A long-term measure would be mapping the cloudburst-prone regions using automatic rain gauges. If cloudburst-prone regions are co-located with landslide-prone regions, these locations can be designated as hazardous.
- The risk at these locations would be huge, and people should be moved, and construction and mining in nearby regions should be restricted as that can aggravate the landslides and flash flood impacts.

- Climate change is projected to increase the frequency and intensity of cloudbursts As the air gets warmer, it can hold more moisture and for a longer time. We call this the Clausius Clapeyron relationship.
- A 1-degree Celsius rise in temperature may correspond to a 7-10% increase in moisture and rainfall.
- This increase in rainfall amount does not get spread moderately throughout the season. As the moisture holding capacity of air increases, it results in prolonged dry periods intermittent with short spells of extreme rains. More deeper cumulonimbus clouds form and the chances of cloudbursts also increase.
Must Read: Cloudbursts
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains: GS 2 (Governance)
Case study: Residents of Nyukmadong village said Border Roads Organisation destroyed more than 80% of the 36 sq. km forest without consultations or compensation.
Background: Almost 60 years after becoming collateral damage in one of the fiercest battles between Indian Army soldiers and Chinese invaders, a village in Arunachal Pradesh is fighting a war to protect a sacred forest from a project for preventing a repeat of 1962.
Violation of Tribal Rights and Loss of Flora and Fauna:
- The place is known for a Buddhist-style war memorial on a 1.5-acre plot overlooking the site of a battle on November 18, 1962.
- According to the Kolkata-based South Asian Forum for Environment, the road project is an example of trespassing and ignoring the rights of a local tribal community to the land and the forest ecosystem they are dependent on.
- The WWF (World Wide Fund for Nature) declared the patch as a community reserve forest because of its rich biodiversity. The red-listed Indian red panda is found in this area.
- Community representatives said the deforestation (for the road) affected their traditional holy sites, locally called phu.
- It could be the first test case for the new Forest Rule 2022 that seeks to rob indigenous people of their right to forest resources.
- The local stakeholders said much of the damage to the sacred forest cannot be reversed. “Nothing can compensate for the loss to the biodiversity, but the community as landowners should be paid for re-greening the bald patche.
- The other impacted areas are Gyandrabrangsa, Halftangmu, Penpeytang, Chendhuphu, Yangphu and Changphunakphu.
Border Roads Organisation (BRO):
- The BRO is a road construction executive force in India that provides support to and is now a part of the Indian Armed Forces.
- BRO develops and maintains road networks in India’s border areas and friendly neighboring countries.
- The BRO consists of Border Roads Wing under the Ministry of Defense and the General Reserve Engineer Force (GREF). Officers are selected through the Indian Engineering Services (IES) Examination conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC).
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains: GS 4 (Dedication to Public Service, Emotional Intelligence) (case study)
Case study: An IPS officer used soft policing to crack down on illegal hooch distilleries in Solapur.
- Tejaswi Satpute, SP ,Solapur Rural, launched Operation Parivartan in September 2021 a four-point action plan that combined soft policing such as counselling with a concerted crackdown on the haath bhattis.
- The region has acquired reputation as the primary supplier of hooch to at least nine districts in the region.
- A year later, nearly 80 percent of haath bhattis in Solapur rural areas have shut down and over 650 families involved in the trade have been rehabilitated which includes Banjara community as a major stakeholder.
- Recently, Tejaswi Satpute awarded the FICCI (Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry) for smart policing special jury award for operation Parivartan.
Source: Indian Express
Baba’s Explainer -Tedious Process of Adoption
Syllabus
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections
Context: Concerned over the declining number of children for adoption in the country, a Parliamentary panel has expressed apprehension that this may point to an illegal child adoption market and trafficking.
Read Complete Details on Tedious Process of Adoption
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to India, Nyukmadong, Gyandrabrangsa, Halftangmu, and Penpeytang are the names of
- Tribal hamlets
- Glaciers
- Community reserve forests
- Tribal languages
Q.2) Consider the following statements
- Tax avoidance refers to the illegal means of avoiding net tax liability by way of fraudulent financial statements and falsification of accounts
- Tax evasion attracts heavy fines and penalties.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both
- Neither
Q.3) Consider the following statements
- Kushiyara river is a distributary of the Brahmaputra River
- It flows through southern Assam and Sylhet in Bangladesh.
- India shares the longest land boundary with Bangladesh followed by China
- Teesta river is a tributary of Brahmaputra River which flows through Assam and Bangladesh
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’12th September 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 10th September – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – c











