IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: Recently Indian Metrological Department (IMD) has forecasted severe cold wave conditions in some parts of Punjab, Haryana, Chandigarh, Delhi, north Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
About Cold Wave:
- It is a condition signify a certain amount of fall of temperature at given places with respect to climatological value.
- In India, cold waves are seen between November to March.
- However, minimum temperatures drop below 8°Cover many parts of northern India during the months of November to February.
- Impact on human health: It varies from Cough and cold, bronchitis and respiratory diseases, Blood pressure issues, Skin problems, and even Bone, joint, and muscle pain due to lack of sunlight.
Criteria for Cold Wave by IMD:
- It is considered when the minimum temperature of a station is 100°C or less for plains and 0°C or less for Hilly regions.
- Based on Departure
- Cold Wave: Negative Departure from normal is 4.5°C to 6.4°C
- Severe Cold Wave: Negative Departure from normal is more than 6.4°C
- Based on Actual Minimum Temperature (For plain stations only)
- Cold Wave: When minimum temperature is ≤ 04°C
- Severe Cold Wave: When minimum temperature is ≤ 02°C
- When minimum temperature departure is -4.5°C or less over a station, “Cold Wave” may be described if the minimum temperature is 150°C or less.
Factors responsible for cold wave in India:
- Build-up of a ridge (an extended area of relatively high atmospheric pressure) in the jet stream over northwest Asia.
- Movement of cold air masses in response to steering by upper-level winds.
- Formation of surface high-pressure over north & central India.
- Triggering mechanism like a strong westerly wave approaching northwest India to enhance winds for transport cold air south eastward.
- Extensive snow covers over northwest Himalayas.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) In the northern hemisphere, the longest day of the year normally occurs in the: (2022)
- First half of the month of June
- Second half of the month of June
- First half of the month of July
- Second half of the month of July
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: The Govt of India recently approved Karnataka’s Kalasa-Banduri drinking water project which is facing opposition from Goa and Maharashtra.
- The Central Water Commission (CWC) has cleared the diversion of 1.72 TMC of water from the Kalasa Dam and 2.18 TMC from the Bhandura dam.
About Kalasa – Banduri Project:
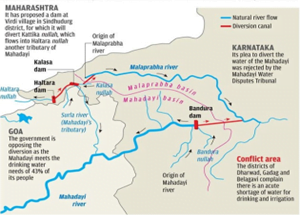
- It is a dam that has been designed to divert water from the Mahadeo basin to the deficit basin of the Mala-Prabha river.
- The plan is aimed at facilitating drinking water for 13 towns in drought-hit northern Karnataka.
- The areas include Dharwad, Belagavi, Bagalkot and Gadag among others.
- These areas together make up the country’s second most arid region after Rajasthan.
About Mahadayi River:
- The Mahadayi river rises in Karnataka (Western Ghats) from the Bhimgad Wildlife Sanctuary in Khanapur taluk of Karnataka’s Belagavi district.
- Flowing westward, it enters the north Goa districts.
- Several streams join the flow of the river to form the Mandovi which is one of two major rivers that flow through Goa.
- It joins the Arabian Sea at Panaji.
- Distribution: Of the total area, 375 sq km lies in Karnataka, 77 sq km in Maharashtra and remaining 1580 sq km is in Goa.
About Central Water Commission (CWC):
- Central Water Commission is a premier Technical Organization of India in the field of Water Resources and is presently functioning as an attached office of the Ministry of Jal Shakti, Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation, Government of India.
- The Commission is entrusted with the general responsibilities of initiating, coordinating and furthering in consultation of the State Governments concerned, schemes for control, conservation and utilization of water resources throughout the country, for purpose of Flood Control, Irrigation, Navigation, Drinking Water Supply and Water Power Development.
- It also undertakes the investigations, construction and execution of any such schemes as required.
- Central Water Commission CWC is headed by a Chairman, with the status of Ex-Officio Secretary to the Government of India.
- The work of the Commission is divided among 3 wings namely, Designs and Research (D&R) Wing, River Management (RM) Wing and Water Planning and Projects (WP&P) Wing.
- A separate Human Resources Management Unit headed by a Chief Engineer, deals with Human Resources Management or Development, Financial Management, Training and Administrative matters of the CWC.
- National Water Academy located at Pune is responsible for training of Central and State in-service engineers and it functions directly under the guidance of Chairman.
- Altogether there are Nineteen organizations located at headquarters in New Delhi and thirteen organizations spread over various locations in India.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following pairs:
Reservoirs : States
- Ghataprabha : Telangana
- Gandhi Sagar : Madhya Pradesh
- Indira Sagar : Andhra Pradesh
- Maithon : Chhattisgarh
How many pairs given above are not correctly matched? (2022)
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs PAY
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) Gandikota canyon of South India was created by which one of the following rivers ? (2022)
- Cauvery
- Manjira
- Pennar
- Tungabhadra
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: A day after Uzbekistan alleged 18 child deaths in Samarkand from consumption of a medicinal syrup manufactured by an Indian drugmaker.
- The Department of Chemicals and Petrochemicals with the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers issued a gazette notification titled Ethylene Glycol (Quality Control) Order, 2022 on December 29.
About Ethylene glycol:

- Ethylene glycol is a colourless and odourless alcoholic compound that can be fatal if consumed.
- It is mostly used as an automotive antifreeze and as a raw material for manufacturing polyester fibres.
- Diethylene glycol and ethylene glycol are adulterants that are sometimes illegally used as solvents in liquid drugs.
- Diethylene glycol and ethylene glycol may be used by pharma companies as an alternative to non-toxic solvents such as glycerine or propylene glycol to cut costs.
- It is also found in several products such as:
- hydraulic brake fluids
- stamp pad inks
- ballpoint pens
- solvents, paints
- cosmetics
- plastics.
About Marion Biotech:
- Marion Biotech is a drug company based in Noida, Uttar Pradesh.
- It is a licensed manufacturer and holds a licence for manufacturing of Dok1 Max syrup and tablets for export purposes granted by UP Drug Control.
- Marion Biotech does not sell Dok-1 Max in India and its only export has been to Uzbekistan.
Details of the Ethylene Glycol (Quality Control) Order, 2022:
- The order came after the Centre consulted the Bureau of Indian Standards on the matter.
- Certification and enforcement authority:
- In respect of specific goods or articles, the Bureau of Indian Standards shall be the certifying and enforcing authority.
- Penalty:
- Any person who contravenes the provisions of this Order shall be punishable under the provisions of the said Act.
Source: DownToEarth
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- Biofilms can form on medical implants within human tissues.
- Biofilms can form on food and food processing surfaces.
- Biofilms can exhibit antibiotic resistance.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements:
- The Serum Institute of India produced COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using vector based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Recently, the Delhi High Court, in the case of Hamdard National Foundation (India) vs Sadar Laboratories Pvt. Ltd., restrained Sadar Laboratories from manufacturing and selling beverages under the impugned trademark ‘Dil Afza’.
- A Division Bench of the Delhi High Court restrained the respondent (Sadar Laboratories Pvt. Ltd.) from manufacturing and selling any product under the trademark ‘Dil Afza’ till the final disposal of the trademark infringement suit.
- The court held that “it is not difficult to conceive that a person who looks at the label of ‘Dil Afza’ may recall the label of ‘Rooh Afza’ as the word ‘Afza’ is common and the meaning of the words ‘Rooh’ and ‘Dil’, when translated in English, are commonly used in conjunction.
About Trade mark:
- Trademark refers to graphical representation of goods or services to make it distinguishable from others.
- It can be words, symbols, sound, colours, shape of goods, graphics representation or packaging etc.
- It protects owner against unfair competition, prevents damage to reputation of owner and consumer welfare.
- In India, trademarks are governed under Trademarks Act, 1999 ( it deals with precise nature of rights one can acquire in respect of trademarks), under aegis of Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion (DIPP), Ministry of Commerce.
- The implementing body is Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trademarks.
About the dispute:
- The manufacturers of ‘Rooh Afza’ moved an appeal against the rejection of its application seeking an interim injunction against Sadar Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. for their product ‘Dil Afza’.
- The appellant stated before the court that the trademark ‘Rooh Afza’ is a highly reputed mark in the market with regard to sharbat (sweet beverage).
- Furthermore, it was claimed that the design of the product ‘Dil Afza’ is deceptively similar to the getup and trade dress of the appellant’s product.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Union Home and Cooperation Minister Shri Amit Shah launched the Border Security Force (BSF) mobile app ‘Prahari’.
- This BSF ‘Prahari’ app is a great example of Proactive Governance, now Jawans can get personal and service related information, housing, Ayushman-CAPF and leave related information on their mobile.
- It will also give information related to:
- Bio Data or grievance redressal on “Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System” (CP-GRAMS) or
- Information on various welfare schemes
- This app will also connect them with the portal of the Ministry of Home Affairs.
About BSF:
- The Border Security Force is India’s border guarding organisation on its border with Pakistan and Bangladesh.
- It is one of the seven Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) of India.
- It was raised in the wake of the 1965 war in 1965.
- It is the only CAPF to have a Water Wing, Air Wing and an Artillery Regiment.
- It comes under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- It currently stands as the world’s largest border guarding force.
- BSF has been termed as the First Line of Defence of Indian territories.
- The BSF maintains a Tear Smoke Unit (TSU), which is unique in India.
About Border Area Development Programme (BADP):
- The Government of India is implementing the Border Area Development Programme (BADP) through the State Governments/UT Administrations in habitations located within 0-10 km.
- The annual action plans of the States/UTs consisting of works related to village infrastructure like roads and bridges, health, education, agriculture, sports, drinking water & sanitation etc. are considered and approved as per BADP guidelines.
- It covers 460 border blocks of 117 border districts in 16 States and 2 UTs: Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Punjab, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal, Jammu and Kashmir (UT) and Ladakh (UT).
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently the Tamil Nadu government launched an initiative for the conservation of the Nilgiri Tahr.
About Nilgiri Tahr:

- The species is locally known as Varaiaadu.
- There are multiple references to the Nilgiri Tahr in Tamil Sangam literature dating back to 2,000 years.
- The late Mesolithic (10,000-4,000 BC) paintings highlight the significance of the Tahr in folklore, culture and life.
- It was designated as the State animal of Tamil Nadu in recognition of its ecological and cultural significance.
- IUCN Status: It has been listed as an endangered species and is protected under Schedule-I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act of India, 1972.
- Habitat and Distribution:
- The animal inhabits meadows with steep cliffs at elevations between 300 metres and 2,600 metres above sea level.
- Historically, the Nilgiri Tahr was known to inhabit a large portion of the Western Ghats.
- But today it remains restricted to a few scattered patches in Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
- It has become locally extinct in around 14% of its traditional shola forest-grassland habitat.
- Population: It is estimated that there are 3,122 Nilgiri Tahrs in the wild.
- October 7 will be celebrated as ‘Nilgiri Tahr Day’ in honour of E.R.C. Davidar.
- He was responsible for pioneering one of the first studies on Nilgiri Tahr in 1975.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements :
- Wild animals are the sole property of the government.
- When a wild animal is declared protected, such animal is entitled for equal protection whether it is found in protected areas or outside.
- Apprehension of a protected wild animal becoming a danger to human life is sufficient ground for its capture or killing.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Q.2) With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements:
- The leader of an elephant group is a female
- The maximum gestation period can be 22 months
- An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only
- Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2021)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 3 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
Q.3) Which of the following Protected Areas are located in Cauvery basin? (2021)
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently, Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs has launched 2 key initiatives: City Finance Rankings 2022 and City Beauty Competition.
About City Finance Rankings 2022
- To evaluate, recognize and reward urban local bodies (ULBs) on basis of their strength across 15 indicators and 3 financial parameters: resource mobilization, expenditure performance and fiscal governance systems.
- Evaluation will be done on the basis of quality of current financial health and improvement with time in financial performance.
- Cities will be ranked at national level on the basis of their scores under following four population categories-
- Above 4 million.
- Between 1-4 million.
- 100K to 1 million.
- Less than 100,000.
- Top 3 cities in each population category will be rewarded.
- It will help ULBs to identify areas in their financial performance where they can make improvements and able to deliver quality infrastructure and services to its citizens.
- Rankings will motivate city/state officials and decision makers, to implement municipal finance reforms.
About City Beauty Competition:
- To encourage and recognize transformational efforts made by cities and wards in India to create beautiful, innovative and inclusive public spaces.
- Wards and public places of cities would be judged against five pillars-
- Accessibility
- Amenities
- Activities
- Aesthetics and
- Ecology
- Most beautiful public places in cities would be awarded first at State level and then will be shortlisted for award at the National level.
- It will encourage urban local bodies to improve their basic infrastructure and make urban spaces beautiful, sustainable and inclusive.
- Participation in the City Beauty Competition is voluntary.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: Recently Former military commander and Two-time coup leader Sitiveni Rabuka takes oath as Fiji’s Prime Minister.
About Fiji:
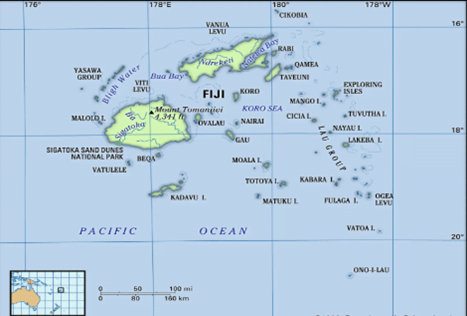
- It is a part of Oceania.
- It was a British colony for almost one hundred years from 1874.
- It gained independence in 1970.
- Capital: Suva
- Main Rivers: The Rewa, Navua, Sigatoka (Singatoka), and Ba (Mba).
- Highest Peak: Tomanivi (Mount Victoria) with 4,344 feet (1,324 metres).
- UNESCO’s world heritage site: Levuka Historical Port Town.
- Its largest island is called Viti Levu.
- It surrounds Koro Sea, north of Auckland, New Zealand.
- These islands are largely formed through volcanic action, sedimentary deposit, and formations of coral.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently, a Report of the Department-related Parliamentary Standing Committee on Transport, Tourism and Culture was released.
- National Tourism Day is celebrated across the country on January 25 every year to appreciate India’s beauty and spread awareness about the importance of tourism and its impact on the economy.
- This year’s theme: for National Tourism Day is ‘Rural and Community Centric Tourism’.
- The central government is organizing the main event in Telangana’s Pochampally village, a weavers’ hamlet on the outskirts of Hyderabad.
- Known for its famous hand-woven Ikat sarees, Pochampally was selected as one of the best tourism villages by the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) in 2021.
Tourism sector in India
- Travel and Tourism in India was the largest service industry: and was worth $234 bn in 2018.
- According to The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC): the tourism industry in India generated $194 bn or 6.8% of India’s GDP in 2019.
- The tourism sector in India: is predicted to grow at an annual rate of 6.9% to $460 bn by 2028 which is 9.9% of GDP.
About National Tourism Policy:

- As per the draft National Tourism Policy, five key areas would be given significant focus in next 10 years that are:
- green tourism
- digital tourism
- destination management
- skilling the hospitality sector and
- supporting tourism-related MSMEs.
- It include ‘perceptions related to safety and security’, and weak engagement between the Centre and the states.
- Government has also identified factors that hamper the growth of the tourism sector in the country.
- It also mentions ‘the menace of touts’ and ‘low standards of cleanliness and hygiene’ as other factors that deter the industry from leveraging its full potential.
- To promote investment in the tourism sector, draft mentions granting of industry status to the sector, along with formally granting infrastructure status to hotels.
- The draft policy offers framework conditions to help this sector, especially in the wake of the pandemic.
Key recommendations of committee:
National Tourism Council (NTC):
- Government should create National Tourism Council (NTC) on the model of GST council.
- Aim: To give recommendations to the Central and State governments on various issues of the tourism sector and its stakeholders.
Tourism, Travel and Hospitality sector:
- Spending Capex above Rs. 25 crores will reduce operating costs for hospitality players through subsidized rates of electricity and water charges, property tax, development tax etc.
- It will also attract investments in the Sector.
- It praises eight States Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Kerala, Karnataka, Punjab, Rajasthan and Uttarakhand which have accorded industry status to hospitality projects.
- Tourism in Concurrent List:
- It recommended to include Tourism in concurrent list.
- It will help in simplifying issues of the pandemic-hit Indian tourism sector since tourism is a multi-sectoral activity.
- It raised concerns over delay in final UC (Utilization Certificate) submission in project.
- It includes projects like “Infrastructure Development at Puri, Shree Jagannath Dham-Ramachandi-Prachi River front at Deuli under Mega Circuit” of the PRASHAD Scheme and Integrated Development of tourist circuit around specific themes (SWADESH DARSHAN) has been pending since 2015.
- It recommends Ministry to identify the issues causing delay in payment of various expenditure items with the ITDC (India Trade Development Corporation).
Facts about India Tourism:
- The country is home to 40 UNESCO heritage sites: The last site to be added to the World Heritage Site list is Dholavira, a Harappan city that is located in the city of Gujarat.
- The country currently has 32 cultural sites, 7 natural sites, and one mixed property.
- India’s most organic state: The Himalayan state of Sikkim has come out as the most organic state in present day India. The state reportedly has some 47.3% under forest cover.
- Highest Rail Bridge in the world: The country is home to the highest rail bridge in the world. The 1,315 m long Chenab Bridge is located in Jammu and Kashmir, and is 35 m higher than the Eiffel Tower.
- One of the most untouched places on earth: India’s North Sentinel Island is one of the most untouched places in the world. The island is home to the Sentinelese people, who have isolated themselves from the world.
- The oldest fort in India: Himachal Pradesh’s Kangra Fort is said to be the oldest in the country. It used to be home to royal treasures, and is said to have been built 3500 years ago.
- Wildlife sanctuaries: The country has a total of 566 wildlife sanctuaries. Ranthambore National Park in Rajasthan is the largest wildlife sanctuary in the country.
- Cleanest village in Asia: Mawlynnong located in the state of Meghalaya is ranked as the cleanest village in Asia.
Challenges Associated with Tourism sector in India:
- The tourism industry has been heavily hit by the coronavirus disease (Covid-19) pandemic: The World Tourism Organization has said that tourist arrivals around the world are not expected to return to their pre-pandemic levels until 2024.
- Fear of Uncertainty: Due to the spread of coronavirus and enforcement of social distancing norms peoples are fearing and unwillingness to come out from their home.
- Lack of arrival of international tourists: International traveling was banned by most of the countries to control the spreading chain of coronavirus. Therefore, the Indian tourism sector got a smaller number of tourists as compared to earlier and no foreign exchange earnings.
- Business Hurdles, Lack of Hygiene and Comfortable accommodation: During COVID-19, restrictions laid down by the government to control outstretch of coronavirus impacted on most tourists and tour operators to get adequate business.
- Revenue loss during COVID-19: People are not ready to go outside of their home and they are not willing to take tours. Due to closure of tour destinations, monuments, heritage sites and lack of arrival of tourists the Indian tourism projected a revenue loss of Rs. 1.25 trillion.
- Tour operators have shut down their business: the majority of registered and unregistered tour operators closed their operations in India; hence it affected much on profitability and productivity of the Indian tourism industry.
- Lack of integrated tourism promotion: Promotional activities are barred due to the spread of COVID-19 and there is no benefit of promotion of tourism during COVID-19.
- Loss of productivity and Profitability: Indian tourism industry was thoroughly put to a stop to their services. Therefore there is no productivity of the tourism activities and profitability.
Government of India’s recent Initiatives:
- Development of tourist’s circuit around specific themes (SWADESH DARSHAN):
- Ministry should take the advantage of the regional, national and international linkages developed in North Eastern States so far in the tourism front.
- All the states and UT/s should be given the exact same amount as per its budgeted allocation.
- The Tourism Ministry has launched the Incredible India Tourist Facilitator Certification (IITFC) portal.
- It is an online programme where one can learn about tourism at their own time, space, path and pace.
- The successful completion of this programme would enable the learner to become a Certified Tourist Facilitator of Ministry of Tourism, government of India.
- Facilitative visa regime is a prerequisite for increasing inbound tourism.
- Ministry of Tourism takes the initiative with Ministry of Home Affairs and Ministry of External Affairs for achieving the same.
- The “Incredible India 2.0” Campaign of the Ministry marks a shift from the generic promotions being undertaken across the world to market specific promotional plans and content creation.
- Recently, in order to promote night tourism, the Culture Ministry has decided to open 10 historical monuments till 9 PM for common visitors across the country.
- Further, it urged all the states and UTs to open their important monuments till late night for visitors.
- Government promotes states to organize surveys in their respective states to understand how the foreign tourists perceive India and should work towards removing negative impressions.
- This will lead to change the perception of India in the mind of foreign tourists which will yield us good results for promotion of tourism.
Way Forward:
As a travel destination, few other nations can offer the diversity of products and experiences found in India. The travel and tourism industry offers significant opportunity for fulfilment of key national growth imperatives including employment generation across all regions of the country, and growth in the sector can contribute to overall economic development in the country. However, tourism in India, though growing consistently, is yet to realize its full potential due to several challenges that plagued the sector. Alleviation of these challenges will be essential for the industry to realize its full potential.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: The India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (IndAus ECTA) has recently come into effect. The ECTA was signed on April 2, 2022, and was ratified on November 21, 2022.
About IndAus ECTA:
Benefits for India:
- India will benefit from preferential market access provided by Australia on 100% of its tariff lines, including all the labour-intensive sectors of export interest to India, such as Gems and Jewellery, Textiles, leather, footwear, furniture among other, the commerce ministry said.
Benefits for Australia:
- India will be offering preferential access to Australia on over 70% of its tariff lines, including lines of export interest to Australia, which are primarily raw materials and intermediaries such as coal, mineral ores and wines
Protection to few products:
- Products like agricultural products and the dairy sector – which were very sensitive for India and without which Australia has never done an agreement before – have been protected.
Employment generation:
- It is estimated that an additional 10 lakh jobs would be created in India under ECTA.
Visa Quotas:
- Indian yoga teachers and chefs are set to gain with the annual visa quota.
Post-study work visa:
- Over 1 lakh Indian students would benefit from a post-study work visa (for 18 months to 4 years) under the ECTA.
Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA):
- The Australian Parliament has also approved an amendment to the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA), a move which would help the Indian IT sector in operating in that market.
- It would stop the taxation on the offshore income of Indian firms providing technical support in Australia.
India-Australia Relations

Historical:
- India and Australia established diplomatic relations in the pre-Independence period, with the establishment of India Trade Office in Sydney in
- With the passage of time, the relationship gained momentum towards a strategic relationship, alongside the existing economic engagement.
Strategic partnership:
- Australia looks at India as an important partner in promoting regional security and stability.
- This led to upgradation of the bilateral relationship to a Strategic Partnership, including a Joint Declaration on Security Cooperation in 2009.
Bilateral Engagement:
- Bilateral mechanisms include high-level visits, Annual Meetings of Prime Ministers, Foreign Ministers’ Framework Dialogue, Joint Trade and Commerce Ministerial Commission, India-Australia ‘2+2’ Foreign Secretaries and Defence Secretaries Dialogue, Defence Policy Talks, Australia-India Education Council, Defence Services Staff Talks, etc.
Multilateral Engagement:
- Both countries have close cooperation in multilateral fora like Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and G20.
- The Quadrilateral Framework (QUAD) of India and Australia along with the US and Japan emphasize the collective resolve to maintain a free, open and inclusive Indo-Pacific region.
- They are also part of the Trilateral Supply Chain Initiative and the Indo-Pacific Economic Forum.
Bilateral Trade:
- India is the 5th largest trade partner of Australia with trade in goods and services at A$ 29 billion representing 3.6% share of the total Australian trade in 2017-18, with export at A$ 8 billion and import at A$ 21 billion.
- Indian exports: India’s main exports to Australia are Refined Petroleum, medicaments, Railway vehicles including hover-trains, Pearls & Gems, Jewellery, and made-up textile articles.
- Indian imports: Imports are Coal, copper ores & concentrate, Gold, vegetables, wool & other animal hair, fruits and nuts, lentils and education-related services.
Science and Technology:
- An Australia-India Strategic Research Fund (AISRF), which was established in 2006, supports scientists in India and Australia to collaborate on leading-edge research.
- AISRF consists of India Australia Biotechnology Fund; India-Australia Science & Technology Fund; Grand Challenge Fund and Fellowship Schemes.
Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement:
- It was signed between the two countries in September 2014 during the visit of the Australian Prime Minister to India.
- The Australian Parliament passed the Civil Nuclear Transfer to India Bill 2016 which ensures that Uranium mining companies in Australia may fulfil contracts to supply Australian uranium to India for civil use.
Defence:
- In 2014, both sides decided to extend defence cooperation to cover research, development and industry engagement and agreed to hold regular meetings at the level of the Defence Minister to conduct regular maritime exercises and convene regular service-to-service talks
- AUSINDEX: The first-ever Bilateral Maritime Exercise, AUSINDEX, was conducted in Visakhapatnam (Bay of Bengal) in September 2015.
- Exercise Pitch Black: In 2018, the Indian Air Force participated for the first time in the Exercise Pitch Black in Australia.
- Exercise of the Australian Navy: INS Sahyadri participated in Kakadu, the biennial exercise of the Australian Navy held in 2018, in which 27 nations participated.
- AUSTRAHIND: The 4th edition of AUSTRAHIND (Special Forces of Army Exercise) was held in September 20
Indian Community:
- The Indian community in Australia continues to grow in size and importance, with a population of nearly half seven lakhs.
- India is now the third-largest source of immigrants to Australia, after the UK and New Zealand and the largest source of skilled professionals for Australia.
- There is a constant flow of students and tourists from India.
Challenges:
- India’s trade deficit with Australia has been increasing since 2001-02 due to India-Australia Free Trade Agreement.
- It is also a contentious issue in the ongoing RCEP negotiations which India left.
- The formation of the Japan–America–India (JAI) partnership at the G20 summit in Buenos Aires in 2018 is cause for Australian concern.
- India’s unwillingness to invite Australia to participate in the Malabar naval exercise, despite Australian lobbying, has sparked speculation over the fate of the Quadrilateral Consultative Dialogue (the ‘Quad) involving India, Australia, Japan and the United States.
- Building consensus on non-nuclear proliferation and disarmament has been a major hurdle given India’s status as a nuclear power.
- Trade and maritime security on the other hand seem the most viable points of collaboration. Although a defence agreement was signed in 2014, the defence relationship has yet to develop fully.
- Although security has received a lot of significance in the relationship, in practice Australia-India defence cooperation remains relatively undeveloped.
- There are a considerable number of defence and security dialogues between the two countries, but none has been translated into more substantive cooperation.
- Increasing Racist attacks on Indians in Australia has been a major issue: The relationship was further strained over the attacks on Indian students studying in Melbourne, and the resulting media coverage caused serious damage to Australia’s standing in India.
Way Forward:
The cooperation and coordination between the two countries have seen exponential momentum in recent years. The shared values, interests, geography, and objectives are the foundation of deepening India-Australia relations. Both India and Australia share a vision of a free, open, inclusive, and rules-based Indo-Pacific region.
India and Australia believe in cooperative use of the seas by following International law including the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and peaceful resolution of disputes rather than through unilateral or coercive actions. The India-Australia ECTA will enhance the already close and strategic relations between the two countries.
Source: PIB
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding Mahadayi river:
- It rises from the Bhimgad Wildlife Sanctuary in Khanapur taluk of Karnataka.
- It flows through Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh, finally joins the Bay of Bengal.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) “Ethylene glycol” often mentioned in news for health concerns finds application in which of the following:
- Hydraulic brake fluids
- Stamp pad inks
- Ballpoint pens
- Solvents, paints
- Cosmetics
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 3 and 4 only
- 2 3 and 5 only
- 1 4 and 5 only
- 1 2 3 4 and 5
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding Nilgiri Tahr:
- It is designated as the State animal of Tamil Nadu
- It has been listed as a critically endangered species IUCN Red list
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 31st December 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 30th December – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – a











