IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, a Nature walk was organised along Palak Lake in Mizoram.
About Palak Lake:-
IMAGE SOURCE: Mizoram map showing the location of nest boxes | Download Scientific Diagram (researchgate.net)
- Palak Lake is the largest natural lake in Mizoram. (UPSC CSE: Assam-Mizoram border dispute )
- It is situated near Phura village which is about 391 km to the south of Aizawl.
- The Palak Lake wetland conservation area falls under the Indo-Burma biodiversity hotspot.
- It is rich in biodiversity.
- It is oval in shape and covers about 1 square km.
- It is surrounded by lush virgin forests rich in flora and fauna.
- It is home to most of the common wetland birds and hill birds (UPSC MAINS: Wetland Conservation)
- It is believed to be a winter stop-over for migrating Pintail Duck.
- A few elephants still roam the surrounding virgin forests.
National Museum of Natural History (NMNH):-
- The National Museum of Natural History (NMNH) is located in New Delhi, India.
- It was established in 1972.
- It opened its doors to the public on 5th June 1978, coinciding symbolically with World Environment Day.
- It works under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India.
- It is an institution devoted to environmental education.
- It derives its strength principally from theme-based exhibition galleries and experiential resource centres.
- Objectives:-
- To extend its activities at the regional/local levels.
- To develop museum-based educational projects.
- To develop environmental education resource materials (such as audio-visual aids, low-cost teaching aids, school loan kits, etc.) to promote environmental education
- To develop national and international cooperation with other organizations, professional bodies or museums.
National Centre for Sustainable Coastal Management (NCSCM):-
- It is under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- It undertakes studies and research in the area of Coastal Zone Management including coastal resources and environment.
- It is located in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- Objective:-
- It aims to promote integrated and sustainable management of the coastal and marine areas in India.
- It works for the benefit and well-being of the traditional coastal and island communities.
- It also intends to promote sustainable coasts through increased partnerships.
- Role:-
- It has various research divisions including, Geospatial Sciences, Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Coastal environmental impact assessment, Conservation of Coastal & Marine Resources, etc.
- Survey of India and NCSCM have mapped the Hazard Line for the entire coast of India.
- It also advises the Union and State Governments and other associated stakeholders on policy, and scientific matters related to Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM).
National Institute of Himalayan Environment:-
- It was established in 1988-89 as an autonomous Institute.
- It is under the Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEF&CC), Govt. of India.
- It is identified as a focal agency to:-
- advanced scientific knowledge
- evolve integrated management strategies
- demonstrate their efficacy for the conservation of natural resources
- ensure environmentally sound development in the entire Indian Himalayan Region (IHR)
- The institute pays particular attention to the preservation of fragile mountain ecosystems, indigenous knowledge systems and sustainable use of natural resources.
MUST READ: COP14 of Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With references to India, Didwana, Kuchaman, Sargol and Khatu are the names of (2021)
- Glaciers
- Mangrove areas
- Ramsar sites
- Saline lakes
Q.2) What is common to the places known as Aliyar, Isapur and Kangsabati? (2019)
- Recently discovered uranium deposits
- Tropical rain forests
- Underground cave systems
- Water reservoirs
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, NTCA wrote to the Chief Wildlife Warden of the State to initiate action against illegal resorts and homestays in enclosures of BRT Tiger Reserve.
About Biligiri Rangaswamy Temple Tiger Reserve:-
IMAGE SOURCE: Location of Biligiri Rangaswamy Temple Tiger Reserve. Triangle… | Download Scientific Diagram (researchgate.net)
- It derives its name ‘BILIGIRI’ from the white rocky cliff on the top of which is a temple of Lord VISHNU locally known as Rangaswamy.
- In Kannada, Biligiri means white hills – hence the name.
- It is situated in the middle of the bridge between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats in South India.
- It was constituted as a Wildlife Sanctuary in 1974. (UPSC CSE: Wildlife Protection )
- BRT Wildlife Sanctuary was declared a Tiger Reserve in 2011. (UPSC PRELIMS: Global Conservation Assured|Tiger Standards (CA|TS))
- Flora:-
- The forests are principally of dry deciduous type and are interspersed with moist deciduous, semi-evergreen, evergreen and shola patches occurring at varying altitudes.
- Fauna:-
- Animals found here include tiger, elephant, leopard, wild dog, bison, sambar, spotted deer, barking deer, four-horned antelope, sloth bear, wild boar, common langur, bonnet macaque, varieties of reptiles, birds, etc.
Tiger Reserves in Karnataka:-
- Karnataka has been declared as No.1 State in Tiger Population in the country.
- At present the Tiger population is estimated around 300.
- As per India Tiger estimate 2010 conducted by the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Govt. of India.
- The State has 5 Tiger Reserves namely:-
- Bandipur:-
- The park is situated at the foothills of the Western Ghats.
- It is known for its rich diversity of flora and fauna.
- It was established as a hunting reserve for the Maharajas of Mysore.
- In 1973, it was declared a national park.
- It was designated as a tiger reserve in 1974 as part of Project Tiger.
- It is one of the highest tiger densities in India.
- The park also has a significant population of other wildlife species such as elephants, leopards, dholes, and gaurs.
- Bhadra:-
- Parts of the current reserve were first declared as Jagara Valley Wildlife Sanctuary in 1951.
- In 1974 the area was expanded and named the Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary.
- In 1998 the sanctuary was included in the Project Tiger Network.
- Flora: Bhadra is the natural habitat of prized timber such as Teak and Rosewood.
- Forest Types: Tropical Moist Mixed Deciduous Forest, Tropical Dry Deciduous Forest, Semi-Evergreen Forest.
- Fauna: Tiger, leopard, elephant, gaur, sambar, barking deer, spotted deer, wild dog, wild boar, sloth bear, etc.
- Nagarahole:-
- It is also known as ‘Rajiv Gandhi National Park.
- It was established as a wildlife sanctuary in 1955.
- It was upgraded into a national park in 1988.
- It was declared as the 37th Tiger reserve under Project Tiger in 1999.
- The Park lies in the Western Ghats.
- It is a part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
- The Nagarahole River flows through the park, which joins the Kabini River which also is a boundary between Nagarahole and Bandipur National Park.
- Flora: The vegetation consists mainly of moist deciduous forests with predominating trees of teak and rosewood.
- Fauna: Asian elephants, chital (spotted deer), Indian mouse deer, gaur, stripe-necked, leopard, tiger, and sloth bear among others.
- Dandeli-Anshi:-
- It was established in 1956 in the central portion of the Uttara Kannada (North Canara) district of Karnataka.
- In 1987, the state proposed carving out a section of the sanctuary to create the Anshi national park, which was implemented.
- The park area was expanded by 90 square kilometres when the final notification was issued in 2002.
- It was granted Project Tiger tiger reserve status in 2007.
- Biligiri Rangaswamy Temple Tiger Reserve
MUST READ: Kali Tiger Reserve
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following Protected Areas are located in the Cauvery basin? (2020)
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Which one of the following protected areas is well-known for the conservation of a sub-species of the Indian swamp deer (Barasingha) that thrives well on hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous? (2020)
- Kanha National Park
- Manas National Park
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Tal Chhapar Wildlife Sanctuary
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope uncovered a complex and fascinating dusty structure around the young star Fomalhaut.
About Fomalhaut:-

IMAGE SOURCE: JWST spies asteroid belt around star Fomalhaut | Popular Science (popsci.com)
- Fomalhaut is located 25 light-years from Earth
- It was one of the first exoplanets ever discovered in visible light by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope in 2004. (UPSC PRELIMS: Exoplanets)
- Exoplanets: are the planets that orbit around stars other than the Sun.
- It is used in navigation because of its conspicuous place in a sky region otherwise lacking in bright stars.
- It is a white star, it has an apparent magnitude of 1.16.
- It lies in the southern constellation Piscis Austrinus, 25 light-years from Earth.
- It is the brightest star in the southern constellation Piscis Austrinus. (UPSC CSE: A star with a heartbeat & without a magnetic field discovered)
- It is surrounded by debris disks that are remnants of collisions between larger bodies, similar to asteroids and comets.
- Astronomers proposed that Fomalhaut b was not a real planet but rather an expanding dust cloud left behind by a collision between two cometlike bodies.
MUST READ: James Webb Space Telescope
SOURCE: TIMES NOW
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following is a reason why astronomical distances are measured in light-years?(2021)
- Distance among stellar bodies does not change
- The gravity of stellar bodies does not change
- Light always travels in a straight line
- The speed of light is always the same
Q.2) Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘black holes’ billions of light-years away from the Earth. What is the significance of this observation? (2019)
- ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected
- ‘Gravitational waves’ were detected
- The possibility of intergalactic space travel through a ‘wormhole’ was confirmed
- It enabled the scientists to understand ‘singularity’
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) rolled out a module for automated scrutiny of GST returns.
About Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC):-
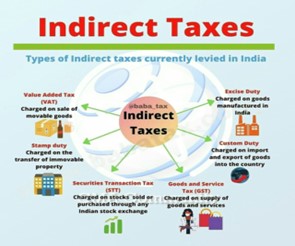
IMAGE SOURCE: indirect taxes India – Bing images
- Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs is a part of the Department of Revenue under the Ministry of Finance.
- It is a statutory body established under the Central Boards of Revenue Act, of 1963.
- It was formed in 1964 when the Central Board of Revenue was split into the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) and the Central Board of Excise and Customs.
- Central Board of Excise and Customs was renamed the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs in 2018.
- It is the nodal national agency responsible for administering:-
- Customs
- GST (UPSC MAINS: GST- Five years on )
- Central Excise
- Service Tax
- Narcotics in India.
- The Board is the administrative authority for its subordinate organizations, including Custom Houses, Central Excise and Central GST Commissionerate and the Central Revenues Control Laboratory. (UPSC MAINS: Tax administration in India)
- Functions performed by the CBIC include:-
- Formulation of policy concerning levy and collection of Customs, Central Excise duties, Central Goods & Services Tax and IGST.
- Prevention of smuggling.
- Administration of matters relating to Customs, Central Excise, Central Goods & Services Tax, IGST and Narcotics to the extent under CBIC’s purview.
MUST READ: ( Tax-GDP ratio )
SOURCE: BUSINESS STANDARD
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) What is/are the most likely advantages of implementing ‘Goods and Services Tax (GST)’? (2017)
- It will replace multiple taxes collected by multiple authorities and will thus create a single market in India.
- It will drastically reduce the ‘Current Account Deficit’ of India and will enable it to increase its foreign exchange reserves.
- It will enormously increase the growth and size of the economy of India and will enable it to overtake China in the near future.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements : (2017)
- Tax revenue as a per cent of the GDP of India has steadily increased in the last decade.
- Fiscal deficit as a per cent of GDP of India has steadily increased in the last decade.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: DGCA recently, suspended an Air India pilot’s licence for three months after he violated safety norms.
About Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA):-
- The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is a statutory body of the Government of India.
- It was formed under the Aircraft (Amendment) Act, of 2020.
- It comes under the Ministry of Civil Aviation. (UPSC CSE: New Director General of Bureau Of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS) appointed)
- It aims to regulate civil aviation in India.
- It primarily deals with safety issues in civil aviation.
- Its headquarters are located in New Delhi.
- It has regional offices in various parts of India.
- Mandate: DGCA is responsible for the regulation of air transport services to/from/within India and for enforcement of civil air regulations, air safety, and airworthiness standards. (UPSC MAINS: Reforms In Civil Aviation Industry)
- Functions:-
- Registration of civil aircraft.
- Formulation of standards of airworthiness for civil aircraft registered in India and grant of certificates of airworthiness to such aircraft.
- Licensing of pilots, aircraft maintenance engineers and flight engineers, and conducting examinations and checks for that purpose.
- Licensing of air traffic controllers.
- Investigating accidents/incidents.
- Taking accident prevention measures.
- Coordination at the national level for flexible use of air space by civil and military air traffic agencies
- Interaction with ICAO for the provision of more air routes for civil use through Indian air space.
- Promoting indigenous design and manufacture of aircraft.
MUST READ: International Air Connectivity Scheme (IACS) scheme
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the “Tea Board” in India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Tea Board is a statutory body.
- It is a regulatory body attached to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The Tea Board’s Head Office is situated in Bengaluru.
- The Board has overseas offices in Dubai and Moscow.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: 25th anniversary of the Pokhran-II test was celebrated recently.
About Pokhran Tests:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Pokhran Tests and India’s Nuclear Journey (ilearncana.com)
- The foundation of India’s nuclear programme was laid by physicist Dr Homi J Bhaba.
- The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) was founded in 1954 with Bhabha as director.
- In May 1998, India conducted a series of nuclear tests at its Pokhran test site in the northwestern state of Rajasthan.
- The tests were hailed as a triumph of Indian science and technology.
- These tests also sparked widespread controversy and condemnation from the global community, leading to a period of diplomatic isolation and economic sanctions for India.
Pokhran 1:-
- It was India’s first nuclear test.
- It was codenamed “Smiling Buddha”.
- It was conducted at the Pokhran site in 1974.
- Vikram Sarabhai (Bhaba’s successor at the DAE) contributed significantly to broadening India’s nuclear technology through these tests.
- It made India the first country outside of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council to conduct a nuclear test.
- The test was carried out under the leadership of Prime Minister Indira Gandhi.
- It marked a significant step forward in India’s nuclear ambitions.
- The test was a “peaceful nuclear explosion” (PNE) intended for civilian purposes.
- However, it raised concerns in the international community about India’s nuclear intentions and led to widespread condemnation and sanctions. (UPSC MAINS: Pokhran gave India a strategic upper hand)
Pokhran 2:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Parmanu – The Story of Pokhran nuclear tests 1998 – HimBuds.com
- It was held in 1998, in Pokhran, Rajasthan.
- It was India’s second wave of nuclear tests.
- It was code-named “Operation Shakti”.
- It included five nuclear explosions, over the course of three days.
- It was under the leadership of Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee.
- A thermonuclear or hydrogen bomb was used in these tests.
- The world community widely condemned the tests, and the United States and other nations hit India with economic penalties as a result.
- The tests, however, enjoyed enormous popularity in India and were viewed as a source of national pride and technological advancement.
India’s nuclear doctrine (presented in 1999) since Pokhran-II:-
- It highlighted a credible minimum deterrence (CMD) and a no-first-use (NFU) policy, while concurrently supporting non-proliferation and universal disarmament.
- The sole purpose of India’s nuclear deterrence is to deter adversaries’ use or threat of use of nuclear weapons. (UPSC CSE: India’s Nuclear Doctrine)
- The policy changed India’s image and the US (once an adversary of India’s nuclear programme) signed a civil nuclear deal with India in 2008.
- It acknowledged India as a responsible nuclear player.
MUST READ: The Return of nuclear weapons on the global platform
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2016)
- PSLVs launch satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-stage launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct.?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
Q.2) Which reference to Agni-IV Missile, the following statements is/are correct? (2014)
- It is a surface-to-surface missile.
- It is fuelled by liquid propellant only.
- It can deliver one-tonne nuclear warheads about 7500 km away.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, a three-parent baby was born in the UK using IVF.
About Three-parent Baby:-
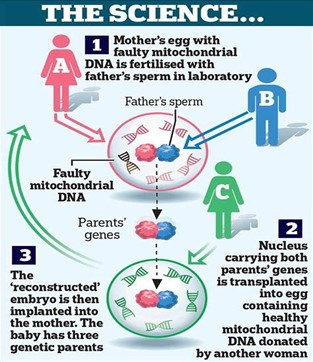
IMAGE SOURCE: Britain’s first three-parent baby is born: Procedure ‘marks the biggest leap forward since IVF created – Business Telegraph
- It s a technique to create to have a child without passing on Mitochondrial diseases caused by faulty mitochondria of the mother.
- Mitochondrial diseases: are long-term, genetic, often inherited disorders that occur when mitochondria fail to produce enough energy for the body to function properly.
- Mitochondria: the cellular structures that provide energy to cells.
- Mechanism:-
- Researchers do this by exchanging the diseased mitochondria of a prospective mother with those of a healthy, unrelated donor: the ‘third parent’.
- The procedure replaces a small amount of faulty DNA in a mother’s egg with healthy DNA from a second woman, so that the baby would inherit genes from two mothers and one father.
- The idea is to prevent certain genetic diseases from being passed on to children.
- The technique used is called ‘Maternal Spindle transfer’ in which maternal DNA is put into the egg of a donor woman, which is then fertilized using the father’s sperm. (UPSC CSE: Test Tube Babies)
- The procedure was developed to help existing IVF treatments in which mothers have mitochondrial diseases.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): a medical procedure in which mature egg cells are removed from a woman, fertilized with male sperm outside the body, and inserted into the uterus of the same or another woman for normal gestation. (UPSC CSE: Surrogacy in India)
- Britain became the first country to allow for a three-parent baby and in 2017.
- The first 3 parent baby was born.
MUST READ: ART and surrogacy
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of the developments in Bioinformatics, the term ‘transcriptome’, sometimes seen in the news, refers to (2016)
- a range of enzymes used in genome editing
- the full range of mRNA molecules expressed by an organism
- the description of the mechanism of gene expression
- a mechanism of genetic mutations taking place in cells
Q.2) The Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee is constituted under the (2015)
- Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006
- Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999
- Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
Syllabus
- Prelims –ART and Culture
Context: Visva-Bharati University is set to become the first living heritage university to receive the Unesco World Heritage tag.
About Visva-Bharati University:-
- The university was set up by Nobel laureate Rabindranath Tagore in 1921 at Santiniketan, West Bengal.
- He called it Visva-Bharati, which means the communion of the world with India.
- Until independence, it was a college.
- Soon after independence, the institution was given the status of a central university in 1951 by an act of the Parliament.
Rabindranath Tagore’s philosophy about Viswa Bharti:-
- Rabindranath Tagore believed in open-air education. (UPSC CSE: Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE))
- He had reservations about any teaching done within four walls.
- This was due to his belief that walls represent the conditioning of the mind.
- Tagore did not have a good opinion about the Western method of education introduced by the British in India. (UPSC CSE: School education)
- On this subject, Tagore and Gandhiji’s opinions matched.
- So, he devised a new system of learning in Visva-Bharati.
- Special feature of Visva Bharti:-
- He allowed students to continue their course till the student and his teacher both are satisfied.
- At Visva-Bharati, if a course demanded by a student is not available, then the university will design a course and bring teachers for that course.
- The university would not be bothered by the consideration of whether there is a demand for the course.
MUST READ: India’s education emergency
SOURCE: INDIA TODAY
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
- Department of Science and Technology
- Ministry of Labour and Employment
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Q.2) What is the aim of the programme ‘Unnat Bharat Abhiyan’? (2017)
- Achieving 100% literacy by promoting collaboration between voluntary organizations and the government’s education system and local communities.
- Connecting institutions of higher education with local communities to address development challenges through appropriate technologies.
- Strengthening India’s scientific research institutions in order to make India a scientific and technological power.
- Developing human capital by allocating special funds for health care and education of rural and urban poor, and organizing skill development programmes and vocational training for them.
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The Uttar Pradesh government has released figures regarding the Prohibition of Unlawful Conversion of Religion Act Amid the ongoing controversy over The Kerala Story movie.
- The government said 427 conversion-related cases were reported between January 1, 2021, and April 30, 2023.
Status of the anti-conversion law in India:
- There are several anti-conversion laws in India that regulate the conversion of one religion to another. These laws vary from state to state, and the specific provisions of the laws can differ significantly.
- Constitutional Provision: Article 25 of the Indian Constitution guarantees the freedom to practise, profess, and propagate any religion.
- It also grants all religious groups the right to control their own religious affairs, subject to public morality, health, and order.
- Existing Laws: Religious conversions have not been subject to any national restrictions or regulations.
- Private Member Bills to control religious conversions, however, have repeatedly been introduced in the Parliament since 1954 (but never passed by it).
- Additionally, the Union Law Ministry stated in 2015 that Parliament lacks the legislative authority to enact legislation prohibiting conversion.
- Several states have passed “Freedom of Religion” laws over the years to prohibit forced, fraudulent, or coerced conversions to another religion.
- In general, however, anti-conversion laws in India require that individuals seeking to convert to another religion must obtain permission from the government before doing so.
- Some states have more stringent anti conversion laws than others, and some states have provisions that specifically target certain religious groups or activities.
- In recent years, there has been significant controversy and debate over the use of anti-conversion laws in India.
- Some people argue that these laws are necessary to protect the cultural and social cohesion of the country,
- while others believe that they are used to suppress minority religions and violate the right to freedom of religion.
- The Supreme Court of India has ruled that anti conversion laws are constitutional as long as they are not used to interfere with an individual’s right to freedom of religion.
- However, there have been cases in which these laws have been used to target and persecute minority religious groups.
Supreme Court’s Observations:
- The Supreme Court verdict in Rev. Stainislaus vs. State of Madhya Pradesh in the 1960s is frequently cited in matters involving religious freedom.
- Then Chief Justice of India A.N. Ray dissected Article 25 to hold that “the Article does not grant the right to convert other persons to one’s own religion but to transmit or spread one’s religion by an exposition of its tenets.”
- Recently, the Supreme Court emphasised that Forced religious conversions are “dangerous” and they affect the security of the nation.
- It urged the Union government to “step in” and apprise the court of the measures being taken to prevent such occurrences.
Arguments in Favour of anti-conversion:
- These laws only ban and punish forceful religious conversion.
- Fundamental rights under Article 25 ‘Right to propagate a religion” did not extend to forced conversions.
- There is no fundamental right to convert another person to one’s own religion.
Arguments against anti-conversion:
- According to some activists “Such laws are used to target religious minorities and interfaith couples”.
- These laws would be used to target even voluntary conversions, and curb the fundamental rights “Freedom of conscience” under Article 25.
- These Acts do not satisfy the test of reasonableness and fairness, and also go against the Fundamental rights under Article 14 and Article 21” of the Constitution.
Right to Freedom of religion in India
- The Indian Constitution allows individuals the freedom to live by their religious beliefs and practices as they interpret these.
- In keeping with this idea of religious freedom for all, India also adopted a strategy of separating the power of religion and the power of the State
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 25: Freedom of conscience and free profession, practice and propagation of religion
- Article 26: Freedom to manage religious affairs
- Article 27: Freedom to pay taxes for promotion of any particular religion
- Article 28: Freedom to attend religious instruction or worship in certain educational institutions.
Way Forward:
The right to religion did not include the right to convert other people to a particular religion, especially through fraud, deception, coercion, allurement, and other means. The conversion laws must be strengthened and rightly so to stop the use of lures and force but they should not discriminate among religions while identifying the perpetrators.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: India’s strategic autonomy and policy of non-alignment have evolved into a multi-alignment approach.
About India’s multi-alignment stand
Origin of India’s non-alignment stand:
- There has been a progressive evolution in Indian thinking on forming and joining regional economic and security groupings, since the days New Delhi declared itself as “Non-Aligned” in the 1950s.
- India, thereafter, remained a leading player in the “Non-Aligned Movement” (NAM).
- The 120 members of NAM professed that they would not get drawn into “Great Power” rivalries between the US and USSR.
India’s current multi-alignment stand:
With Russia:
- The disintegration of the Soviet Union in the 1990s led to new groupings and alliances.
- But we are now happily in a position where we are partners, in different ways, with all major global power centres. Economics and economic integration play a far more central role as bridges of cooperation today.
West Asia:
- The most notable decision taken in recent days was after the first summit meeting of the recently established I2U2 grouping, comprising India, Israel, the US and the UAE.
- This was the first time when India and the US partnered two West Asian countries to focus cooperation on use of water resources, food security, health, transportation and space.
USA and QUAD:
- India finds itself linked with the US and Japan far more closely than in the past, in a world order which is becoming more China-centric than in the past.
- This has been the rationale of Quadrilateral Security Dialogue or QUAD, comprising Australia, India, Japan and the US.
Southeast Asian Nations:
- While India has a free trade agreement (FTA) with ASEAN, New Delhi has chosen, for understandable reasons, not to join the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), containing 15 East Asian and Pacific nations, including ASEAN members, Australia, New Zealand and China.
Eurasia:
- India holds membership of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), which is a permanent intergovernmental international organisation of Eurasian Nations with a secretariat in Beijing.
India’s view on Ukraine-Russia Conflict:
- India has been actively engaging with Ukraine and expressing solidarity with the Nation in the face of the ongoing conflict with Russia.
- This is in contrast to China’s move with Moscow in order to cement China’s relationship with Russia.
- India has been committed to supporting peace efforts in Ukraine and sees itself as a mediator in the conflict.
- The United States sees this engagement as important because it aligns with its own response to the conflict and helps to bring the two countries’ positions into closer alignment.
Reasons for India’s ambiguity:
- India’s position on the Ukraine war is nuanced and reflects a balancing act between its traditional ties with Russia and its democratic values.
- While India has expressed disapproval of Russia’s military actions in Ukraine.
- it has avoided taking a clear position on the issue in many UN resolutions, which may be due to India’s military and geopolitical dependence on Russia.
- However, India’s views on sovereignty align with universally acceptable Westphalian notions and clash with China’s political philosophy of ‘might is right,‘ which has led to China’s support for Russia in the conflict.
Problem with India’s multi-alignment stand
- India lacks hard power .It has been recently argued that had India been adequately powerful it could have stopped the Ukraine conflict.
- While India has expressed disapproval of the Ukraine war but it has avoided taking any clear positions in several UN resolutions.
- This is understandable that India has often taken an evasive position on conflicts that involve traditional allies.
- However critics argue that India’s ambiguity does not behove a nation aspiring to become a permanent member of the UNSC, which implies a commitment to speak as a global voice against territorial aggression and human rights violations like the case of the Russia -Ukraine conflict.
- This is based on the military dependence of India as it is on the anti-colonial standard of India’s strategic autonomy doctrine.
Way Forward:
A pursuit of ‘multi-alignment’ may have given New Delhi some diplomatic space in the ongoing war in Ukraine. However, it may not be sufficient for India to play the role of a mediator between Russia and Ukraine. India currently lacks the material resources to match the extent of China’s economic and military potential.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA):
- It is a statutory body of the Government of India.
- It comes under the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- Its headquarters are located in Hyderabad.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC):
- It is a statutory body.
- It comes under the ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 and 2
Q.3) The palak lake often mentioned in the news located in
- Manipur
- Mizoram
- Assam
- Jharkhand
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 12th May 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 11th May – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – c














