IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Government has set a target to open ten thousand Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Kendras (PMBJKs) under Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP) by March 2024.
About Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana(PMBJP):-
- Launched:2008. (PMBJP)
- Historical Background:-
- It was launched by the Department of Pharmaceuticals under the name Jan Aushadhi Campaign in 2008.
- 2015: It was re-launched as ‘Pradhan Mantri Jan Aushadhi Yojana’ (PMJAY).
- 2016: it was again renamed “Pradhan Mantri Bharatiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana” (PMBJP).
- Ministry: Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
- Implementing Agency: the Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI).
- Objectives of PMBJP: to provide quality medicines at affordable prices to people through special Kendras known as Pradhan Mantri Bharatiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana Kendra.
- Funding: Financial Support is provided by the government to eligible NGOs/Trusts/agencies/individuals to establish Jan Aushadhi stores.
- Benefit of PMBJP: The scheme ensures easy reach to affordable medicine to the people in every nook and corner of the country.
Salient Features of PMBJP:-
- Ensure access to quality medicines.
- Create awareness about generic medicines through education and publicity so that quality is not synonymous with only high prices.
- The scheme ensures easy reach to affordable medicine to the people in every nook and corner of the country.
- Create demand for generic medicines by improving access to better healthcare through low treatment cost and easy availability wherever needed in all therapeutic categories.
- Janaushadhi Sugam facilitates the public by providing a digital platform at the tip of their fingers.
- Jan Aushadhi Sugam: a mobile app that helps in locating the nearest Janaushadhi Kendra and the availability of medicines with its price.
- Pharmaceutical & Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI) has been established for co-coordinating procurement, supply and marketing of generic drugs through the Jan Aushadhi Stores. (Pradhan Mantri Janaushadhi Kendra (PMJK))
- The quality, safety and efficacy of medicines are ensured to the required standards before the same are supplied to Supers stockists /Jan Aushadhi Stores from the Warehouse.
MUST READ: Ayushman Bharat PMJAY
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in relation to Janani Suraksha Yojana (2023)
- It is a safe motherhood intervention of the State Health Departments.
- Its objective is to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality among poor pregnant women.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women.
- Its objective includes providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under the Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy: (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for preschool children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with a special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) implemented the Advance Authorisation Scheme.
Background:-
- The Scheme was implemented under the Foreign Trade Policy.
- It allows duty-free import of inputs for export purposes.
About Advance Authorisation Scheme:-
- Launched: 2015. (Advance Authorization Scheme (AAS))
- Ministry: Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Objective: to make India’s products competitive in the global market.
- It is a type of duty exemption scheme introduced by the Government of India under the Foreign Trade Policy 2015-2020. (New Foreign Trade Policy)
Salient Features of AAS:-
- Under this scheme, exemption from the payment of import duties is given to raw materials/inputs required for the manufacture of export products.
- They are not allowed to sell the products in the domestic market.
- Validity: Advance Authorization is valid for 12 months from the date of issue of such Authorization.
- Composition fee formula: The revised composition fee formula is based on a specific rate for different levels of the ‘CIF (cost, insurance, freight) value of authorization.
- The fees levied under these 3 slabs:-
- ₹5,000 for a cost, insurance, freight (CIF) value of advance authorization license valued at up to ₹2 crores.
- ₹10,000 for a value between ₹2 crore and 10 crores
- ₹15,000 for value over ₹10 crores.
- The simplification of calculations for composition fees helps in automation and faster service delivery by making the process more efficient and easier to understand.
- The eligibility of inputs is determined by Sector-specific Norms Committees based on input-output norms.
- The quantity of inputs allowed for a given product is based on specific norms defined for that export product, which considers the waste generated in the manufacturing process.
- DGFT provides a sector-wise list of Standard Input-Output Norms (SION) under which the exporters may choose to apply.
Benefits of Advance Authorization Scheme:-
- When duties paid on raw materials are saved, it automatically brings down the cost of the final export product.
About Directorate General of Foreign Trade:-
- It is an attached office of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Headed by: Director General of Foreign Trade.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Inception:
- Keeping in line with liberalization and globalization and the overall objective of increasing exports, DGFT has since been assigned the role of “facilitator”.
- Objective: implementing the Foreign Trade Policy and promoting India’s exports.
Functions of DGFT:-
- It also issues licenses to exporters.
- It monitors their corresponding obligations through a network of 25 Regional Offices.
- All regional offices provide facilitation to exporters in regard to developments in International Trade i.e. WTO agreements, Rules of Origin and anti-dumping issues, etc.
- It helps exporters in their import and export decisions in an internationally dynamic environment.
MUST READ: Conditional Market Authorization
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2022)
- An increase in Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) indicates the appreciation of the rupee.
- An increase in the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) indicates an improvement in trade competitiveness.
- An increasing trend in domestic inflation relative to inflation in other countries is likely to cause an increasing divergence between NEER and REER.
Which of the above statements is correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Retail investors through Demat account can invest in Treasury Bills and Government of India Debt Bonds in the primary market
- The “Negotiated Dealing System-Ordering Matching” is a government securities trading platform of the Reserve Bank of India.
- The “Central Depository Services Ltd” is jointly promoted by the Reserve Bank of India and the Bombay Stock Exchange.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2021)
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: The Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying (DAHD) has introduced the Credit Guarantee Scheme under the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF).
About the Credit Guarantee Scheme of AHIDF:-
- The credit guarantee scheme facilitates access to finance for un-served and under-served livestock sector.
- It aims to strengthen the credit delivery system and ensure smooth access to finance for entrepreneurs engaged in the Livestock sector. ( Dairy Cooperatives)
- Implementing Agency: Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF).
- Objective: to support the Livestock sector’s Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) without the need for collateral security.
- Funding: a credit guarantee fund trust of Rs 750 crore, which will cover up to 25 per cent of credit facilities extended to eligible MSMEs by lending institutions.
- The trust, formed in partnership with NAB Sanrakshan Trustee Company Private Ltd, a subsidiary of NABARD, ensures credit guarantees for MSMEs under the AHIDF scheme. (Special Livestock Sector Package)
Key features of the scheme:-
- Interest subvention of three per cent.
- Loan of up to 90 per cent of the total project cost from any Scheduled Bank, National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC).
Eligibility under the scheme:-
- The scheme targets underserved sections of society, including first-generation entrepreneurs and underprivileged individuals, who often lack collateral security for their ventures.
Benefits under the scheme:-
- By providing access to financial assistance, it promotes investments in various areas of the livestock sector.
- These include sectors such as dairy and meat processing, animal feed plants, breed improvement technology, waste management, and veterinary vaccine and drug manufacturing facilities.
About the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF):-
- Launched:2021.
- Ministry: Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
- Implementing Agency: Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying.
- It is the Nation’s first-ever fund trust under the Credit guarantee scheme of AHIDF in the agriculture and Animal Husbandry sector.
Objectives of AHIDF:-
- To help to increase milk and meat processing capacity and product diversification thereby providing greater access for unorganized rural milk and meat producers to organized milk and meat market.
- To make available increased price realization for the producer.
- To make available quality milk and meat products for the domestic consumer.
- To fulfil the objective of protein-enriched quality food requirement of the growing population of the country and prevent malnutrition in one of the highest malnourished children populations in the world.
- Develop entrepreneurship and generate employment.
- To promote exports and increase the export contribution in the milk and meat sector.
- To make available quality concentrated animals feed to the cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig and poultry to provide balanced ration at affordable prices.
ACTIVITIES ELIGIBLE FOR AVAILING BENEFITS UNDER AHIDF:-
- Dairy processing and value addition.
- Meat processing and value addition.
- Animal Feed manufacturing units and strengthening of existing Units/plant.
- Breed Improvement Technology and Breed Multiplication Farm.
- Setting up of Veterinary Vaccine and Drugs Production facilities.
- Animal Waste to Wealth Management (Agri-waste management).
MUST READ: Improving Livestock Breeding
SOURCE: BUSINESS STANDARD
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements with reference to India: (2023)
- According to the ‘Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006’, ‘medium enterprises’ are those with investments in plant and machinery between (‘ 15 crore and 25 crore).
- All bank loans to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises qualify under the priority sector.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
India accounts for 3·2% of the global export of goods.
Statement-II:
Many local companies and some foreign companies operating in India have taken advantage of India’s Production-linked Incentive’ scheme.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: In recent times, due to rising antibiotic resistance scientists are considering bacteriophages as a cure for bacterial infections.
About bacteriophages:-
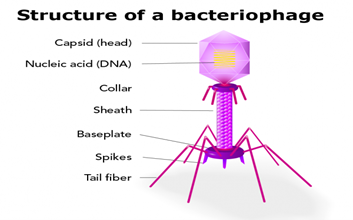
IMAGE SOURCE: Let’s Talk Science
- Discovered by: they were discovered independently by Frederick W. Twort in Great Britain (1915) and Félix d’Hérelle in France (1917).
- Naming: D’Hérelle coined the term bacteriophage, meaning “bacteria eater,”.
- These viruses kill bacteria in our microbiomes.
- They only attack bacteria and are harmless to people, animals, and plants.
- Bacteriophages also known as
- Habitat: They are found in soil, sewage, water, and other places bacteria live.
- Classification: Phages are classified in a number of virus families some examples include Inoviridae, Microviridae, Rudiviridae, and Tectiviridae.
- Physical Structure:-
- Like all viruses, phages are simple organisms that consist of a core of genetic material (nucleic acid) surrounded by a protein capsid.
- Capsid of a bacteriophage can be icosahedral, filamentous, or head-tail in shape.
- Head-tail structure seems to be unique to phages and their close relatives.
- Genetic make-up: Phage genomes can consist of either DNA or RNA.
- Two different cycles that bacteriophages may use to infect their bacterial hosts:-
- The lytic cycle: The phage infects a bacterium, hijacks the bacterium to make lots of phages, and then kills the cell by making it explode (lyse).
- The lysogenic cycle: The phage infects a bacterium and inserts its DNA into the bacterial chromosome, allowing the phage DNA (now called a prophage) to be copied and passed on along with the cell’s own DNA.
Phage Therapy:-
- Phage therapy (PT) is also called bacteriophage therapy.
- It uses viruses to treat bacterial infections.
MUST READ: World Antimicrobial Awareness Week 2022
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Some microorganisms can grow in environments with· temperatures above the boiling point of water.
- Some microorganisms can grow in environments with temperatures below the freezing point of water.
- Some microorganisms can grow in highly acidic environments with a pH below 3.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) With reference to the role of biofilters in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems, consider the following statements: (2023)
- Biofilters provide waste treatment by removing uneaten fish feed.
- Biofilters convert ammonia present in fish waste to nitrate.
- Biofilters increase phosphorus as a nutrient for fish in water.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: As per recent announcements, the first C-295 transport aircraft manufactured by Airbus for the Indian Air Force is scheduled to be delivered in September 2023.
Background:-
- 16 aircraft would come in fly-away condition, manufactured at the Airbus facility in Seville, Spain, and 40 would be manufactured in India by Airbus jointly with Tata.
About Airbus C-295 aircraft:-
- Airbus C295 is a new-generation tactical airlifter in the light and medium segment. (U C-295 aircraft deal)
- It conducts multi-role operations worldwide under all weather conditions.
- It is fully certified and routinely operates day and night in combat missions in all weather extremes, from desert to maritime environments, from extremely hot to extremely cold temperatures.
- Missions and operations: The robustness and versatility of the C295 make it the ideal platform for any type of military or civic operations for the benefit of society.
Features Airbus C-295 aircraft:-
- The aircraft, with a flight endurance of up to 11 hours.
- It can carry out multi-role operations under all weather conditions. ( Induction of C-295MW in Indian Air Force (IAF))
- It can routinely operate day as well as night combat missions from desert to maritime environments.
- It has a rear ramp door for quick reaction and para-dropping of troops and cargo.
- Short take-off/land from semi-prepared surfaces is another of its features.
Replacement:-
- It will replace the Indian Air Force’s ageing fleet of Avro-748 planes.
- Avro-748 planes: are a British-origin twin-engine turboprop, military transport and freighter.
MUST READ: Hansa aircraft
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Ballistic missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flights, while cruise missiles are rocket-powered only in the initial phase of flight.
- Agni-V is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile, while BrahMos is a solid-fuelled intercontinental ballistic missile.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following actions: (2023)
- Detection of car crashes/collisions, which results in the deployment of airbags almost instantaneously.
- Detection of accidental free fall of a laptop towards the ground which results in the immediate turning off of the hard drive.
- Detection of the tilt of the smartphone which results in the rotation of the display between portrait and landscape mode.
In how many of the above actions is the function of the accelerometer required?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recent reports claimed that India recorded all-time high DPT3 immunisation coverage in 2022.
Background:-
- The coverage rate for DPT3 vaccines (diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus) in India reached an all-time high of 93% in 2022, surpassing the pre-pandemic record of 91% in 2019.
- This significant increase from the 85% coverage in 2021 was reported by the World Health Organization (WHO).
About DPT3 Vaccine:-
- DPT3 vaccines refer to a combination vaccine that provides protection against three infectious diseases: diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), and tetanus. (‘ZyCov-D’ vaccine)
- Naming: The “DPT” in DPT3 stands for the initials of these three diseases.
- Diphtheria: a bacterial infection that primarily affects the respiratory system.
- Effects: It can cause severe throat and nose congestion, difficulty breathing, and in severe cases, it can lead to heart and nerve damage.
- Pertussis (Whooping Cough): a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis.
- Symptoms: It is characterized by severe coughing fits, often accompanied by a “whooping” sound when gasping for breath.
- Pertussis can be particularly dangerous for infants and young children.
- Tetanus: a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Clostridium tetani.
- It enters the body through wounds or cuts and produces a toxin that affects the nervous system, leading to muscle stiffness and spasms, particularly in the jaw and neck muscles.(Nation’s first mRNA-based vaccine)
Dosage of DPT3 vaccines:–
- The primary dose of DPT is provided as part of the pentavalent vaccine.
- Pentavalent vaccine: a combination vaccine with five individual vaccines conjugated into one.
- Two booster doses are given at 16 -24 months and 5-6 years, respectively.
MUST READ: iNCOVACC
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Microsatellite DNA’ is used in the case of which one of the following? (2023)
- Studying the evolutionary relationships among various species of fauna.
- Stimulating ‘stem cells to transform into diverse functional tissues.
- Promoting clonal propagation of horticultural plants.
- Assessing the efficacy of drugs by conducting a series of drug trials in a population.
Q.2) In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent the COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Serum Institute of India produced a COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using an mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using a vector based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen-based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Marital Rape in India
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Society) and GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The Supreme Court would list a batch of petitions pertaining to the matters related to marital rape.
About Marital rape:
- Marital rape (or spousal rape) is an act in which one of the spouses indulges in sexual intercourse without the consent of the other.
- Rape in India continues with the patriarchal outlook of considering women to be the property of men post marriage, with no autonomy or agency over their bodies.
- They deny married women equal protection of the laws guaranteed by the Indian constitution.
- Today, more than 100 countries have criminalized marital rape but, unfortunately, India is one of the only 36 countries where marital rape is still not criminalized.
Current Scenario:
- Marital rape has been impeached in more than 100 countries but, unfortunately, India is one of the only 36 countries where marital rape is still not criminalized.
- In 2013, the UN Committee on Elimination of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW) recommended that the Indian government should criminalize marital rape.
- The JS Verma committee set up in the aftermath of nationwide protests over the December 16, 2012 gang rape case had also recommended the same.
- As per the NCRB report, in India, a woman is raped every 16 minutes, and every four minutes, she experiences cruelty at the hands of her in-laws.
- National Family Health Survey (NFHS) shows that sexual violence is most often committed by individuals with whom women have an intimate relationship.
Section 375 of the Indian Penal Code
- It defines rape as “sexual intercourse with a woman against her will, without her consent, by coercion, misrepresentation or fraud or at a time when she has been intoxicated or duped, or is of unsound mental health and in any case if she is under 18 years of age.
- Consent is defined as clear, voluntary communication that the woman gives for a certain sexual act.
- Exceptions to Section 375: Sexual intercourse by a man with his own wife, who is above the age of 18, is not sexual assault.
- Punishment: Except in certain aggravated situations, the punishment will be imprisonment of not less than seven years but it may extend to imprisonment for life, and shall also be liable to fine.
- In aggravated situations, punishment will be rigorous imprisonment for a term which shall not be less than 10 years but which may extend to imprisonment for life, and shall also be liable to fine.
Arguments for criminalizing Marital Rape
- The doctrine of Coverture: The marital exception to the IPC’s definition of rape was drafted based on Victorian patriarchal norms that did not recognize men and women as equals.
- It did not allow married women to own property, and merged the identities of husband and wife under the “Doctrine of Coverture.”
- Article 14: Indian women deserve to be treated equally under article 14 and an individual’s human rights do not deserve to be ignored by anyone, including by their spouse.
- Further, a married woman has the same right to control her own body, as does an unmarried woman.
- Bodily Integrity is intrinsic to Article 21: A woman is entitled to refuse sexual relations with her husband as the right to bodily integrity and privacy is an intrinsic part of Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Supreme Court has included sanctity of women, and freedom to make choices related to sexual activity under the ambit of Article 21.
- In the State of Karnataka v. Krishnappa, the Supreme Court held that sexual violence apart from being a dehumanizing act is an unlawful intrusion of the right to privacy and sanctity of a female.
- In the Suchita Srivastava v. Chandigarh Administration, the Supreme Court equated the right to make choices related to sexual activity with rights to personal liberty, privacy, dignity, and bodily integrity under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- Rape not ground for Divorce: As marital rape is not a ground for a divorce in any personal laws and even the Special Marriage Act, 1954, It cannot be used as a ground for divorce and cruelty against the husband Thus, the women remain helpless and keep suffering in silence.
- Rape is rape, irrespective of the identity of the perpetrator, and the age of the survivor.
- A woman who is raped by a stranger lives with a memory of a horrible attack; a woman who is raped by her husband lives with her rapist throughout her life .
- Criminalizing marital rape: It will ensure that women remains safer from abusive spouses and they can receive the help needed to recover from marital rape and can save themselves from domestic violence and sexual abuse
- The United Kingdom, whose common law was followed by India, made marital rape a criminal offence in 1991.
Arguments against criminalising marital rape:
- Threat to the institution of marriage: Criminalisation of marital rape is often viewed as a threat to the institution of marriage, in which both the spouses have conjugal rights over each other.
- Conjugal rights: Section 9 of the Hindu Marriage Act gives either spouse in a marriage the legal right to “restitution of conjugal rights”.
- Misuse of the law is a big reason why several individuals, jurists and even men’s rights activists have raised alarm over the criminalisation of marital rape.
- According to some activists, as huge as 85% of dowry cases turn out to be false and India cannot deal with another failed catastrophic law that will amount to “legal terrorism”.
- Burden of proof: The burden of proof is a hugely complex issue that has prevented marital rape to be criminalised.
- In the case of marital rape, one has to consider that intercourse is a part of any marriage.
- Now, if marital rape itself is criminalised, the question remains who would the burden of proof be on and what would that burden be.
- Gender Neutrality: Arguments to make the definition of ‘rape’ gender-neutral have been put forward on many occasions, and the same argument is put forward in the case of marital rapes too.
- Even if the exception of IPC section 375 is removed or criminal provisions are added to the Domestic Violence act, husbands will not be able to use those.
Way Forward
It is high time that the legislature should take cognisance of this legal infirmity and bring marital rape within the purview of rape laws by eliminating Section 375 (Exception) of IPC. By removing this law, women will be safer from abusive spouses.
It is important that legal prohibition on marital rape is accompanied by changes in the attitude of the prosecutors, police officers and those in society generally. The need of the hour is that marriage and divorce must come under secular law and there cannot be any difficulty in having a common code of law for all communities at least for marriage and divorce.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Society) and GS 2 (Polity and Governance)
Context: National Commission for Women (NCW) has condemned the incident of Manipur where women were paraded naked.
About NCW:
- It was set up as statutory body in 1992 under the National Commission for Women Act, 1990.
- It aims to review the Constitutional and Legal safeguards for women; recommend remedial legislative measures; facilitate redressal of grievances and advise the Government on all policy matters affecting women.
- The Commission shall consist of:
- A Chairperson, nominated by the Central Government.
- Five Members with expertise in law and issues related to women, nominated by the Central Government.
- At least one Member each shall be from amongst persons belonging to the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes respectively
- Member Secretary must be a central gazetted officer having management and sociological expertise and nominated by the Central Government.
- The National Commission for Women submits all its reports to the Central Government, which is laid before the Parliament during sessions.
- During the investigation of any matter before it, National Commission for Women has all the powers of a civil court.
Functions:
- Inquiry, Investigation and Examination of matters related to safeguards of women.
- Recommendation: to the Union as well State regarding improving the conditions of the women.
- Review different laws related to women and suggest amendments to them.
- Violation Cases: Takes up violation cases pertaining to the provisions of the Constitution and other laws related to women.
- Suo-Moto Notice on matters pertaining to deprivation of women’s rights, non-implementation of laws, non-compliance policy decisions related to women etc.
- Research: Undertake promotional and educational research to find ways to represent women in all spheres of life and improve their efficiency.
- Planning: Participate in the process of planning related to the socio-economic development of women.
- Progress Evaluation: Evaluate the progress related to the development of women in the State and the Union.
- Inspection: Inspect the jail, remand homes etc., where women are kept as prisoners.
- Funding Litigations relating to funds affecting large women body.
Major limitations of National Commission for Women making it toothless:
- Not concrete powers: The NCW is only recommendatory and has no power to enforce its decisions.
- Often it acts only if the issues are brought to light.
- Unreported cases of oppression and suppression of women are not attended to.
- Legal powers: Commission lacks constitutional status, and thus has no legal powers to summon police officers or witnesses.
- In addition, it has no power to take legal actions against the Internal Complaint Committees that prevent grievance redressal of women facing harassment.
- Less funding: NCW’s functions are dependent on the grants offered by the central government.
- Financial assistance provided to the Commission is very less to cater to its needs.
- Political interference: It does not have the power to choose its own members.
- The power-selecting members is vested with the Union government leading to political interference at various levels.
Government efforts for the protection and welfare of women
Constitutional provisions
- Fundamental rights: It guarantees all Indians the right to equality (Article 14), no discrimination by the State based on gender (Article 15(1)), and special provisions to be made by the State in favour of women (Article 15(3)).
- Fundamental Duties: It ensures that practices derogatory to the dignity of women are prohibited under Article 51 (A).
Legislative Framework:
- Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005
- The Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961
- The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, 2013
- The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO), 2012
Way Forward: Suggestive measures
- Amending NCW Act: Women’s role is continuously expanding in today’s India and the expansion of the role of the NCW is the need of the hour.
- Further, the State Commissions must also widen their ambit.
- Increasing Minimum Age for Marriage: The age of marriage of daughters is being attempted to be raised to 21 years so that marriage at an early age does not hinder the education and career of daughters.
- Addressing Violence against Women (Violence against Women): Women’s violence remains a barrier to attaining equality, development, and peace, as well as the realization of women and girls’ human rights.
- Overall, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) goal of “leaving no one behind” cannot be realized without ending violence.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Advance Authorisation Scheme brings down the cost of the final export product.
Statement-II:
It is under the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Bacteriophages only attack bacteria and are harmless to people, animals, and plants.
Statement-II:
Bacteriophages can only multiply and grow inside a bacterium.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following pairs:
Vaccine Disease
- Dengvaxia : Diptheria
- DPT3 : Whooping cough
- Pediarix : Hepatitis B
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- None
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) What is the role of the National Commission for Women? Has it been effective in addressing women issues in India? Critically examine (250 words).
Q.2) The laws in India related to rape have undergone several changes since pre-independence except marital. Critically examine (250 words).
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 22nd July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 21st July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – b
Q.3) -b











