IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the summit of the United Nations International Maritime Organization (IMO) concluded in London.
Background:-
- Maritime countries upgraded their Greenhouse House Gas (GHG) emissions strategy to reach net zero “by or around” 2050 without specifying a definite year agreed to upgrade their Greenhouse House Gas (GHG) emissions strategy to reach net zero “by or around” 2050.
About International Maritime Organization:-

IMAGE SOURCE: south-star-ltd.com
- IMO is the United Nations specialized agency.
- Establishment:
- HQ: London, United Kingdom.
- Objective: to create a regulatory framework for the shipping industry that is fair and effective, universally adopted and universally implemented.
- Membership: IMO currently has 175 Member States and three Associate Members.
- India joined the IMO in (UPSC CSE: International Maritime Organization (IMO) & India)
- Functions:-
- Its role is to create a level playing field so that ship operators cannot address their financial issues by simply cutting corners and compromising on safety, security and environmental performance.
- IMO’s work supports the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The IMO is not responsible for enforcing its policies.
- It has the responsibility for the safety and security of shipping and the prevention of marine and atmospheric pollution by ships. (UPSC CSE: Maritime Security)
- Key Conventions of IMO:
- International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS)
- International Convention on Standards of Training, Certification, and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (STCW)
- International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL)
MUST READ: Green Ports & Green Shipping in India
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
Carbon markets are likely to be one of the most widespread tools in the fight against climate change.
Statement-II:
Carbon markets transfer resources from the private sector to the State.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-11 is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Q.2) “Climate Action Tracker” which monitors the emission reduction pledges of different countries is a: (2022)
- Database created by a coalition of research organisations
- Wing of “International Panel of Climate Change”
- Committee under “United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change”
- Agency promoted and financed by United Nations Environment Programme and World Bank
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Bureau of Water Use Efficiency (BWUE) and the Indian Plumbing Association (IPA) have signed a MoU with the aim of achieving a Water Positive India.
Background:-
- The MoU focuses on creating awareness and promoting rainwater harvesting structures, low-flow fixtures and sanitary ware, treatment of grey and black water, and water audit of the built environment.
About the Bureau of Water Use Efficiency (BWUE):-
- Establishment: 2022.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- The Bureau of Water Use Efficiency (BWUE) has been set up under the scheme of the National Water Mission.
Functions of said Bureau:-
- To plan and execute a nationwide program for the promotion of efficient use of water in irrigation, domestic water supply, and municipal and/or industrial uses in the country.
- To make necessary regulatory directions to promote Water Use Efficiency.
- Prescribing guidelines for water conservation codes, standardizing and developing codes and facilitating their notification from concerned authorities.
- Developing standards for water-efficient fixtures, appliances, sanitary wares and other equipment using water in both urban/rural areas.
- Evolving a system of efficiency labelling.
- Evolve a system for incentivizing promotional efforts to increase water use efficiency.
- Create a Resource Centre and Data Bank related to various aspects of Water Use Efficiency.
- Promote research and development including research in the field of water conservation.
Indian Plumbing Association (IPA)
- Establishment: 1993
- It is the apex body of plumbing professionals in the country.
Objectives of IPA:-
- To uplift the dignity of the profession by encouraging members to:
- Adopt correct professional practices. (UPSC CSE: Catch The Rain Awareness Generation Campaign)
- Adhere to ethical codes of conduct.
- Aim for the highest standards of workmanship.
- Promote and foster healthy relationships within the fraternity.
- To promote the advancement of plumbing services in the country by:
- Organizing seminars, exhibitions, and symposiums to educate members of the trade and the general public.
- Providing a platform for the dissemination of information and exchange of ideas on matters related to the plumbing profession.
- Establishing harmonious means of communication to facilitate better interface between the plumbing community, government/quasi-government agencies, statutory bodies, NGOs and private agencies.
- Establishing training and education programmes to create plumbing professionals.
Mission of IPA:-
- Redefining Plumbing Standards in India.
- Striving for an overall improvement of the plumbing profession in India at par with international standards.
- Active participation with the global body in the plumbing profession.
National Water Mission:
- It is one of the eight missions launched under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) for combating the threats of global warming. (UPSC CSE: Jal Jeevan Mission)
- NAPCC: it is a Government of India’s programme launched in 2008 to mitigate and adapt to the adverse impact of climate change.
- Launched: 2008.
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- Objective of the National Water Mission:-
- To conserve water.
- To minimise the wastage of the water.
- To ensure equitable distribution across the country and within States through integrated water resources management.
- Goals of the National Water Mission:-
- Comprehensive water database in the public domain and assessment of the impact of climate change on water resources.
- Promotion of citizen and state actions for water conservation, augmentation and preservation.
- Focused attention to vulnerable areas including over-exploited areas.
- Increasing water use efficiency by 20%.
- Promotion of basin-level integrated water resources management.
MUST READ: National Water Policy
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in relation to Janani Suraksha Yojana : (2023)
- It is a safe motherhood intervention of the State Health Departments.
- Its objective is to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality among poor pregnant women.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women.
- Its objective includes providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under the Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for preschool children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with a special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defence
Context: The Seventh edition of the Indian Navy – US Navy (IN – USN) Salvage and Explosive Ordnance Disposal exercise, SALVEX was conducted recently.
About SALVEX:-
- It was conducted from 26 Jun – 06 Jul 23 at Kochi.
- Started :
- Background: Indian Navy(IN) and US Navy(USN) have been participating in joint Salvage and EOD exercises since (UPSC CSE: 26th Exercise Malabar)
- EOD: it is a specialized technical area in military and law enforcement.
- The exercise saw participation from both the navies which included the ships – INS Nireekshak and USNS Salvor in addition to Specialist Diving and EOD teams.
- Duration: it spans over 10 days. (UPSC CSE: Exercise TARKASH)
Key engagements and outcomes:-
- Shared Learning on Maritime Salvage: The Diving teams from both countries engaged in the exchange of experiences, lessons, and best practices in maritime salvage operations.
- Training Synergies on EOD Operations: The exercise provided an ideal platform for joint training exercises, allowing divers and EOD teams to enhance their interoperability and refine their skills.
- Mastery of Mine Detection and Neutralization: The participating divers received comprehensive training in the detection and neutralization of mines, enabling them to mitigate potential threats in underwater environments.
- Efficient Wreck Location and Salvage Techniques: The exercise focused on honing the teams’ abilities to locate and salvage wrecks, a critical skill for ensuring safe navigation and effective disaster response.
MUST READ: India-US relations
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following actions : (2023)
- Detection of car crash/ collision which results in the deployment of airbags almost instantaneously. B
- Detection of accidental free fall of a laptop towards the ground which results in the immediate turning off of the hard drive
- Detection of the tilt of the smartphone which results in the rotation of the display between portrait and landscape mode
In how many of the above actions is the function of the accelerometer required?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) has a ‘Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air’.
- The UNCAC is the ever-first legally binding global anti-corruption instrument.
- A highlight of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the inclusion of a specific chapter aimed at returning assets to their rightful owners from whom they had been taken illicitly.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is mandated by its member states to assist in the implementation of both UNCAC and UNTOC.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: GST Council will discuss the exemption for cancer medicine Dinutuximab (Qarziba) in its upcoming meeting.
Background:-
- The Council, chaired by the Union finance minister and comprising state ministers, will also decide on GST exemption for satellite launch services provided by private players. (UPSC CSE: GST)
- The tax rate for online gaming, on multiplex food and drinks is also on the agenda for the meeting.
About Dinutuximab (Qarziba):-
- Qarziba is a cancer medicine used to treat neuroblastoma, a cancer of nerve cells, in patients over 1 year of age.
- Neuroblastoma: Cancer of immature nerve cells arising from the adrenal gland, nerve ganglia or the neck.
- It is used in 2 groups of patients who have high-risk neuroblastoma (which has a high chance of coming back):
- patients who have had some improvement with previous treatments, which included blood stem-cell transplantation (a transplant of blood-producing cells)
- Patients whose neuroblastoma has not improved with other cancer treatments or has come back.
Working Mechanism:-
- Qarziba is a monoclonal antibody (a type of protein) that has been designed to recognise and attach to a structure called GD2.
- Monoclonal antibody: an antibody produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell.
- GD2: present in high amounts on the surface of neuroblastoma cells, but not normal cells.
- When Qarziba attaches to the neuroblastoma cells, it makes them a target for the body’s immune system which then kills the cancer cells.
- Immune system: a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases.
About GST Council
- The GST Council is a constitutional body. (UPSC CSE: GST Council)
- It was established under Article 279A of the Indian Constitution. (UPSC CSE: GST Appellate Tribunal)
- Article 279-A: gives the President the authority to appoint a GST Council by executive order.
- The 101st Amendment Act of 2016 (122nd Amendment Bill), paved the way for the implementation of GST.
- Functions:–
- As per Article 279, it is meant to “make recommendations to the Union and the states on important issues related to GST, like the goods and services that may be subjected or exempted from GST, model GST Laws”.
- It also decides on various rate slabs of GST.
- Chairman: The GST Council is chaired by the Union Finance Minister.
- Other members: these include the Union State Minister of Revenue or Finance and Ministers in charge of Finance or Taxation of all the States.
MUST READ: Platinum drugs
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) ‘Microsatellite DNA’ is used in the case of which one of the following? (2023)
- Studying the evolutionary relationships among various species of fauna.
- Stimulating ‘stem cells to transform into diverse functional tissues.
- Promoting clonal propagation of horticultural plants.
- Assessing the efficacy of drugs by conducting a series of drug trials in a population.
Q.2) ‘Aerial metagenomics’ best refers to which one of the following situations? (2023)
- Collecting DNA samples from the air in a habitat in one go.
- Understanding the genetic makeup of avian species of a habitat.
- Using air-borne devices to collect blood samples from moving animals.
- Sending drones to inaccessible areas to collect plant and animal samples from land surfaces and water bodies.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, the UN adopted the Marine Biodiversity of Areas beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) or the High Seas Treaty.
Background:-
About High Seas Treaty:-
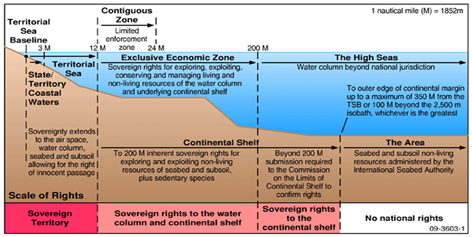
IMAGE SOURCE: ResearchGate
- It is an international agreement on the conservation and sustainable use of marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction. (UPSC CSE: UN High Seas Treaty)
- The UN adopted the Marine Biodiversity of Areas beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) or the High Seas Treaty in 2023.
- Objective: to achieve a more holistic management of high seas activities, which should better balance the conservation and sustainable use of marine resources.
- Jurisdiction: It encompasses the high seas, beyond the exclusive economic zones or national waters of countries.
- This new instrument is being developed within the framework of the UNCLOS ( United Nations Convention for the Law of the Sea). (UPSC CSE: BBNJ Treaty)
- The agreement has five aspects:
- Environmental impact assessments for activities taken up on high seas.
- Conservation of marine genetic resources.
- Capacity building.
- Technology transfer.
- Cross-cutting issues such as institutional structure and financial support.
UNCLOS( United Nations Convention for the Law of the Sea)
- It is an international agreement that establishes the legal framework for marine and maritime activities.
- Historical Background: The Convention which concluded in the year 1982 replaced the quad-treaty of 1958.
- Establishment: It came into effect in the year
- It is the only international convention which stipulates a framework for state jurisdiction in maritime spaces.
- It provides a different legal status to different maritime zones.
- It divides marine areas into 5 zones :
- Internal-waters
- Territorial seas
- Contiguous Zone
- Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
- Continental shelf or High seas
- India has been a party to the convention since 1995.
MUST READ: Deep-Sea Mining
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best describes the ‘Polar Code’? (2022)
- It is the international code of safety for ships operating in polar waters.
- It is the agreement of the countries around the North Pole regarding the demarcation of their territories in the polar region.
- It is a set of norms to be followed by the countries whose scientists undertake research studies at the North Pole and the South Pole.
- It is a trade and security agreement of the member countries of the Arctic Council.
Q.2) With reference to the United Nations Convention on the Law of Sea, consider the following statements: (2022)
- A coastal state has the right to establish the breadth of its territorial sea up to a limit not exceeding 12 nautical miles, measured from a baseline determined in accordance with the convention.
- Ships of all states, whether coastal or landlocked, enjoy the right of innocent passage through the territorial sea.
- The Exclusive Economic Zone shall not extend beyond 200 nautical miles from the baseline from which the breadth of the territorial sea is measured.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Recently, Peru declared a state of emergency for 60 days in areas around Ubinas volcano.
Background:-
- According to the Geophysical Institute of Peru, the volcano has been spewing ash and gas since earlier this week.
- The smoke cloud has travelled over towns that are 10 kilometers away from the volcano, according to the institute. Some 2,000 people live in the affected areas.
About Ubinas volcano:-
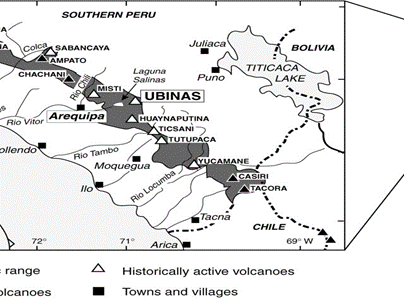
IMAGE SOURCE: researchgate.net
- Ubinas is an active stratovolcano. (UPSC CSE: Volcano)
- Stratovolcano: it is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava.
- It is located in the Moquegua Region of southern Peru, approximately 60 kilometers east of the city of Arequipa.
- It is part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes and stands at an elevation of 5,672 meters above sea level.
- The volcano’s summit contains a 1.4-kilometer-wide and 150-meter-deep caldera, within which lies a smaller crater.
- This distinct feature adds to the volcano’s geological significance.
- Caldera: it is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption.
- Ubinas I and Ubinas II: The volcano exhibits an upwards-steepening cone shape, with a notable notch on its southern side.
- The lower part is referred to as Ubinas I while the steeper upper section is known as Ubinas II.
- This represents different stages in the volcano’s geological history.
- The region where Ubinas is situated falls within the Ring of Fire.
- Ring of Fire: an area around the Pacific Ocean known for its high volcanic and seismic activity.
History of Volcanic activity:-
- Ubinas is recognized as the most active volcano in Peru. (UPSC CSE: Volcanic eruption at Mount Semeru)
- It has a history of small to moderate explosive eruptions and persistent degassing.
- Notable Eruptions: The volcano has experienced notable eruptions throughout history, including the 2006–2007 event that resulted in eruption columns, ash fall, health concerns, and evacuations in the region.
- Recent Activity: From 2013 to 2017, Ubinas exhibited lava flow within the crater, accompanied by ash falls, leading to further evacuations in nearby towns.
MUST READ: Mt. Mauna Loa
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
The region often mentioned in the news: Country
- Anatolia Turkey
- Amhara Ethiopia
- Cabo Delgado Spain
- Catalonia Italy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
How India can leverage its biggest strength
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Society) and GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The next 25 years could be the golden years for the country, provided it makes the best use of its favourable demographic composition.
About Demographic dividend:
- Demographic dividend, as defined by the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), is “the economic growth potential that can result from shifts in a population’s age structure, mainly when the share of the working-age population (15 to 64) is larger than the non-working-age share of the population (14 and younger, and 65 and older)”.
India’s demographic dividend:
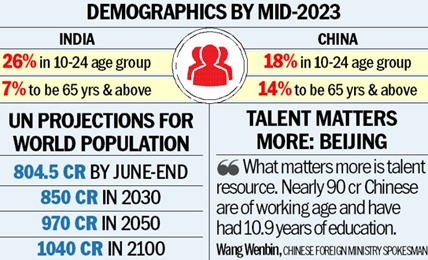
- India’s average age is 29 years, whereas the average age in US, China, France, Germany and Japan is 38, 38, 42, 45 and 48 years, respectively.
- Therefore, India is the youngest among the most populous countries in the world.
Advantages of India’s demographic dividend:
- Higher Economic Growth: A large and young working-age population can increase the labour supply, productivity, savings, and investment in the economy, leading to higher GDP growth and per capita income.
- Greater Competitiveness: A skilled workforce can enhance India’s competitiveness in the global market, especially in labour-intensive sectors such as manufacturing, services, and agriculture.
- India can also benefit from the rising demand for its exports in the ageing markets of developed countries.
- Social Development: It can contribute to social development by improving health, education, gender equality, and social cohesion.
- An empowered population can also participate more actively in democratic processes and civic engagement.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: A creative population can foster innovation and entrepreneurship in various fields, such as science, technology, arts, and culture.
- An aspirational population can also create new markets and opportunities for economic diversification.
Challenges associated with Demographic dividend:
- Asymmetric demography: The growth in the working-age ratio is likely to be concentrated in some of India’s poorest states and the demographic dividend will be fully realized only if India is able to create gainful employment opportunities for this working-age population.
- Lack of skills: Most of the new jobs that will be created in the future will be highly skilled and lack of skill in Indian workforce is a major challenge.
- India may not be able to take advantage of the opportunities, due to a low human capital base and lack of skills.
- Low human development parameters: India ranks 130 out of 189 countries in UNDP’s Human Development Index, which is alarming.
- Therefore, health and education parameters need to be improved substantially to make the Indian workforce efficient and skilled.
- Informal nature of economy in India is another hurdle in reaping the benefits of demographic transition in India.
- Jobless growth: There is mounting concern that future growth could turn out to be jobless due to de-industrialization, de-globalization, the fourth industrial revolution and technological progress.
- As per the NSSO Periodic Labour Force Survey 2017-18, India’s labour force participation rate for the age-group 15-59 years is around 53%, that is, around half of the working age population is jobless.
Indian government’s initiatives to reap the demographic dividend in India:
- The government has launched programmes like Jan Shikshan Sansthan, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, and National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme to improve employability through skilling, re-skilling, and up-skilling.
- These initiatives aim to make the Indian labour force more productive and efficient. The MSDE Vision 2025 further aims to improve the linkage between education and skill.
- The Ayushman Bharat and Swachh Bharat Mission seek to improve health equity in India.
- The Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana aims to make drug prices affordable and accessible, enhancing overall public health.
- The National Education Policy 2020, alongside the Samagra Shiksha programme, is focused on providing inclusive, equitable, and quality education at all school levels, ensuring a productive labour force in the future.
- Recognizing MSMEs as the backbone of Indian manufacturing, the government has endeavoured to support them in improving competitiveness, achieving scale, digital infrastructure, technology upgrades, and branding.
- The government has introduced flagship programmes like Skill India, Make in India, and Start-up India to enhance the productivity of the labour force and to foster innovation and entrepreneurship.
Way Forward:
If India has to reap the benefits of ‘demographic dividend’ in the years ahead, it is imperative that investments in social infrastructure by way of education, skill development, training and provision of health care facilities are made to enhance productivity of workforce and welfare of the population.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: The Union Cabinet cleared the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Bill 2022, paving the way for it to be introduced in Parliament.
History of Digital Personal Data Protection:
- In 2017 the S. Puttaswamy vs. Union of India judgement declared that right to privacy a fundamental right as part of right to life and liberty under Article 21 of the Constitution.
- To protect the personal data the data protection Bill has been in the works since 2018 when a panel led by Justice B N Srikrishna had prepared a draft version of the Bill.
- It is India’s first attempt to domestically legislate on the issue of data protection.
- The government has made several revisions to this draft and introduced it as the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2022.
Provisions of the Bill:
- The Bill will apply to the processing of digital personal data in India, whether it is collected online or offline and then digitized.
- It will also apply to the processing of digital personal data outside of India if it involves offering goods or services or profiling individuals in India.
- Personal data may be processed only for a lawful purpose for which an individual has given consent.
- Consent may be deemed in certain cases.
- Data fiduciaries will be obligated to maintain the accuracy of data, keep data secure, and delete data once its purpose has been met.
- The Bill grants certain rights to individuals including the right to obtain information, seek correction and erasure, and grievance redressal.
- The central government may exempt government agencies from the application of provisions of the Bill in the interest of specified grounds such as security of the state, public order, and prevention of offences.
- The central government will establish the Data Protection Board of India to adjudicate non-compliance with the provisions of the Bill.
Significance of personal data protection in India:
- Privacy protection: It guarantees that an individual’s privacy is not breached, as was the case with the Aadhaar data leak in 2018.
- It helps to avoid identity theft and other types of fraud.
- For example, consider the 2018 Cambridge Analytica controversy.
- Data accuracy is ensured through personal data protection, which guarantees that the data is correct and up to date.
- Personal data protection avoids data abuse and unlawful access, as shown in the WhatsApp data-sharing scandal in 2021.
- Personal data protection guarantees that data is safe and protected from cyberattacks.
- Personal data protection secures sensitive data, such as the health and financial data of persons, as well as sensitive health data.
- Individual empowerment: As previously said in 2018 Justice Srikrishna Committee Report Recommendations, personal data protection empowers people by giving them control over their personal data.
- Compliance with worldwide standards: Compliance with global data protection standards, such as GDPR compliance, requires personal data protection.
Concerns associated with the Bill:
- Government Control: The Bill is learnt to have prescribed that the central government can exempt “any instrumentality of the state” from adhering to the provisions on account of national security, relations with foreign governments, and maintenance of public order among other things.
- The control of the central government in appointing members of the data protection board — an adjudicatory body that will deal with privacy-related grievances and disputes between two parties — is learnt to have been retained as well.
- Dilutes the Right to Information (RTI) Act as personal data of government functionaries is likely to be protected under it, making it difficult to be shared with an RTI applicant.
- No Criminal Liability: The Bill only prescribes monetary penalties (under Schedule 1 of the DPDP Bill) for breaches and non-compliances and limits such penalties to breaches/non-compliances that the Data Protection Board determines to be ‘significant’.
- The DPD Bill has done away with criminal liabilities, as well as penalties that are directly linked to the turn-over or revenue of an erring Data Fiduciary.
- Penalties vary from INR 50 crore to INR 250 crore. Section 25 stipulates maximum penalty to be limited to INR 500 crore.
- Data of Children: The Bill requires parental consent for age less than 18 years.
- Parental consent would be required every time they want to access the internet.
Global Scenario:
- EU model: The GDPR focuses on a comprehensive data protection law for processing of personal data.
- It has been criticised for being excessively stringent, and imposing many obligations on organisations processing data, but it is still the template for most of the legislation drafted around the world.
- US model: Privacy protection is largely defined as “liberty protection” focused on the protection of the individual’s personal space from the government.
- It is viewed as being somewhat narrow in focus, because it enables collection of personal information as long as the individual is informed of such collection and use.
- China model: New Chinese laws on data privacy and security issued over the last 12 months include the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL), which came into effect in November 2021.
- It gives Chinese data principals new rights as it seeks to prevent the misuse of personal data.
Way Forward:
While protecting the rights of the data principal, data protection laws need to ensure that the compliances for data fiduciaries are not so onerous as to make even legitimate processing impractical.
The challenge lies in finding an adequate balance between the right to privacy of data principles and reasonable exceptions, especially where government processing of personal data is concerned.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Exercise SALVEX was conducted between Indian Navy and the Japanese Navy.
Statement-II:
The seventh edition of the exercise was conducted in Kochi, India.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-11 is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q2) Consider the following pairs:
- Stratovolcano: it is a conical volcano built up by much hardened lava.
- Ring of Fire: it is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption.
- Caldera: an area around the Pacific Ocean known for its high volcanic and seismic activity.
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- None
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
The Bureau of Water Use Efficiency makes necessary regulatory directions to promote Water Use Efficiency.
Statement-II:
It has been set up under the scheme of the National Water Mission.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Mains practice question:
Q.1) India is on the right side of demographic transition that provides golden opportunity for its rapid socio-economic development. What are the challenges associated with this transition? What measures needs to be taken to overcome those challenges? (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 8th July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 7th July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – c











