IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –IMPORTANT INDICES
Context: Global Hunger Index 2023 was released recently.
Key Highlights:-

IMAGE SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
- The 2023 GHI shows that, after many years of advancement up to 2015, progress against hunger worldwide remains largely at a standstill.
- As the effects of crises multiply and intensify, more and more people are experiencing severe hunger, with the situation expected to worsen throughout the year.
- South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa are the global regions characterized by the most severe hunger levels, both holding a GHI score of 27, signifying a serious state of hunger.
- India topped the list of countries with the highest child-wasting rate in the world, at 18.7 per cent, reflecting acute undernutrition.
- The country’s child wasting rate is higher than that of conflict-ridden Yemen (at 14.4 per cent) and Sudan at (13.7 per cent), which hold the second and third positions, respectively
- India has been ranked at the 111th position out of 124 countries, with neighbouring Pakistan (102th), Bangladesh (81st), Nepal (69th) and Sri Lanka (60th) faring better than it in the index.
- The country slipped four notches from its 107th position in 2022.
- Child wasting: refers to the share of children under age five who have low weight for their height.
- Indian government’s stand: The Indian government has questioned the methodology of GHI.
Initiatives taken by the government:-
- National Food Security Act, 2013: It legally entitled up to 75% of the rural population and 50% of the urban population to receive subsidized food grains under the Targeted Public Distribution System.
- Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Scheme: Launched on 2nd October 1975, the ICDS Scheme offers a package of six services (Supplementary Nutrition, preschool non-formal education, Nutrition & health education, Immunization, Health check-up and Referral services) to children in the age group of 0-6 years, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana: A centrally sponsored scheme executed by the Ministry of Women and Child Development, is a maternity benefit programme being implemented in all districts of the country with effect from 1st January 2017.
- POSHAN Abhiyan: Launched in 2018, it aims to reduce stunting, undernutrition, and anaemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls).
- Food Fortification: Food Fortification or Food Enrichment is the addition of key vitamins and minerals such as iron, iodine, zinc, and Vitamin A & D to staple foods such as rice, milk and salt to improve their nutritional content.
About Global Hunger Index 2023:-
- Time period: Annual.
- Published by: Concern Worldwide and Welthungerhilfe.
- The Global Hunger Index (GHI) is a tool for comprehensively measuring and tracking hunger at global, regional, and national levels. GHI scores are based on the values of four component indicators:
- Undernourishment: the share of the population with insufficient caloric intake.
- Child stunting: the share of children under age five who have low height for their age, reflecting chronic undernutrition.
- Child wasting: the share of children under age five who have low weight for their height, reflecting acute undernutrition.
- Child mortality: the share of children who die before their fifth birthday, partly reflecting the fatal mix of inadequate nutrition and unhealthy environments.
- Based on the values of the four indicators, a GHI score is calculated on a 100-point scale.
- The scale reflects the severity of hunger, where 0 is the best possible score (no hunger) and 100 is the worst.
- Each country’s GHI score is classified by severity, from low to extremely alarming. (Understanding the Global Hunger Index)
MUST READ: Food security
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following infrastructure sectors : (2023)
- Affordable housing
- Mass rapid transport
- Health care
- Renewable energy
On how many of the above does the UNOPS Sustainable Investments in Infrastructure and Innovation (S3i) initiative focus on its investments?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under the Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy : (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for preschool children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with a special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims –ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
Context: Recent reports show that Bihar’s Kawar Lake has been neglected and is on the brink of drying up.
Background:-
- While Bihar has many wetlands, only one is recognized Kawar Lake.
About Kawar Lake:-
- Location: Begusarai, Bihar.
- It is also known as Gokhur Lake or Kabartal Wetland.
- It is a residual oxbow lake formed by the changing course of the River Gandak.
- It is the largest freshwater oxbow lake in Asia.
- It was declared a Ramsar site in August 2020. (COP14 of Ramsar Convention on Wetlands)
- It was declared a notified area under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972.
- To check the poaching of birds, it was declared a protected zone by the Bihar state government in 1986.
- The government of India declared it a bird sanctuary in 1989.
- It is one of the most important wetlands for waterfowl in the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- It supports huge numbers of migratory ducks and Coot through the winter, as well as large concentrations of resident species such as ruficollis and Asian Openbill.
- The lake has been home to 58 migratory birds.
- It served as an important stopover along the Central Asian Flyway with at least 58 migratory water birds.
Threats:-
- Encroachment
- Conflicts between farmers and fisherfolk
- Illegal activities exacerbate the degradation.
- The lake has been experiencing a steady decrease in water levels since 2010.
- The lake faces challenges due to policy implementation gaps, illegal activities like migratory bird hunting, and a lack of effective conservation measures.
About Gandak River:-
- It is a tributary of the
- The Gandaki River system lies in the central part of Nepal.
- Its river basin is also referred to as the Narayani river system.
- It is a transboundary river system, originating from the Tibetan Plateau, flowing through central Nepal and draining into the Ganges River in India.
- About 69% of the total area lies in Nepal.
- It is the second-largest river basin of Nepal.
- Tributaries: Marsyangdi, Daraudi, Seti, Madi, Kali Gandaki, Budi Gandaki and Trishuli are the seven major tributaries of the Gandaki river basin.
- It flows southwest into India and then turns southeast along the Uttar Pradesh–Bihar state border and across the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
MUST READ: (India Designates 5 New Ramsar Sites)
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following has been constituted under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986? (2022)
- Central Water Commission
- Central Ground Water Board
- Central Ground Water Authority
- National Water Development Agency
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Under Ramsar Convention, it is mandatory on the part of the Government of India to protect and conserve all the wetlands in the territory of India.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 were framed by the Government of India based on the recommendations of the Ramsar Convention.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 also encompass the drainage area or catchment regions of the wetlands as determined by the authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –GOVERNANCE
Context: The Inaugural session of the 17th Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) Annual Tourism Summit was held recently.
Background:-
- Addressing the inaugural session of the 17th CII Annual Tourism Summit held in Mumbai today, Ms V Vidyavathi said that we should be deliberating on how to reach this goal.
About the 17th Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) Annual Tourism Summit:
- Date: 13 October 2023.
- Venue: Mumbai.
- Theme: ‘Strengthening Tourism through Economic and Green Opportunities’.
- CII has organized the 17th CII Tourism Summit to bring together all stakeholders on one platform to discuss and deliberate the challenges and path forward.
- It was said that tourism is one of the largest service industries in India fuelling job creation.
- Several recommendations to the Ministry of Tourism were put forward.
- The Ministry was requested to bring mechanisms in place where licenses are given without any delays.
- The branding and promotion of Incredible India was advised to be done across the world and throughout the year on a continuous basis.
- It was emphasized that all stakeholders need to work together while balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability and create a tourism sector that is not only economically robust but also a model of responsible and green tourism.
About Confederation of Indian Industry (CII):-
- Establishment: 1895.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It is a non-government, not-for-profit, industry-led and industry-managed organization.
- Objectives: It works to create and sustain an environment conducive to the development of India, partnering with industry, Government, and civil society, through advisory and consultative processes.
Functions of CII:-
- To identify and strengthen the industry’s role in the economic development of the country. ( CII)
- To act as a catalyst in bringing about the growth and development of Indian Industry.
- To reinforce the industry’s commitment to society.
- To provide up-to-date information and data to industry and government.
- To create awareness and support the industry’s efforts on quality, environment, energy management, and consumer protection.
- To identify and address the special needs of the small sector to make it more competitive. (Cooperative Sector Reforms)
- To promote cooperation with counterpart organizations.
- To work towards the globalization of Indian industry and integration into the world economy.
MUST READ: Quality Council of India (QCI)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following heavy industries: (2023)
- Fertilizer plants
- Oil refineries
- Steel plants
Green hydrogen is expected to play a significant role in decarbonizing how many of the above industries?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
India accounts for 3·2% of the global export of goods.
Statement-II :
Many local companies and some foreign companies operating in India have taken advantage of India’s ‘Production-linked Incentive’ scheme.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Syllabus
- Prelims –IMPORTANT AWARDS
Context: Recently, the Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation launched the 5th National Water Awards 2023.
Background:-
- All the applications for the awards will be received through the online portal till 15th December.
About the 5th National Water Awards 2023:-
- First National Water Award: 2018.
- Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- The awards were introduced to recognize and encourage exemplary work and efforts made by States, Districts, individuals, and organizations, across the country in accomplishing the government’s vision of Jal Samridh Bharat.
- It aims to sensitize the public about the importance of water and motivates them to adopt the best water usage practices.
Objectives:-
- To encourage the stakeholders to adopt a holistic approach towards water resources management in the country.
- To create awareness among the people about the importance of water and attempt to motivate them to adopt the best water usage practices.
- Start-ups, leading organizations and people can engage, deliberate and strengthen existing partnerships on issues concerning water conservation and management activities.
Eligibility for the awards:-
- Any State, District, Village Panchayat, Urban Local Body, School/College, Institution (other than school/college), Industry, Civil society, Water User Association or an individual who has done exemplary work in the field of water conservation and management are eligible to apply.
Trophy and Citation:-
- For the categories – ‘Best State’ and ‘Best District’, winners will be felicitated with a trophy and citation.
- In the remaining categories – ‘Best Village Panchayat’, ‘Best Urban Local Body’, ‘Best School/College’, ‘Best Institution (other than school/college)’, ‘Best Industry’, ‘Best Civil Society’, ‘Best Water User Association’, ‘Best Industry’, and ‘Best Individual for excellence’ winners will be felicitated with cash prize along with trophy and citation.
- Cash prizes for the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd winners are 2 lakhs, Rs.1.5 lakhs, and Rs.1 lakh, respectively.
Selection Process:-
- All applications received for the National Water Awards are scrutinized by a Screening Committee of the DoWR, RD & GR.
- The shortlisted applications are placed before a Jury Committee headed by a retired Secretary level officer.
- Thereafter, ground truthing of the shortlisted applications is carried out by the organizations of DoWR, RD & GR viz. Central Water Commission (CWC) and Central Ground Water Board (CGWB).
- The Jury Committee evaluate the applications on the basis of reports of ground truthing and recommends the winners.
- The recommendations of the Committee are submitted to the Union Minister (Jal Shakti) for approval.
- The names of the winners are announced on a suitable date and an award distribution ceremony is organized.
Significance:-
- India has more than 18% of the world’s population, it has only 4% of the world’s renewable water resources. ( Water Crisis in India)
MUST READ: Rashtriya Puruskar Portal
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to green hydrogen, consider the following statements : (2023)
- It can be used directly as a fuel for internal combustion.
- It can be blended with natural gas and used as fuel for heat or power generation.
- It can be used in the hydrogen fuel cell to run vehicles.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) With reference to organic farming in India, consider the following statements: (2018)
- The National ‘Programme for Organic Production’ (NPOP) is operated under the guidelines and ‘directions of the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
- The Agricultural and Processed Food Product Export Development Authority ‘(APEDA) functions as the Secretariat for the implementation of NPOP.
- Sikkim has become India’s first fully organic State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: India’s first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy was approved recently.
Background:-
- For treating relapsed-refractory B-cell lymphoma and leukaemia, Mumbai-based Immunoadoptive Cell Therapy Private Limited (ImmunoACT) announced the approval of India’s first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) on October 13, 2023.
- Priorly, CAR-T cell therapy cost around $400,000 or over Rs 3.3 crore and patients could avail of it in the United States.
- With this development, the therapy will be accessible at 20 Indian government and private hospitals treating cancer across major cities at around Rs 30-35 lakh per patient.
About (CAR) T-cell therapy:-
- Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is a kind of cancer treatment that uses cells from your own immune system.
- It treats certain cancers by turning your T-lymphocytes or T-cells into more efficient cancer-fighting machines.
- CAR T-cell therapy is proving to be a very effective way of treating certain blood cancers.
Treatment Mechanism:-
- The blood is first drawn from the patient.
- Then, immune cells called T-cells are genetically modified in a laboratory.
- These modified T-cells are injected back into the patient to enable the cells to locate and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
Applications:-
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved several CAR T-cell therapies for people who have certain blood cancers that don’t respond to chemotherapy and other treatments. (National Cancer Registry Programme Report 2020)
- This therapy is also used to treat people who have blood cancer that returns after other successful treatments.
Challenges:-
- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS): This happens when CAR T-cells begin attacking cancer and trigger an immune response in your body.
- Brain and nervous system problems.
- Serious infections.
MUST READ: ICMR’s ‘Clinicopathological Profile of Cancers in India’ Report
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) ‘Microsatellite DNA’ is used in the case of which one of the following? (2023)
- Studying the evolutionary relationships among various species of fauna
- Stimulating ‘stem cells’ to transform into diverse functional tissues
- Promoting clonal propagation of horticultural plants
- Assessing the efficacy of drugs by conducting a series of drug trials in a population
Q.2) ‘Aerial metagenomics’ best refers to which one of the following situations? (2023)
- Collecting DNA samples from air in a habitat at one go
- Understanding the genetic makeup of avian species of a habitat
- Using air-borne devices to collect blood samples from moving animals
- Sending drones to inaccessible areas to collect plant and animal samples from land surfaces and water bodies
Syllabus
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
Context: Recent reports by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) show that farmers lost $3.8 trillion to disasters over 30 years.
Background:-
- An estimated $3.8 trillion worth of crops and livestock production has been lost due to natural disasters over the last 30 years, with Asia experiencing the largest share of the total economic losses, according to the report.
About the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO):-
- Founded: 1945 in Quebec City, Canada.
- Parent organization: United Nations Economic and Social Council.
- HQ: Rome, Italy.
- Motto: “Let there be bread”. (The millet mission)
- Members: With 195 members – 194 countries and the European Union, FAO works in over 130 countries worldwide.
- Objective: to achieve food security for all and make sure that people have regular access to enough high-quality food to lead active, healthy lives.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations.
- It leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. (FAO Food Price Index)
- Its sister bodies are the World Food Programme and the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD).
Flagship Publications:-
- The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA).
- The State of the World’s Forests (SOFO).
- The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI).
- The State of Food and Agriculture (SOFA).
- The State of Agricultural Commodity Markets (SOCO).
MUST READ: Food Security in India
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following trees : (2023)
- Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus.)
- Mahua (Madhuca indica)
- Teak (Tectona grandis)
How many of the above are deciduous trees?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Consider the following statements : (2023)
- Some mushrooms have medicinal properties.
- Some mushrooms have psychoactive properties.
- Some mushrooms have insecticidal properties.
- Some mushrooms have bioluminescent properties.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Green Methanol: India’s Future
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context:
- NITI Aayog has prepared a comprehensive plan advocating the adoption of methanol as the preferred cooking fuel in households as well as commercially.
- Blending 15% methanol in gasoline can result in at least a 15% reduction in the import of gasoline/crude oil.
About Green methanol:
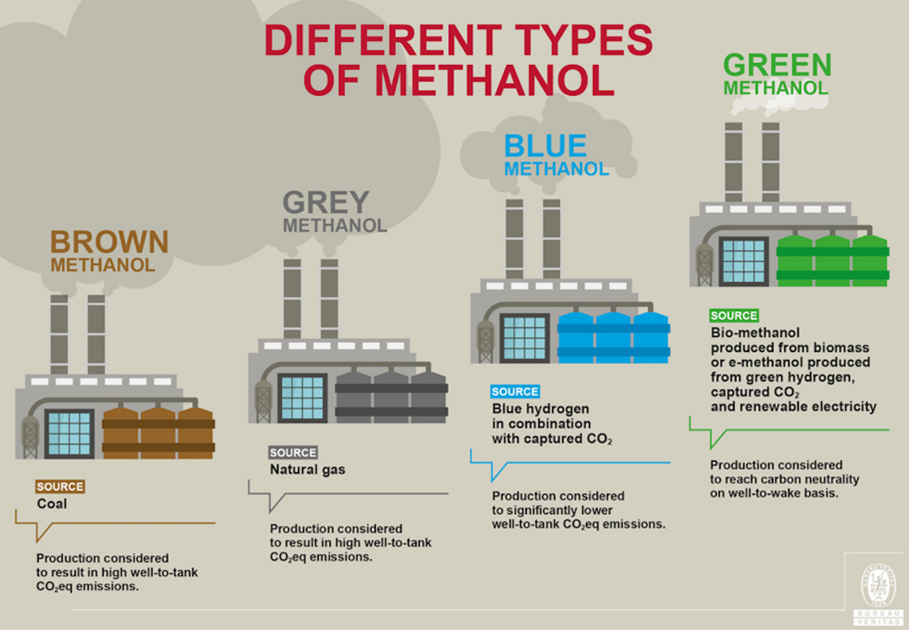
- It is a low-carbon fuel that can be made from either biomass gasification or renewable electricity and captured carbon dioxide (CO2).
- This chemical compound can be used as a low-carbon liquid fuel and is a promising alternative to fossil fuels in areas where decarbonisation is a major challenge, such as maritime transport.
Applications:
- As a fuel: It is often blended with gasoline to enhance combustion and reduce emissions.
- Green methanol, produced from renewable sources and without polluting emissions, serves as a low-carbon liquid fuel and is a promising alternative to fossil fuels, particularly in sectors like maritime transport.
- It’s also be used in the production of biodiesel.
- Alternative for renewable energy: Methanol can be produced from renewable sources like biomass and used as a potential energy carrier or fuel in fuel cells and other energy applications.
- Antifreeze: In automotive applications, particularly in windshield washer fluid, methanol is used as an antifreeze.
- Chemical Feedstock: Methanol is a crucial feedstock for the production of various chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, and methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE).
- Used as a Solvent: Methanol is a versatile solvent employed in various industrial processes, including chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and the production of paints, varnishes, and coatings.
Advantages of Methanol:
- Environmental Benefits: When produced from green hydrogen and with carbon capture technologies, methanol can contribute to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants.
- This makes it a more environmentally friendly option, particularly when used as a fuel or energy source.
- Lower Production Costs: Methanol can be produced at a lower cost compared to other alternative fuels, which makes it an economically viable option for various applications.
- Lower Flammability Risk: Methanol has a lower risk of flammability compared to gasoline, which can enhance safety in certain applications.
- Emission Control: By adding water to the combustion process, methanol can help meet stringent emission limits, such as the Tier III regulation for nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions.
- This makes it a useful choice in applications where emissions need to be controlled.
- High Octane and Horsepower: Methanol has the ability to produce high octane ratings and can deliver equivalent horsepower to super high-octane gasoline.
- This can make it a suitable option for high-performance engines.
- Versatile Use: Methanol can be used in various ways as an engine fuel, including in dedicated methanol engines, as part of binary and ternary alcohol blends (such as M15, M85, and M100).
- It is also suitable for use in shipping, aviation, fuel reforming using engine waste heat, and industrial electricity generation.
- Handling and Transportation: Methanol is relatively easy to handle and transport under normal temperatures and pressure conditions.
- It is also compatible with existing infrastructure, which simplifies its adoption in various industries.
The NITI Aayog’s ‘Methanol Economy’ program is a strategic initiative in India with several key objectives which includes:
- Reducing oil import: can be achieved by blending methanol with gasoline, which can result in a substantial reduction in the import of gasoline and crude oil.
- The use of methanol as a fuel can significantly lower GHG emissions compared to traditional fuels like gasoline and diesel.
- This reduction is estimated at 20% in terms of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and Sulfur oxides (SOx), which can lead to improved urban air quality.
- The program promotes the use of methanol in various sectors, including road transport, rail, marine, energy production (e.g., DG sets and boilers), tractors, commercial vehicles, and retail cooking.
- This diversification can enhance energy security by reducing reliance on a single type of fuel.
- The program aims to save consumers money by blending 20% Di-methyl Ether (DME), a derivative of methanol, in liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
- This blending can result in savings of Rs 50-100 per cylinder for consumers, making clean cooking fuel more affordable and accessible.
Challenges associated with India’s Methanol Economy:
- India has limited natural gas reserves and relies heavily on imports to meet its demand.
- Natural gas is the most economical and efficient feedstock for methanol production, but importing natural gas increases the cost and reduces the competitiveness of methanol.
- India lacks the necessary infrastructure for methanol production, distribution, storage, and utilization.
- India has a large and diverse population with different preferences and habits for energy consumption.
- There is a lack of awareness and acceptance among the public and stakeholders about the benefits and challenges of the methanol economy.
- India can invest in advanced technologies for coal and biomass conversion to methanol to reduce emissions and processing costs.
- Additionally, sourcing low-ash coal from other regions or countries may be considered.
Way Forward:
Therefore the solutions for the challenges posed by the India’s green methanol programme lies within the various stakeholders. These solutions require a concerted effort involving government agencies, industry players, and the public to overcome the challenges and promote the Methanol Economy in India.
Source: TH
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The World Mental Health Day is celebrated on October 10, focuses on the theme of ‘mental health as a universal human right.’
- One frequently disregarded group in discussions about mental health is informal workers.
About Mental Disorders:
- The WHO defines Mental Health as, Mental health is a state of mental well-being that enables people to cope with the stresses of life, realize their abilities, learn well and work well, and contribute to their community.
- It is an integral component of health and well-being that underpins our individual and collective abilities to make decisions, build relationships and shape the world we live in.
- Mental disorders include: depression, bipolar affective disorder, schizophrenia and other psychoses, dementia, intellectual disabilities and developmental disorders including autism.
State of Mental Health
- Globally: A study by the International Labour Organization (ILO) reveals that 15% of working-age adults worldwide live with a mental disorder.
- In India: The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that approximately 7.5% of Indians currently experience a mental disorder.
- Moreover, it is predicted that by the end of the year, this number will escalate to around 20%, indicating a significant mental health challenge in the country.
- A study by the India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative showed that the disease burden in India due to mental disorders increased from 2.5% in 1990 to 4.7% in 2017 in terms of DALYs1 (disability-adjusted life years), and was the leading contributor to YLDs (years lived with disability).
Determinants of Mental Health:
- Mental health is influenced by a complex interplay of social, psychological, and biological factors.
- Factors that cause mental illness: Factors such as violence, ongoing socio-economic pressures, especially related to sexual violence, are recognized as significant risks to mental well-being.
- Certain psychological traits and personality factors, along with genetic influences, can make individuals vulnerable to mental health issues.
Challenges faced by India’s Informal workforce:
- Gender Disparities: More than 95% of working women in India engage in precarious informal employment, enduring not only economic instability but also patriarchal social and familial structures that further impact their mental health.
- Absence of Protections: India’s informal workforce, constituting over 90% of the population, lacks regulatory protection, toiling in unsafe conditions with limited social and financial support, leading to increased mental health risks.
- Employment Challenges for the Elderly: Around 33 million elderly individuals work post-retirement in informal sectors, lacking financial and health security, exacerbating their vulnerability and affecting their mental health.
- Youth Unemployment: India faces high youth unemployment rates, contributing to significant mental health challenges among young individuals who often accept precarious work conditions due to desperation, further worsening their well-being.
Government of India Initiatives
- National Mental Health Programme (NMHP): NMHP ensures accessible mental healthcare, especially for vulnerable populations, addressing the mental health needs of the underprivileged.
- Mental Healthcare Act, 2017: This act decriminalized suicide attempts, incorporated WHO guidelines, introduced advanced directives, and restricted controversial treatments, focusing on destigmatizing mental health issues in society.
- Kiran: A 24/7 toll-free helpline called Kiran was established by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment in 2020 to offer support to those dealing with anxiety, stress, depression, suicide thoughts, and other mental issues.
- Tele-MANAS service: Comprehensive mental health care service.
Way Forward:
The World Mental Health Report 2022 highlights the importance of enhancing community-based care, focusing on people-centered, recovery-oriented, and human rights-based approaches. These proactive policies are necessary to enhance mental health awareness and interventions.
The efforts are crucial for safeguarding the fundamental human right to overall well-being, including mental health, and for progressing toward achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 3 concerning ‘good health and well-being,‘ and SDG 8, which emphasizes ‘decent work for all and economic growth.’
Source: TH
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| RAMSAR SITES | YEAR OF DESIGNATION |
| 1.Kolleru Lake | 1999 |
| 2.Kabartal Wetland | 2020 |
| 3.Sultanpur National Park | 2023 |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I :
First National Water Award was launched in 2015.
Statement-II :
The Cash prizes for the Fifth National Water Award 1st, 2nd, and 3rd winners are Rs.2 lakhs, Rs.1.5 lakhs, and Rs.1 lakh, respectively.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) With reference to the CAR T-Cell Therapy, consider the following statements:
- Brain and nervous system problems can be a side effect of this treatment.
- As per the mechanism the modified T-cells are injected back into the patient.
- It can be used to treat acute lymphocytic leukaemia in kids and young adults.
How many of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- and 3 only
- 2 only
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) Discuss the key objectives and potential benefits of India’s Methanol Economy Programme. (250 words)
Q.2) Analyse the effectiveness of Indian governmental initiatives in addressing mental health challenges among informal workers. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 14th October 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 13th October – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – c











