IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, NITI Aayog released the Export Preparedness Index 2022 report.
About Export Preparedness Index 2022 report:-
- Released by: Vice Chairman, NITI Aayog.
- This is the third edition of the Export Preparedness Index (EPI).
- EPI is a comprehensive tool which measures the export preparedness of the States and UTs in India. (UPSC CSE: Export Preparedness Index 2021)
Objectives of the report:–
- To present a comprehensive picture of a state’s and UT’s export preparedness.
- To highlight the achievements of states/UTs and encourage peer learning among the states/UTs.
- To uphold the spirit of competitive federalism.
Assessment Process:-
- EPI assess the performance of the States and UTs across four pillars – Policy, Business Ecosystem, Export Ecosystem, and Export Performance.
- Each pillar is composed of sub-pillars, which in turn capture a state’s performance using relevant indicators.
Policy Pillar
- It evaluates states’ and UTs’ performance based on its adoption of export-related policy ecosystem at a state and district level as well as the institutional framework surrounding the ecosystem.
Significance of the report:-
- It gives an overview of the country’s sector-specific export performance.
- It highlights the need to develop our districts as export hubs in the country and undertakes a district-level analysis of merchandise exports in the country.
- The index undertakes a comprehensive analysis of States and UTs across export-related parameters in order to identify their strengths and weaknesses.
Key Highlights of Export Preparedness Index 2022 report:-
- The report discusses India’s export performance amid the prevailing global trade context in FY22. (UPSC CSE: Export Preparedness Index 2020)
- The coastal states have performed well.
- Top performers: Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Gujarat.
- The higher average of coastal states represents their better preparedness and higher contribution to national export.
- 73 per cent of districts in the country have an export action plan, and over 99 per cent are covered under the One District One Product scheme.
- One District One Product scheme: The initiative aims to select, brand, and promote at least One Product from each District (One District – One Product) of the country for enabling holistic socioeconomic growth across all regions. (UPSC CSE: One District One Product(ODOP))
- It was launched by the Ministry of Food Processing Industries.
- 100 districts in the country are responsible for nearly 87 per cent of the country’s export.
- Lack of adequate transport connectivity: the report mentions that the absence of air connectivity hampers the movement of goods across regions especially in the landlocked states.
- Recommendations of the report:-
- For the states which are lagging in terms of export commission, the central government should extend support to enable them to build the necessary ecosystem to facilitate their export.
- Indian states need to invest in research and development for developing market-specific products and improving product quality.
MUST READ: India’s Agricultural and processed food products exports
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
India accounts for 3·2% of the global export of goods.
Statement-II:
Many local companies and some foreign companies operating in India have taken advantage of India’s ‘Production-linked Incentive’ scheme.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q.2) In the context of finance, the term ‘beta’ refers to (2023)
- the process of simultaneous buying and selling of an asset from different platforms ·
- an investment strategy of a portfolio manager to balance risk versus reward
- a type of systemic risk that arises where perfect hedging is not possible
- a numeric value that measures the fluctuations of a stock to changes in the overall stock market.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: As per the recent data of the Employees’ State Insurance Scheme (ESIC), more than 20 lakh new employees enrolled in ESI Scheme in May.
About Employees’ State Insurance Scheme (ESIC):-
- The Employees’ State Insurance Scheme (ESI)is an integrated measure of social Insurance embodied in the Employees’ State Insurance Act, of 1948. (UPSC CSE: ESIC)
- Implementing Agency: Employees’ State Insurance Corporation.
Applicability of ESI Scheme:-
- It applies to factories and other establishments Road Transport, Hotels, Restaurants, Cinemas, Newspaper, Shops, and Educational/Medical Institutions wherein 10 or more persons are employed.
- However, in some States threshold limit for coverage of establishments is still
Beneficiary Selection:-
- Employees of the aforesaid categories of factories and establishments, drawing wages up to Rs.15,000/- a month, are entitled to social security cover under the ESI Act.
- ESI Corporation has also decided to enhance the wage ceiling for coverage of employees under the ESI Act from Rs.15,000/- to Rs.21,000.
Coverage of the ESI Scheme:-
- 1952: In the beginning, the ESI Scheme was implemented at just two industrial centers in the country, namely Kanpur and Delhi
Funding of ESI Scheme:-
- The Employees’ State Insurance Scheme (ESI Scheme) is financed by contributions from employers and employees.
- The rate of contribution by employer is 3.25% of the wages payable to employees.
- The employees’ contribution is at the rate of 75% of the wages payable to an employee.
Employees’ State Insurance Corporation
- Establishment: 1952.
- It is a state-run organization set up under the Employee State Insurance Act of 1948.
- Objective: It is responsible for overseeing the ESI plan.
- Ministry: The Ministry of Labour & Employment.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Function: It provides socio-economic protection to the worker population and immediate dependent or family covered under the ESI scheme.
MUST READ: Finding Unemployment Benefits
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In India, which one of the following compiles information on industrial disputes, closures, retrenchments, and lay-offs in factories employing workers? (2022)
- Central Statistics Office
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade
- Labour Bureau
- National Technical Manpower Information System
Q.2) Consider the following statements with reference to India: (2023)
- According to the ‘Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006’, ‘medium enterprises are those with investments in plant and machinery between (‘ 15 crores and ’25 crore).
- All bank loans to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises qualify under the priority sector.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: Foreign Minister S. Jaishanker recently attended the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) retreat in Bangkok.
About the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC):-
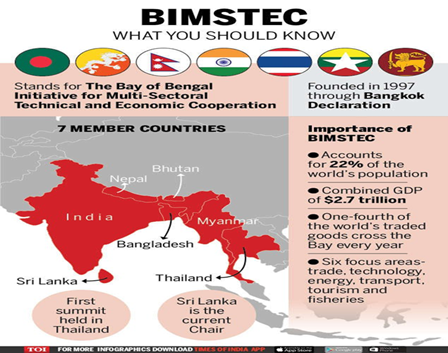
IMAGE SOURCE: IASBABA
- Establishment:1997. (UPSC CSE: BIMSTEC)
- HQ: Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- It is a regional organization that was established with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration.
- Initially known as BIST-EC (Bangladesh-India-Sri Lanka-Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- 1997: It was renamed ‘BIMST-EC’, following the inclusion of
- 2004: Bhutan and Nepal were admitted.
- Members: India, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Nepal and Sri Lanka.
- The BIMSTEC Charter was signed and adopted during the ‘Fifth BIMSTEC Summit’ held in the virtual format in Colombo, Sri Lanka, in 2022.
- Chairmanship-the Chairmanship of BIMSTEC rotates according to the alphabetical order of the English names of the Member States.
- India hosted the first meeting of Governing Board of BIMSTEC Energy Centre in Bengaluru in 2023.
Objectives of BIMSTEC:-
- To revive the Connectivity of the Bay of Bengal region.
- To revive the focus on Blue Economy.
- Bridge between two sub-regions: BIMSTEC not only connects South and South-East Asia but also the ecologies of the Great Himalayas and the Bay of Bengal.
Significance of BIMSTEC:-
- Major Shipping route: A fourth of the world’s traded goods cross the Bay of Bengal every year. (UPSC CSE: BIMSTEC & Maritime Protection)
- Huge Market: BIMSTEC grouping is home to around 1.5 billion people which constitute around 22% of the global population.
- High Growth Potential: With a combined gross domestic product (GDP) of 3.8 trillion economy, BIMSTEC member States have been able to sustain an average 6.5% economic growth trajectory in the recent past.
MUST READ: SAARC
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
The ‘Stability and Growth Pact’ of the European Union is a treaty that
- limits the levels of the budgetary deficit of the countries of the European Union
- makes the countries of the European Union share their infrastructure facilities
- enables the countries of the European Union to share their technologies
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
Context: Recently, Foreign minister of India co-chaired the 12th Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC) meeting in Bangkok along with Foreign Minister of Laos.
Background:-
- In his opening remarks at the 12th Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC) Mechanism meeting, the Foreign Minister said the lower Mekong region holds immense significance for India both in a historic sense and a contemporary one.
About Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC):-
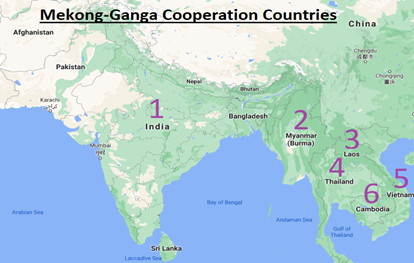
IMAGE SOURCE: buddyconcept.in
- Launched: 2000.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Naming: The organization takes its name from the Ganga and the Mekong, two large rivers in the region.
- The grouping was initially called Ganga Suvarnabhumi Programme (GMSP).
- Objective: Both the Ganga and the Mekong are civilizational rivers, and the MGC initiative aims to facilitate closer contact among the people inhabiting these two major river basins.
- Members: India and five ASEAN countries, namely, Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam
- Chairmanship: The MGC meetings are co-chaired alternatively every year between India and one of the 5 Mekong countries.
Areas of Cooperation:-
- Four foundational areas of cooperation: tourism, culture, education, and transport & communication.
- It has further expanded to include new areas like health and traditional medicine, agriculture and allied sectors, small and medium enterprises, water resources management, science and technology, skill development, and capacity building.
Ministerial meeting:-
- 1st MGC Ministerial meeting: Vientiane,2000.
- 12th MGC Ministerial meeting: Thailand, 2023. (UPSC CSE: BRICS – 14th Summit)
MUST READ: India-Vietnam relations
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Recently, all the countries of the United Nations have adopted the first-ever compact for international migration, the ‘Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration (GCM)’.
- The objectives and commitments stated in the GCM are binding on the UN member countries.
- The GCM addresses internal migration or internally displaced people also in its objectives and commitments.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) In the Mekong-Ganga Cooperation, an initiative of six countries, which of the following is/are not a participant/ participants? (2015)
- Bangladesh
- Cambodia
- China
- Myanmar
- Thailand
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1 and 3
- 1, 2 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, a Tigress was spotted with three cubs in Ramgarh Visdhari Reserve (RVTR).
About Ramgarh Visdhari Reserve:-
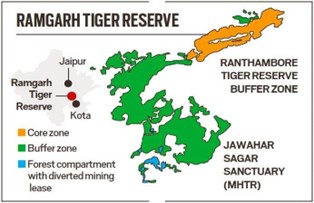
IMAGE SOURCE: firstpost.com
- Location: Bundi, Rajasthan.
- 1982: The area was declared a sanctuary
- 2022: Became a tiger reserve.
- It is Rajasthan’s fourth tiger reserve after Ranthambore, Sariska and Mukundra. (UPSC CSE: Indravati Tiger Reserve)
- Vegetation: It comprises hilly dry deciduous forests on Vindhyan formations.
- Flora: Mango, Dhok, Khair and Salar.
- Fauna: It is home to a large number of wild animals such as the Indian Wolf, leopard, striped hyena, sloth bear, golden jackal, chinkara, nilgai and fox.
- Important Historical and cultural sites: Bhimlat, Ramgarh Palace, etc.
Significance of the creation of Ramgarh Vishdhari tiger reserve:-
- While Ramgarh doesn’t have a high tiger population, it plays a critical role in the movement of tigers.
- The newly created tiger reserve will connect the Ranthambore Tiger Reserve in Sawai Madhopur district in the northeast with the Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve in the Kota district on the southern side. (UPSC CSE: Valmiki Tiger Reserve)
- This reserve will also help control overpopulation and the consequent effect of overcrowding in Ranthambore.
MUST READ: Cheetahs and Others: know the 7 big cats
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements : (2023)
- In India, the Biodiversity Management Committees are key to the realization of the objectives of the Nagoya Protocol.
- The Biodiversity Management Committees have important functions in determining access and benefit sharing, including the power to levy collection fees on the access of biological resources within its jurisdiction.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) In which one of the following states is Pakhui wildlife sanctuary located? (2018)
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Nagaland
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, North Korea tested its latest intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) named Hwasong-18.
About Hwasong-18:-
- Developed by: Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) or North Korea.
- Tested in
- It is a type of solid-fuel intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM)
- ICBM: a long-range (greater than 5,500 km or 3,500 miles) ballistic missile typically designed for nuclear weapons delivery, that is, delivering one or more nuclear warheads.
- It is North Korea’s first ICBM to use solid fuel.
- Solid propellants can fire faster and accelerate more quickly at liftoff.
- It allows for faster launches.
- It is part of North Korea’s missile program and is believed to have a range capable of reaching targets beyond the Korean Peninsula.
Significance of the launch:-
- The development and potential deployment of the Hwasong-18 missile by North Korea raises concerns among the international community due to its long-range capability and the potential threat it poses to regional and global security.
- North Korea’s state media claimed that the latest test fire was conducted according to the “strategic judgement of the Central Military Commission of the Workers’ Party of Korea, at a grave period when the military security situation on the Korean peninsula. (UPSC CSE: Tension in Korean Peninsula)
- It also showed suspicion about the Washington Declaration, an agreement that was signed recently between US President Biden and South Korea’s President Yoon Suk-yeol during a bilateral meeting to mark 70 years of the US-South Korea alliance to be a cause of future nuclear engagement against it. North Korea.
- The country’s media thus claims that the test was conducted as part of the efforts to bolster the legitimate right to self-defense to reliably defend the security of the state and regional peace.
MUST READ: North and South Korea found guilty of violating armistice agreements
SOURCE: INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following countries: (2023)
- Bulgaria
- Czech Republic
- Hungary
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Romania
How many of the above-mentioned countries share a land border with Ukraine?
- Only two
- Only three
- Only four
- Only five
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Ballistic missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flights, while cruise missiles are rocket-powered only in the initial phase of flight.
- Agni-V is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile, while BrahMos is a solid-fuelled intercontinental ballistic missile.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Lightning as a ‘Natural Disaster’
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Disaster Management)
Context: The Union government is not in favour of declaring lightning a natural disaster as deaths caused by it can be prevented by making people aware of safety steps.
About Lightning:
- It is the natural process of “an electrical discharge of very little duration and high voltage between a cloud and the ground or within a cloud,” accompanied by a bright flash, a loud sound, and occasionally thunderstorms.
- Cloud-to-ground (CG) lightning is dangerous because it can electrocute people due to its high electric voltage and current.
- Inter- or intra-cloud lightning is visible and safe.
Process of Lightning:
- Lightning is caused by a difference in electrical charge between the top and bottom of a cloud, which generates a huge current of electricity.
- Water vapor in the cloud condenses and rises, generating heat and pushing water molecules further up until they become ice crystals.
- Collisions between the ice crystals trigger the release of electrons, leading to a chain reaction that results in a positively charged top layer and negatively charged middle layer in the cloud.
- When the difference in charge becomes large enough, a huge current of electricity flows between the layers, producing heat that causes the air column to expand and produce shock waves that create thunder sounds.
Lightening cases in India:
- India is among only five countries in the world that has an early warning system for lightning. The forecast is available from five days to up to three hours.
- However, lightning strikes are not currently covered under the State Disaster Response Fund, which means that states have to use their own resources to respond to lightning-related disasters.
- National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data show that 2,880 people died in lightning strikes in 2021.
- The deaths made up 40% of all accidental deaths caused by forces of nature.
- The frequency of lightning was the highest in northeastern States and in West Bengal, Sikkim, Jharkhand, Odisha and Bihar.
- However, the number of deaths is higher in the central Indian States of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh and Odisha.
Demands for covering it as natural disaster:
- The States such as Bihar and West Bengal have been demanding that lightning deaths be covered as a natural disaster.
Significance:
- Once this is notified, the victims will be entitled to compensation from the State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF).
- Cyclone, drought, earthquake, fire, flood, tsunami, hailstorm, landslip, avalanche, cloudburst, pest attack, frost and cold wave are now considered disasters under the SDRF.
Major Causes of lightning:
- Lightning is an electrical discharge caused by imbalances between storm clouds and the ground, or within the clouds themselves.
- During a storm, colliding particles of rain, ice, or snow inside storm clouds increase the imbalance between storm clouds and the ground, and often negatively charge the lower reaches of storm clouds.
- Objects on the ground, like steeples, trees, and the Earth itself, become positively charged creating an imbalance that nature seeks to remedy by passing current between the two charges.
- This heat causes surrounding air to rapidly expand and vibrate, which creates the pealing thunder heard a short time after seeing a lightning flash.
- When the positive and negative charges grow large enough, a giant spark – lightning – occurs between the two charges within the cloud.
- Most lightning happens inside a cloud, but sometimes it happens between the cloud and the ground.
- A build-up of positive charge builds up on the ground beneath the cloud, attracted to the negative charge in the bottom of the cloud and the ground’s positive charge concentrates around anything that sticks up – trees, lightning conductors and even people.
- The positive charge from the ground connects with the negative charge from the clouds and a spark of lightning strikes.
Impacts of lightning:
Impact on rural areas:
- Mainly, rural and forest areas are the most vulnerable due to lighting because of the presence of water bodies and tall trees and almost 96 percent of deaths occurred in rural areas due to lightning compared to the urban area.
- Regarding deaths due to lightning, the population in rural areas is more vulnerable than in urban areas.
Impact on farmers:
- Frequent lightning strikes adversely affect small and marginal farmers.
- Around 77 percent of farmers are killed due to lightning as they work in agricultural fields during the Kharif cropping season in the monsoon period.
Impact on tribal population:
- The Annual Lightning Report 2020-2021 has confirmed that 60-70 percent of deaths occurred in tribal populations due to lightning in Jharkhand, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, and other states.
Way Forward
- Early Warning Systems: To warn people of impending thunderstorms and lightning strikes, India should invest in early warning systems.
- Weather radar, lightning detection networks, and smartphone applications are a few examples of these systems.
- Lightning Safety Measures: It is important to inform India’s rural communities about quick and easy lightning safety precautions.
- This can involve putting lightning rods on homes, staying indoors during thunderstorms, and taking cover in secure structures.
- Research and Development: To better understand lightning and discover creative ways to lower the risk, the Indian government should support research and development projects.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Science and Technology)
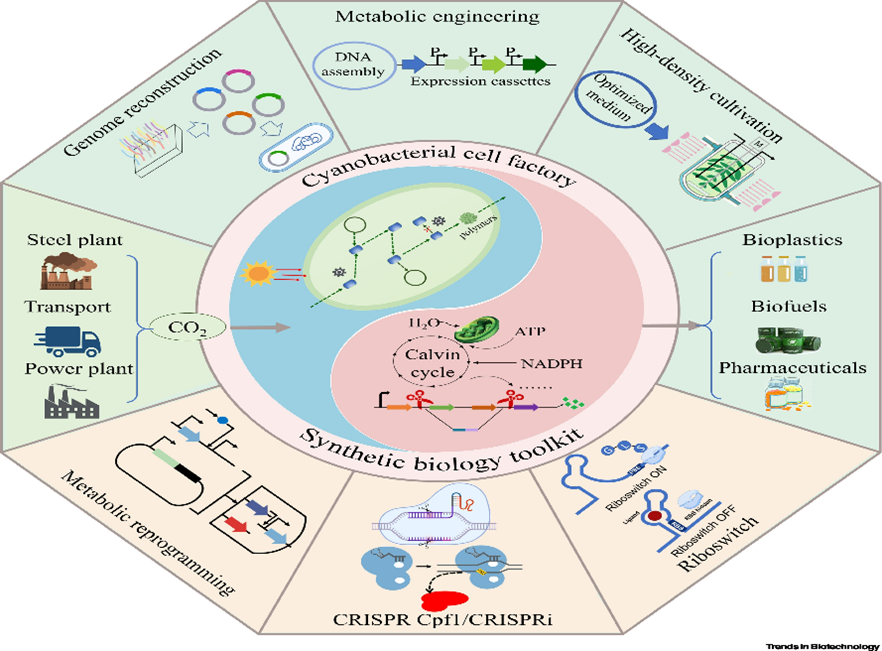
Context: A new field of science has been emerging called synthetic biology.
About Synthetic Biology:
Source: cell.com
- Synthetic biology refers to the science of using genetic sequencing, editing, and modification to create unnatural organisms or organic molecules that can function in living systems.
- Synthetic biology enables scientists to design and synthesize new sequences of DNA from scratch.
- The term ‘synthetic biology’ was first used by Barbara Hobomin in 1980, to describe bacteria that had been genetically engineered using recombinant DNA technology.
- Synthetic biology was initially synonymous with ‘bioengineering’.
- In 2000, the term ‘synthetic biology’ was again introduced by Eric Kool and other speakers at the annual meeting of the American Chemical Society in San Francisco.
Applications of Synthetic Biology:
- Standardised Biological Parts: identify and categorize standardized genomic parts that can be used (and synthesized quickly) to build new biological systems.
- Applied Protein Design: Redesign existing biological parts and expand the set of natural protein functions for new processes.
- For e.g., Modified rice to produce beta-carotene (a nutrient usually associated with carrots), that prevents Vitamin A deficiency.
- Natural Product Synthesis: Engineer microbes to produce all of the necessary enzymes and biological functions to perform complex multistep production of natural products.
- For e.g., Microorganisms harnessed for bioremediation (use of living microorganisms to degrade environmental contaminants into less toxic forms) to clean pollutants from water, soil and air.
- Synthetic Genomics: Design and construct a ‘simple’ genome for a natural bacterium.
- For e.g., Yeast engineered to produce rose oil as an eco-friendly and sustainable substitute for real roses that perfumers use to make luxury scents.
Concerns related to the synthetic biology
Economic concerns:
- It can create a huge surge in the economy causing a shift towards biotechnology-based economies.
- This will mostly affect the rural economy and low-income tropical countries.
- Natural products are usually grown and harvested in low-income countries and this could be displaced by advancements in synthetic biology.
Environmental concerns:
- When a new species is created or when a species is intensely modified, the activity of species and their coexistence with other organisms is mostly unpredictable.
Ethical Concerns:
- The scientists would go in and edit the genes of human embryos, removing genetic material that codes for harmful or fatal diseases, creating genetically modified humans, and genetically engineering humans could accidentally give rise to new social inequalities.
Regulation:
- Robust and independent regulation is key; the public did not trust a voluntary or self-regulation system.
- International co-ordination and regulation to control technology development in global markets is a major challenge.
Indian regulatory system related to synthetic biology:
- Drugs and Cosmetics Rules – 1988,
- Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Act, 2001,
- Biological Diversity Act, 2002
- Food Safety and Standards Act 2006
Way Forward:
Synthetic Biology offers innovative approaches for engineering new biological systems or re-designing existing ones for useful purposes. To achieve the UN Sustainable Development Goals, there is a need to think innovatively and synthetic biology could full fill the SDG target. The need of the hour is to ecological balance and cut down pollution and plastic waste from our industrial processes and day-to-day activities.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Employees’ State Insurance Scheme (ESI) covers maternity and disability benefits.
Statement-II:
The scheme is financed by contributions from employers and employees.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Ramgarh Visdhari Reserve (RVTR) is the third Tiger reserve in Rajasthan.
Statement-II:
Its vegetation comprises hilly dry deciduous forests on Vindhyan formations.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following pairs:
Declaration International Grouping
- Fortaleza Declaration: BRICS
- Vientiane Declaration: BIMSTEC
- Bangkok Declaration: ASEAN
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- None
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) Synthetic biology had been emerging as an advanced technology at the heart of the bio economy, capable of delivering new solutions to global healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and environment. In this context, critically evaluate the potential benefits associated challenges. (250 Words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 18th July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 17th July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) -a














