IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Art and Culture
Context: Recently, President Droupadi Murmu greeted people on the occasion of Buddha Purnima.
About Buddha Purnima:-
- Buddha Purnima is celebrated to mark the birth of Gautam Buddha, the founder of Buddhism.
- It is also known as Vesak.
- In 1999, it became an UN-designated day, to acknowledge the contribution of Buddhism to society.
- It is believed that this was also the day he attained enlightenment.
- It is considered a ‘triple-blessed day’ as it is Tathagata Gautam Buddha’s birth, enlightenment, and Maha Parnirvana.
- Buddha Purnima falls on a full moon night, usually between April and May.
- It is a gazetted holiday in India.
- Many devotees visit Mahabodhi Temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, located in Bodh Gaya, Bihar, on this occasion.
- Bodhi Temple is the location where Lord Buddha is said to have attained enlightenment.
About Budhha:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Karma Buddhism | Does Buddhism Believe in Karma | TheMindFool
- Siddhartha Gautama, or Buddha was a spiritual leader and the founder of Buddhism. (UPSC MAINS: Wisdom of the Buddha)
- He lived from 563 B.C. to 483 B.C.
- He was born in the Shakya clan in Lumbini, Kapilvastu, Nepal.
- At the age of 29, he abandoned his home and began to live as a homeless ascetic and practised rigorous meditation for a year.
- At the age of 49, he sat down under a Pipal tree at Bodhgaya (present-day Bihar), where he finally attained Nirvana (perfect enlightenment) and came to be known as the Buddha.
- Buddha gave his first sermon in Sarnath. (UPSC PRELIMS: The Buddhist Circuit)
- This is called Dhammacakkappavattana (turning off the wheel of law).
- Buddha passed away in 483 BCE at Kushinagara, Uttar Pradesh.
- This event is termed
- Five forms that represent Buddha are:-
- Lotus and Bull – Birth
- Horse – Renunciation
- Bodhi Tree – Mahabodhi
- Dhamma Chakra Pravartana – First sermon
- Footprints – Nirvana
- Three pillars of his teachings are:-
- Buddha – Founder/Teacher
- Dhamma – Teachings
- Sangha – Order of Buddhist Monks and Nuns
- Eight-Fold Paths:-
- Right Vision (Samma-Ditthi)
- Right Thought or Attitude (Samma-sankappa)
- Right or Whole Speech (Samma-Vacca)
- Right or Integral Action (Samma-Kammanta)
- Right or Proper Livelihood (Samma-Ajiva)
- Right Effort or Energy (Samma-Vayama)
- Right Mindfulness (Samma-Sati) or Thorough Awareness (Samma-Sati)
- Right Concentration (Samma-Samadhi)
Buddhist Councils:-
- 1st Council
- Year: 483 BC
- Venue : Saptaparni Cave, Rajgir
- Chairman :Maha Kassapa
- King: Ajatshatru
- Key Developments : Sutta & Vinaya Pitaka compiled
- 2nd Council
- Year: 383 BC
- Venue: Vaishali
- Chairman : Sabakami
- King: Kalasoka
- Key Developments: Monks got split into Sthavir Madins & Mahasanghikas
- The dispute arose over the ‘Ten Points During the 2nd Buddhist Council:
- 3rd Council
- Year: 250 BC
- Venue: Pataliputra
- Chairman : Mogalliputta Tissa
- King: Ashoka
- Key Developments: Abhidhammapitaka compiled
- 4th Council
- Year: 72 AD
- Venue: Kundalvan, Kashmir
- Chairman: Vasumitra & Ashvaghosha
- King: Kanishka
- Key Developments: Buddhists got split into Hinayana & Mahayana
- Buddhist Literature
- Tripitaka or three baskets include the prominent Buddhist scriptures.
- Others include Jatakas, Mahavamsa, Bodhi Vamsa.
- Tripitakas
- Vinaya Pitaka: Contains monastic rules of conduct for monks.
- Sutta Pitaka: This scripture describes the first Buddhist council.
- Abhidhamma Pitaka: It is a detailed scholastic analysis and summary of the Buddha’s teachings.
- Milinda Panha
- It is a dialogue between Indo-Greek king Meander and Buddhist monk
- Written in Pali
- Dipavamsa
- It deals with the arrival of Buddha‘s teaching and preachers in Sri Lanka.
- Written in Pali
- Mahavamsa
- It deals with the royal dynasties of the Indian subcontinent.
- The consecration of Asoka and details of Selucus and Alexander have been detailed in it.
- Buddha Charita
- It is an epic poem on the life of Buddha
- It is written in
- It was written by a Buddhist philosopher Ashwaghosha who was a member of King Kanishka’s court.
MUST READ: Neo-Buddhism
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the religious history of India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- Sthaviravadins belong to Mahayana Buddhism
- The Lokottaravadin sect was an offshoot of the Mahasanghika sect of Buddhism
- The deification of Buddha by Mahasanghikas fostered Mahayana Buddhism
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the cultural history of India, consider the following pairs:
- Parivrajaka — Renunciant and Wanderer
- Shramana — Priest with a high status
- Upasaka — Lay follower of Buddhism
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: The penumbral lunar eclipse was observed recently.
About the Penumbral lunar eclipse:-
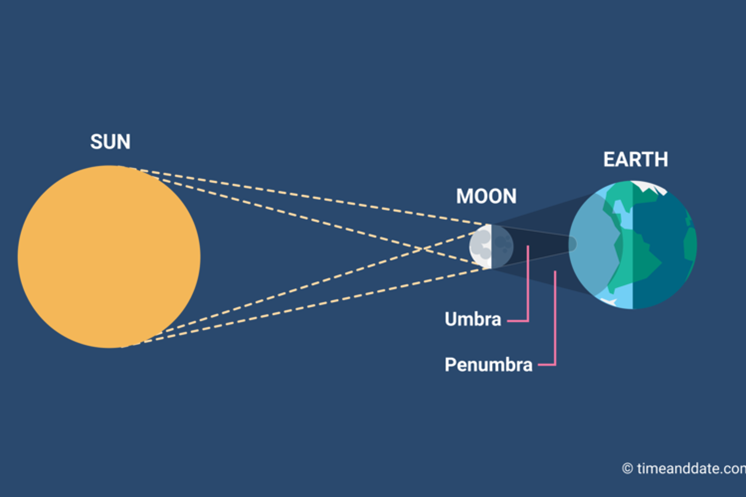
IMAGE SOURCE: Eclipse Shadow: What Is the Penumbra? (timeanddate.com)
- An eclipse happens when a planet or a moon gets in the way of the sun’s light. (UPSC PRELIMS: Eclipses )
- The lunar eclipse is a celestial phenomenon where the sun, moon, and earth come in a straight line.
- In the Lunar Eclipse, the Earth arrives in between the sun and the moon.
- In this way, the shadow of the earth falls on the moon.
- The lunar eclipse can only happen during the Full Moon.
- But, the orbits of the moon and earth are different.
- That’s why the lunar eclipse happens only up to 3-4 times a year.
- There are three types of lunar eclipses:-
- Total lunar eclipses, partial lunar eclipses, and penumbral lunar eclipses. (UPSC PRELIMS: Beaver blood moon)
- A penumbral lunar eclipse happens when the moon moves through the outermost region of the Earth’s shadow known as the penumbra.
- Penumbra: the lighter outer part of a shadow.
- The Moon’s penumbra causes partial solar eclipses, and the Earth’s penumbra is involved in penumbral lunar eclipses.
- During this event, the moon appears slightly darker than usual.
- Since the penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when the moon stands in the penumbral shadow. Thus, it is not very visible.
MUST READ: Supermoon
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the northern hemisphere, the longest day of the year normally occurs on the: (2022)
- The first half of the month of June
- The second half of the month of June
- The first half of the month of July
- The second half of the month of July
Q.2) On 21st June, the Sun (2019)
- does not set below the horizon at the Arctic Circle
- does not set below the horizon at Antarctic Circle
- shines vertically overhead at noon on the Equator
- shines vertically overhead at the Tropic of Capricorn
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the RBI and Bank for International Settlements (BIS) launched the G20 TechSprint.
About G20 TechSprint:-
- G20 TechSprint is a global technology competition. (UPSC PRELIMS: India and G20 Presidency)
- The fourth and 2023 TechSprint is a joint initiative between the BIS Innovation Hub and the Reserve Bank of India.
- It will focus on three problem statements on cross-border payments formulated by the RBI and the BIS Innovation Hub. (UPSC CSE: Restoring Cross Border Mobility by WEF’s Common Trust Network )
- Technology solutions: to reduce illicit finance risk around anti-money laundering, countering the financing of terrorism and sanctions.
- Foreign exchange and liquidity technology solutions: to enable settlement in emerging markets and developing economy currencies.
- Technology solutions for multilateral cross-border central bank digital currency platforms. (UPSC PRELIMS: Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC))
- The competition is open for developers around the world.
- The shortlisted teams will be invited to develop their solutions over a six-week period.
- Each team will be eligible for a stipend of eight lakh rupees approximately 10,000 US dollars.
- An independent panel of experts will select the most promising solution to each problem statement from the shortlisted solutions.
- The winners for each problem statement will receive an award of forty lakh rupees approximately 50,000 US dollars.
MUST READ: Unified Payments Interface
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the “G20 Common Framework”, consider the following statements: (2022)
It is an initiative endorsed by the G20 together with the Paris Club.
It is an initiative to support Low-Income Countries with unsustainable debt.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding Smart India Hackathon 2017? (2017)
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme for developing every city in our country into Smart Cities in a decade.
- It is an initiative to identify new digital technology innovations for solving the many problems faced by our country.
- It is a programme aimed at making all the financial transactions in our country completely digital in a decade.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, the Supreme Court agreed to examine the validity of the practice of talaq-e-Hasan.
About Talaq-e-hasan:-
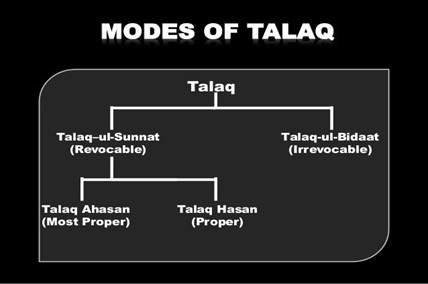
IMAGE SOURCE: TALAQ AND TALAQ E TAFWEEZ (slideshare.net)
- Talaq-e-Hasan is a form of ‘triple talaq’. (UPSC CSE:Personal Laws in Marriage)
- Under this, a Muslim man can divorce his wife by pronouncing ‘talaq’ at three separate intervals.
- The gap is at least one month or one menstrual cycle.
- According to Sharia or the Muslim personal law, men are allowed to practice polygamy that is, they can have more than one wife at the same time, up to a total of four. (UPSC PRELIMS: Uniform Civil Code)
- Nikah halala is a process in which a Muslim woman has to marry another person and get divorced from him before being allowed to marry her divorcee husband again.
- Triple talaq allows a husband to divorce his wife by repeating the word “talaq” (divorce) three times in any form, including email or text message.
- In Islam, talaq and khula are two terms for divorce for men and women respectively.
- A man can part ways through ‘talaq’ while a woman can separate from her husband through ‘Khula’.
MUST READ: Religion and Indian Constitution
SOURCE: THE TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The mind of the makers of the Constitution of India is reflected in which of the following? (2017)
- The Preamble
- The Fundamental Rights
- The Directive Principles of State Policy
- The Fundamental Duties
Q.2) Which one of the following objectives is not embodied in the Preamble to the Constitution of India? (2017)
- Liberty of thought
- Economic liberty
- Liberty of expression
- Liberty of belief
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: The stock price of Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL) doubled in the last two months.
About Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL):-
- RVNL is a Central Public Sector Enterprise.
- It works under the Ministry of Railways. (UPSC PRELIMS: Rail Development Authority)
- It was established in 2003 to implement railway infrastructure projects and raise extra-budgetary resources for Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs). (UPSC MAINS: Development of railways by the British)
- RVNL began operations in 2005.
- It is responsible for undertaking Rail project development and execution of works, creating project-specific SPVs, and handing over completed railway projects to the relevant Zonal Railway for operation and maintenance.
- RVNL was granted Mini-Ratna status in 2013.
- It has now been granted Navratna status.
MUST READ: Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana
SOURCE: BUISINESS LINE
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements : (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Recognition of Prior Learning Scheme’ is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to (2017)
- Certifying the skills acquired by construction workers through traditional channels.
- Enrolling the persons in Universities for distance learning programmes.
- Reserving some skilled jobs to rural and urban poor in some public sector undertakings.
- Certifying the skills acquired by trainees under the National Skill Development Programme.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recent studies suggest that King Cobra may be under-threat in India.
About King Cobra:-
- They are one of the most venomous snakes on the planet.
- It is also the longest of all venomous snakes.
- The venom is not the most potent among venomous snakes, but the amount of neurotoxin they can deliver in a single bite up to two-tenths of a fluid ounce is enough to kill 20 people or even an elephant.
- They are the only snakes in the world that build nests for their eggs, which they guard ferociously until the hatchlings emerge.
- Habitat:-
- They live mainly in the rainforests and plains of India, southern China, and Southeast Asia.
- They are comfortable in a variety of habitats, including forests, bamboo thickets, mangrove swamps, high-altitude grasslands, and in rivers.
Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable.
- CITES: Appendix II. (UPSC PRELIMS: CITES COP19)
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule II. (UPSC PRELIMS: Wildlife Protection)
MUST READ: (Mangrove Breakthrough )
SOURCE: INDIA TODAY
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following is not a bird? (2022)
- Golden Mahseer
- Indian Nightjar
- Spoonbill
- White Ibis
Q.2) With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements : (2022)
- Wild animals are the sole property of the government.
- When a wild animal is declared protected, such animal is entitled to equal protection whether it is found in protected areas or outside.
- Apprehension of a protected wild animal becoming a danger to human life is sufficient ground for its capture or killing.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Art and Culture
Context: Recently, Mridangam artiste, Karaikudi Mani, passed away.
About Mridangam:-
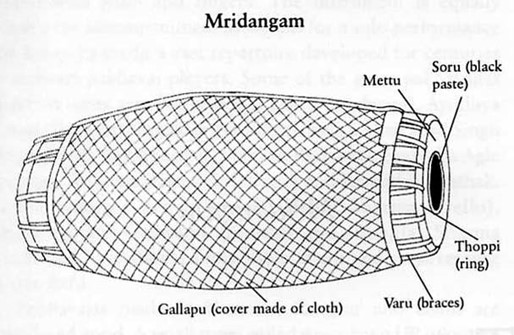
IMAGE SOURCE: Mridangam – India Instruments (India-instruments.de)
- The mridangam is the classical drum of South Indian music.
- It is also known by the name of medal or maddalam.
- It is one of the oldest Indian percussion instruments, originating 2,000 years ago.
- This traditional instrument is found in various parts of South India.
- The body of the mridangam is scooped out of a single block of wood.
- Jackwood or redwood is the ideal choice of mridangam makers, but the wood of the morogosa tree or the core of the coconut tree and the palm tree is also used for this purpose.
- It is a popular bifacial drum of Carnatic music and is used as an accompaniment in South Indian Classical music. (UPSC MAINS: Most recurring themes of Indian music)
- A similar instrument, the pakhavaj, is played in the Hindustani tradition of northern India, as well as in Pakistan and Bangladesh. (UPSC MAINS: gharana tradition’ in Hindustani music)
MUST READ: Thirukokarnam Ranganayaki Ammal
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the cultural history of India consider the following statements (2018)
- Most of the Tyagaraja Kritis are devotional songs in praise of Lord Krishna
- Tyagaraja created several new fits of rage
- Annamacharya nad Tyagaraja are contemporaries
- Annamacharya kirtanas are devotional songs in praise of Lord Venkateshwara
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) With reference to Manipuri Sankirtana, consider the following statements: (2017)
- It is a song and dance performance
- Cymbals are the only musical instruments used in the performance
- It is performed to narrate the life and deeds of Lord Krishna
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the cash-strapped no-frills carrier Go Airlines (India) Ltd (Go First), said that it was filing for voluntary insolvency proceedings with the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)
About Voluntary insolvency proceedings:-
- The Process of Voluntary Winding up of a solvent company is now shifted from the Companies Act,
- 2013 to Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 w.e.f. 1st April 2017.
- The shifting of Jurisdictional Authority from the High Court to NCLT will result in faster execution.
- The settlement of cases since Insolvency Professionals have been bestowed with powers for completing the winding-up process and reporting to NCLT. (UPSC PRELIMS: National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT))
- With the passing of a special resolution at the Member’s meeting and declaration of solvency.
- An applicant can commence with the winding up proceedings
- Section 59 (3) (c) of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 says:- (UPSC MAINS: Insolvency & Bankruptcy: Issues & Way forward)
- Within 4 weeks of the Declaration of Solvency Voluntary Winding up of the Company and
- Appointment of an Insolvency Professional to act as Liquidator subject to the approval of the
- Members in General Meetings through Special
- Resolution:-
- To pass the Special Resolution for Voluntary
- Winding up and Appointment of Insolvency
- Professional to act as a Liquidator.
MUST READ: Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Bill, 2020
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In India, which one of the following compiles information on industrial disputes, closures, retrenchments and lay-offs in factories employing workers? (2022)
- Central Statistics Office
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade
- Labour Bureau
- National Technical Manpower Information System
Q.2) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Retail investors through Demat account can invest in Treasury Bills and Government of India Debt Bonds in the primary market
- The “Negotiated Dealing System-Ordering Matching” is a government securities trading platform of the Reserve Bank of India.
- The “Central Depository Services Ltd” is jointly promoted by the Reserve Bank of India and the Bombay Stock Exchange.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
- 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently, Maharashtra has launched Aspirational Cities Programme (ACP) modelled on the Aspirational District Programme of the NITI Aayog.
About Urbanization:
- Urbanization refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change.
- It is the process through which cities grow as higher percentages of the population come to live in the city.
Classification:
- Urban area or Census Town: A habitation is declared urban (excluding a municipality, corporation, cantonment board and a notified town area committee) if it has
- a minimum population of 5,000;
- at least 75 per cent of the male working population in non-agricultural pursuits;
- population density is at least 400 people per sq km
- Metropolitan City: As per census are those Indian cities having a population of more than 4 million.
- Metropolitan Area: As per 74th Amendment 1992, is an area specified by the Governor by public notification to be a Metropolitan area having
- a population of 10 Lakh or 1 Million or more,
- comprised in one or more districts and
- consisting of two or more Municipalities or Panchayats or other contiguous areas,
- Urban Agglomeration: As per Census, is a continuous urban spread constituting a town and its adjoining outgrowths (OGs) or two or more physically contiguous towns together with or without outgrowths of such towns.
Urban population of India:
- According to the Census of India 2011, the urban population of India was 377 million, which accounted for 31.16% of the total population.
- Around 590 million people would live in the cities by 2030.
- According to Mckinsey Global Institute study in 2010, Indian cities having only 3% of the land could generate
- 70 percent of net new jobs
- Around 70 percent of Indian GDP
- Near fourfold increase in per capita incomes
- Urban population will soar from 340 million in 2008 to 590 million in 2030, half the time taken before 2008.
- India needs to invest $1.2 trillion just in capital expenditure in its cities over the next 20 years, nearly eight times of today’s expenditure.
- The World Urbanization Prospects, 2018 report of UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) notes that India, China and Nigeria will account for 35% of the projected global urban population growth and by 2050, India will have added 416 million urban dwellers.
Current process of “urbanisation” and urban growth in India
- India is rapidly urbanising and is estimated to host 50 per cent of its population in cities by 2050.
- India is witnessing one of the largest urban growth spurts in history.
- This presents Indian cities with an unprecedented opportunity to look at urban planning and development through a long-term strategic lens to enable economic, environment and social impact.
Challenges of urbanization in Maharashtra
- Deficient Infrastructure: Maharashtra’s cities are grappling with issues of deficient infrastructure, such as inadequate roads, public transport, water supply, and waste management systems.
- Mobility and Migration: Maharashtra’s cities continue to face the challenge of frequent mobility and migration, with an inward net movement of people for better livelihood opportunities.
- Air Pollution: Urbanization has led to an increase in air pollution in Maharashtra’s cities, primarily due to vehicular emissions and industrial activities.
- Social Inequities: The growth of informal settlements and slums in Maharashtra’s cities has led to social inequities, with the urban poor lacking access to basic services, such as healthcare, education, and housing.
- Vulnerabilities to Disasters and Climate Change: Rapid urbanization has increased the vulnerability of Maharashtra’s cities to disasters and climate change, such as floods and heatwaves.
- Poor Urban Planning: Many of the challenges faced by Maharashtra’s cities are a result of poor urban planning, with a lack of coordination between various government departments and inadequate implementation of policies and programmes.
Suggestive Measures:
- Development of infrastructural facilities in rural and semi urban areas: Focus on idea of PURA (Provision of Urban Amenities in Rural Area) given by Dr APJ Abdul Kalam, now taken up under Shyama Prasad Mukherjee RURBAN Mission.
- Environmental Sustainability: Cleaning up of rivers and ponds, Integration of green spaces, prevent encroachment of wetlands, proper waste management through ‘reduce, reuse, recycle strategy’ apart from the use of modern technology.
- Ensuring better urban infrastructural facilities– education, health, water, sewage, power, proper transport planning and investment in public transport sector and pedestrian pavements.
- Ensuring Good urban Governance: Decentralization and devolution of funds, functions and functionaries to the local governments, modern framework for spatial planning of cities and standardized designs for public utilities for Inclusive urbanization taking care of the needs of the urban poor and other vulnerable groups for ease of living.
- Proper implementation of major urban policies like One Nation One Ration Card scheme, AMRUT, Housing for All by 2022, Smarts City Mission, National Urban Livelihood Mission and Master Plans for Mega Cities like Delhi Master Plan 2031.
Thus, urban areas are the growth engines for the country and need to be healthy and sustainable. Focus should be on developing better facilities in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities and connectivity to bigger cities for better ecosystem and prevent excessive migration. Bringing employment opportunities and civic facilities to rural areas will be essential to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 11 for India.
About Aspirational Cities Programme (ACP): It is an initiative of the Government of Maharashtra aimed at addressing the challenges of rapid urbanization in the state by adopting a holistic approach to urban governance.
- The ACP has identified 57 cities that have been proposed for the programme. Service level benchmarking will be done for the cities based on the data collected on the Performance Assessment System of the Government of Maharashtra.
- The performance of the 57 selected cities would be monitored and ranked quarterly through a standard digital monitoring platform with indicators on the themes of urban infrastructure, education, urban services, skill development, and climate change.
- The ACP is based on three priority areas: inclusive urban development, scientific data methods for assessing and monitoring outcomes, and citizen participation in civic affairs.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: A recent investigation revealed that more than half of India’s 30 national sports federations do not have an Internal Complaints Committee (ICC) which is a legal requirement under the Prevention of Sexual Harassment (PoSH) Act, 2013.
About Prevention of Sexual Harassment (Posh) Act, 2013: The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, often known as the PoSH Act, was passed in 2013.
- The Act defines sexual harassment as any unwelcome act or behaviour (whether directly or by implication) such as;
- Physical contact and advances
- A demand or request for sexual favours
- Making sexually coloured remarks
- Showing pornography
- Any other unwelcome physical, verbal or non-verbal conduct of sexual nature.
- The Act provides a mechanism for the prevention, prohibition, and redressal of complaints of sexual harassment in the workplace.
- The 2013 law expanded and legitimised the Vishaka Guidelines, which were established by the Supreme Court in a 1997 decision.
- The Vishaka Guidelines defined sexual harassment and imposed on institutions three key obligations: prohibition, prevention, and reparation.
- The Supreme Court ordered that a Complaints Committee be formed to investigate allegations of sexual harassment of women in the workplace.
- The guidelines were made legally binding by the court.
Key Provisions of the act:
- It mandated that every employer must constitute an Internal Complaints Committee (ICC) at each office or branch with 10 or more employees.
- It lay down procedures and defined various aspects of sexual harassment, including the aggrieved victim, who could be a woman “of any age whether employed or not”, who “alleges to have been subjected to any act of sexual harassment”.
- The aggrieved victim under the Act can be a woman “of any age whether employed [at the workplace] or not”, who “alleges to have been subjected to any act of sexual harassment”.
- In effect, the Act protects the rights of all women who are working or visiting any workplace, in any capacity.
- The Act in its Section 2n, defines sexual harassment. Sexual harassment includes any one or more of the following unwelcome acts or behaviour (whether directly or by implication), namely
- Physical contact and advances, or
- A demand or request for sexual favours, or
- Making sexually coloured remarks, or
- Showing pornography, or
- Any other unwelcome physical, verbal, nonverbal conduct of sexual nature
- Section 3 (2) of the Act further elaborates that if any of the following circumstances occurs or is present in relation to or connected with any act or behavior of sexual harassment among other circumstances, it may amount to sexual harassment-
- Implied or explicit promise of preferential treatment in her employment, or
- Implied or explicit threat of detrimental treatment in her employment, or
- Implied or explicit threat about her present or future employment status, or
- Interference with her work or creating an intimidating or offensive or hostile work environment for her, or
- Humiliating treatment likely to affect her health or safety
- Procedure for complaint: It is not compulsory for the aggrieved victim to file a complaint for the ICC to act.
- she “may” do so — and if she cannot, any member of the ICC “shall” render “all reasonable assistance” to her to complain in writing.
- The complaint must be made “within three months from the date of the incident”.
- After the ICC has filed its report: If the allegations of sexual harassment are proven, the ICC will recommend to the employer to act “in accordance with the provisions of the service rules” of the company.
- These may vary from company to company.
- The ICC may also recommend that the company deduct the salary of the person found guilty, “as it may consider appropriate”.
Key Issues/Challenges:
- There could be feasibility issues in establishing an Internal Complaints Committee at every branch or office with 10 or more employees.
- The Internal Complaints Committee has been given the powers of a civil court.
- However, it does not require members with a legal background nor are there any provisions for legal training.
- The act provides for action against the complainant in case of a false or malicious complaint.
- This could deter victims from filing complaints.
- Two different bodies are called the ‘Local Complaints Committ
- The Bill does not clearly demarcate the jurisdiction, composition and functions of these Committees.
- Unlike sexual harassment legislation in many other countries, this Bill does not provide protection to men.
Way Forward: The Justice Verma committee was formed in 2013 to provide recommendation on prevention of sexual harassment in workplaces. Some of its recommendations include:
- Employment tribunal: An employment tribunal must be set up under PoSH act instead of ICC. The tribunal need not function as a civil court but may choose its own procedure to deal with each complaint.
- Expanding scope: The act must be expanded to include domestic workers. The definition of ‘sexual harassment’ must be expanded to consider perception of the victim.
- Other provisions: The committee recommended doing away with 90 days’ time limit and penalty for wrong complaints.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding King Cobra species:
- They are the only snakes in the world that build nests for their eggs.
- They have been mentioned in the schedule I of Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which of the statements is not correct regarding the Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL)?
- RVNL is a Central Public Sector Enterprise.
- RVNL is a Navratna Company
- It works under the Ministry of Railways
- All statements are correct
Q.3) With reference to Buddhism in India, consider the following statements:
- Melinda Panha is a dialogue between Indo-Greek king Meander and Buddhist monk Nagasena.
- Mahavamsa deals with the arrival of Buddha‘s teaching and preachers in Sri Lanka.
- Dipavamsa deals with the royal dynasties of the Indian subcontinent.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 6th May 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 5th May – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – d











