IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
Context: A Supreme Court-appointed committee recently declared 12 private resorts, along the Segur elephant corridor, illegal.
Background:-
- The committee’s ruling highlighted that the resorts had constructed unlawful structures that impeded the natural movement of elephants.
- Despite assertions from resort owners who disputed the corridor’s designation as an elephant habitat, the committee ultimately sided with preserving the corridor’s integrity.
- While this decision secures the protection of the corridor, it carries economic implications for the local communities that depend on employment opportunities provided by these resorts.
About Segur elephant corridor:-
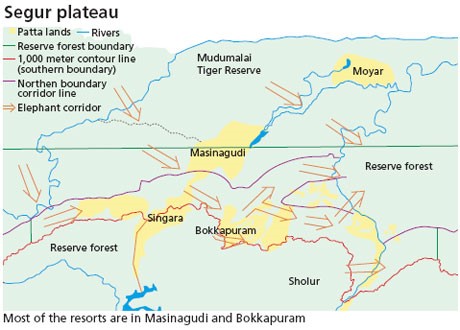
IMAGE SOURCE: downtoearth.org.in
- The Segur elephant corridor serves as a crucial passageway for the movement of elephants and various other wildlife species between different habitats within the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve. ( Endangered Asian elephant in Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve)
- The corridor is situated in the ecologically fragile Sigur plateau.
- Sigur plateau connects the Western and the Eastern Ghats.
- It facilitates easy movement of about 6,300 Asiatic elephants from Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka.
- It sustains elephant populations and their genetic diversity. (Elephant Conservation)
- The elephants cross the plateau in search of food and water.
- It has the Nilgiri Hills on its southwestern side.
- Moyar River Valley is on its northeastern side.
- The plateau is a low-rainfall marginal land.
- It has poor soils and in recent times, also had a low population density.
- There are five major streams in the Sigur plateau: Moyar River, Sigur River, Avarahalla River, Kedarhalla River, and Gundattihalla River.
- All these rivers originate in the Nilgiris plateau.
MUST READ: Project Re-Hab
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following makes a tool with a stick to scrape insects from a hole in a tree or a log of wood? (2023)
- Fishing cat
- Orangutan
- Otter
- Sloth bear
Q.2) With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Wild animals are the sole property of the government.
- When a wild animal is declared protected, such animal is entitled to equal protection whether it is found in protected areas or outside.
- Apprehension of a protected wild animal becoming a danger to human life is sufficient ground for its capture or killing.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
Context: Recently, 15 countries joined the UN Convention on the International Effects of Judicial Sales of Ships.
Background:-
- The convention was opened for signatures at a ceremony in Beijing on September 5, 2023, according to the United Nations.
- 15 countries, including China, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, and Switzerland, signed the UN Convention.
About the UN Convention on the International Effects of Judicial Sales of Ships:-
- Date of adoption: 7 December 2022.
- Objective: to promote legal certainty and predictability at the international level by creating a uniform regime for the international effects of ‘judicial’ sales of ships.
- Background:-
- It was developed by the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL).
- It was to address the problem of bona fide new owners and those financing the purchase of vessels who, for instance, find themselves dealing with previous creditors laying claim to the ship as security for a loan.
- The convention is also known as the Beijing Convention on the Judicial Sale of Ships.
- It establishes a harmonized regime for giving international effect to judicial sales while preserving domestic law governing the procedure of judicial sales and the circumstances in which judicial sales confer clean title.
- By ensuring legal certainty as to the title that the purchaser acquires in the ship as it navigates internationally, the Convention is designed to maximize the price that the ship is able to attract in the market and the proceeds available for distribution among creditors and to promote international trade.
Key Provisions:-
- Basic rule of the Convention:-
- A judicial sale conducted in one State Party which has the effect of conferring clean title on the purchaser has the same effect in every other State Party (article 6).
- The basic rule is subject only to a public policy exception (article 10).
- Additional rules of the Convention:-
- The first is a requirement that the ship registry deregister the ship or transfer registration at the request of the purchaser (article 7). (UN biodiversity Summit)
- The second is a prohibition on arresting the ship for a claim arising from a pre-existing right or interest (i.e. a right or interest extinguished by the sale) (article 8).
- The third is the conferral of exclusive jurisdiction on the courts of the State of judicial sale to hear a challenge to the judicial sale (article 9).
- The Convention provides for the issuance of two instruments: a notice of judicial sale (article 4) and a certificate of judicial sale (article 5).
- It also establishes an online repository of those instruments which is freely accessible to any interested person or entity (article 11).
- The Convention regime is “closed”, in the sense that it applies only among States Parties (article 3), but “not-exclusive”, in the sense that it does not displace other bases for giving effect to judicial sales, for instance under more favourable domestic law regimes (article 14).
MUST READ: UN High Seas Treaty
SOURCE: BUSINESS LINE
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the United Nations Convention on the Law of Sea, consider the following statements: (2022)
- A coastal state has the right to establish the breadth of its territorial sea up to a limit not exceeding 12 nautical miles, measured from a baseline determined in accordance with the convention.
- Ships of all states, whether coastal or land-locked, enjoy the right of innocent passage through the territorial sea.
- The Exclusive Economic Zone shall not extend beyond 200 nautical miles from the baseline from which the breadth of the territorial sea is measured.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) has a ‘Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air’.
- The UNCAC is the ever-first legally binding global anti-corruption instrument.
- A highlight of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the inclusion of a specific chapter aimed at returning assets to their rightful owners from whom they had been taken illicitly.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is mandated by its member states to assist in the implementation of both UNCAC and UNTOC.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: A National Workshop on e-NAM 2.0 and Agri Marketing Reforms was conducted recently.
Background:-
- 28 new mandis were approved recently for integration to take the total count of APMCs to 1389 on e-NAM.
About e-NAM 2.0:-
- Launched: 2016
- Implementing agency: Small Farmers Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC).
- Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare.
- Objective: integrating the existing Mandis into a “One Nation One Market” for agricultural commodities in India.
Salient Features:-
- e-NAM 2.0 will be an advanced version of existing e-NAM.
- The eNAM platform is an online trading platform for agricultural commodities in India.
- It is a pan-India electronic trade portal linking agricultural produce market committees (APMCs) across all states.
- It facilitates farmers, traders, and buyers with online trading in commodities.
- It provides for contactless remote bidding.
- It provides for mobile-based anytime payment for which traders do not need to either visit mandis or banks for the same.
Benefits:-
- e-NAM has been able to bring competence in APMC mandi operations via technology interventions like:-
- accuracy in weighing via digital weighbridge and weighing scale.
- accuracy in assaying via advanced assaying equipment.
- real-time online information on commodity prices.
- access to more buyers/sellers and transparency in trade.
- transparency in payment via multiple online payment modes.
- better efficiency in overall mandi operations via digitalization.
Challenges:-
- Lack of internet connectivity.
- Farmers feel more comfortable with physical trading rather than going online as they face issues with transportation for their produce.
- A very small percentage of the total mandis are connected through the e-NAM platform.
MUST READ: Integration of E-MANDIS into E-NAM Platform
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to foreign-owned e-commerce firms operating in India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2022)
- They can sell their own goods in addition to offering their platforms as marketplaces.
- The degree to which they can own big sellers on their platforms is limited.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which of the following factors/policies were affecting the price of rice in India in the recent past? (2020)
- Minimum Support Price
- Government’s trading
- Government’s stockpiling
- Consumer subsidies
Syllabus
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
Context: The Pazhathottam area in Anamudi Shola National Park, near Munnar, in Idukki has been transformed into a green heaven teeming with life, by the initiative of the Forest department.
- An eco-development committee named “Haritha Vasantham”was formed for the project, involving local residents in its implementation.
About Anamudi Shola national park:-

IMAGE SOURCE: munnarinfo.in
- Location: in Devikulam, Idukki, Kerala.
- It is located in the western Ghats.
- The Munnar Wildlife division includes Eravikulam National Park, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary, and the Shola National Parks.
- It was declared National Park, in the year 2003.
- It is located in the high ranges of the Southern Western Ghats. (Eravikulam National Park)
- It has the largest Shola Forest patch in South India.
- The Park is contiguous with Anamalai Tiger Reserve, Palani Hills, and the forests of Kannan Devan Hills.
- It also forms the catchment area of Mattupetti Dam and Amaravathi Dam.
- Vegetation: Southern Sub-tropical Hill Forests and Southern Montane Wet Temperate Forests.
- Fauna: mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, butterflies, odonates and ants.
- Flora: plant species belonging to Pteridophytes and Angiosperms.
MUST READ: Silent Valley National Park
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following Protected Areas are located in the Cauvery basin? (2020)
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) With reference to India’s Desert National Park, which of the following statements is correct? (2020)
- It is spread over two districts.
- There is no human habitation inside the Park.
- It is one of the natural habitats of the Great Indian Bustard.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –DEFENSE
Context: A Coastal security drill ‘Operation Sajag’ was conducted recently.
Background:-
- It was conducted by the Indian Coast Guard along the West Coast.
- It was conducted by the Indian Coast Guard along the west coast on September 18, 2023.
About Operation Sajag:-
- The day-long drill is conducted every month and the outcomes are further progressed for improvement in the coastal security construct.
- Objective: The drill facilitates revalidation of the coastal security mechanism and brings awareness among the fishermen at sea.
- During the drill, extensive checking and verification of documents and crew passes of all fishing boats, barges, and craft at sea was undertaken.
- A total of 118 ships including those from Customs, Marine Police, Ports & and Indian Navy participated in the drill.
- In order to strengthen the coastal security construct, a slew of measures have been incorporated ranging from:-
- Issuance of Biometric cards for the fishermen.
- Colour coding of fishing boats as per each state.
- Manning of fish landing centres and
- Access control at entry/exit checkpoints.
- Coastal mapping, designating specific marine band frequency for security agencies.
- Training of marine police personnel by the Indian Coast Guard amongst others.
- Besides monitoring of dhows, island security, and community interaction programmes have been institutionalized under the coastal security construct.
Significance:-
- The drill involves a thorough review of various coastal security (Defence Acquisition Council)
- It highlights important lessons and emerging trends in coastal security.
- The drill enables to verification implementation of various coastal security measures besides bringing out important lessons and highlighting trends in coastal security.
MUST READ: International Maritime Organization (IMO) & India
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (2023)
- Australia
- Canada
- Israel
- Japan
Q.2) With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements : (2018)
- IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers the entire India and about 5500 sq. km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims –ART AND CULTURE
Context: The Sangeet Natak Akademi recently, announced the Sangeet Natak Akademi Amrit Awards.
Background:-
- It was announced on September 15, 2023.
- The award commemorates 75 years of India’s independence to 84 artists, who are above the age of 75 years and haven’t been accorded any national honour in their career so far.
About Sangeet Natak Akademi Amrit Awards:-
- Sangeet Natak Akademi Amrit Awards is a national honor .
- It honors and commends excellence in the performing arts, spanning music, dance, theatre, and related domains.
- The accolades are bestowed upon artists, educators, and scholars who have made remarkable contributions to these fields, particularly those aged 75 and above.
Nominations:-
- Nominees are proposed by the Government of India, State Governments, and Union Territories.
Selection:-
- The recipients have been selected by the Akademi’s General Council.
- It consists of distinguished musicians, dancers, theatre artists, and scholars in these disciplines as well as nominees of the Centre, States, and Union Territories.
Decoration:-
- a purse money of ₹1,00,000 and a citation.
- a Tamrapatra (copper plaque), and
- an Angavastram (traditional stole).
Awardees:-
- Raghubir Malik and Dina Nath Mishra for Hindustani vocal. (Shashi Tharoor wins Akademi’s 2019 award for English)
- Gowri Kuppuswamy and Anasuya Kulkarni for Carnatic vocal.
- Lalitha Srinivasan and Vilasini Devi Krishnapillai for Bharatnatyam and
- Smita Shastri and Kumkum Lal for Kuchipudi and Odishi, respectively.
- The awardees also include those from the folk genre like Mahabir Nayak from Jharkhand for music, Harishchandra Prabhakar Borkar from Maharashtra for theatre, and Dharmeswar Nath of Asssam for dance.
MUST READ: National Lalit Kala Akademi awards
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of the Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards. (2021)
- Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards are titled under Article 18(1) of the Constitution of India.
- Padma Awards, which were instituted in the year 1954, were suspended only once.
- The number of Bharat Ratna Awards is restricted to a maximum of five in a particular year.
Which of the above statements is not correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to Manipuri Sankirtana, consider the following statements: (2017)
- It is a song and dance performance
- Cymbals are the only musical instruments used in the performance
- It is performed to narrate the life and deeds of Lord Krishna
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –POLITY/INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
Context: President Droupadi Murmu recently, inaugurated the conference of National Human Rights Institutions of the Asia Pacific region in New Delhi, India.
About the conference of National Human Rights Institutions of the Asia Pacific region:-
- Hosted by: National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), India
- Date: 20 – 21, September, 2023.
- Venue: Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi.
- The two-day conference will celebrate the 75th anniversary of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and 30 years of National Human Rights Institutions and the Paris Principles.
- A sub-theme on the environment and climate change was also held.
- Additionally, the National Human Rights Commission will organize a seminar on Business and Human Rights.
- The event aims to ensure that businesses prioritize human rights and environmental sustainability in their operations.
- It is a Biennial Conference of National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs) of Asia Pacific.
- Earlier, in 2002 and 2014, such an AGM of Asia Pacific Forum and conference was held in India.
About Asia Pacific Forum:-
- Founded:1996.
- The APF was founded to promote the establishment of independent NHRIs in the Asia Pacific region and to support them in their work to promote and protect human rights as effectively as possible.
- Objective: to promote the establishment of independent NHRIs in the Asia Pacific region and to support our members to do their work as effectively as possible.
- Membership:-
- From five founding members, the APF membership has expanded to 26 NHRIs.
- NHRC, India is one of the founding members of the Asia Pacific Forum of the NHRIs.
- As a coalition of national human rights institutions, it works together and shares expertise to help make its vision a reality.
- It works closely with governments, civil society organizations, regional human rights bodies, and the international community.
- It aims to build strong partnerships and strengthen the impact of our members as they work to build fair, inclusive, and resilient communities.
- Its network now supports over 4,000 dedicated human rights defenders who work tirelessly on the ground to protect the rights of those most vulnerable.
- Significance: It has created a strong and united platform that brings together National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs) from all corners of the Asia Pacific to address some of the most serious human rights challenges in our region.
MUST READ: Giving Human Rights Commissions more teeth
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Under the Indian constitution concentration of wealth violates :(2021)
- The Right to Equality
- The Directive Principles of State Policy
- The Right to Freedom
- The Concept of Welfare
Q.2) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Judicial custody means an accused is in the custody of the concerned magistrate and such an accused is locked up in a police station, not in jail.
- During judicial custody, the police officer in charge of the case is not allowed to interrogate the suspect without the approval of the court.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Women’s Reservation Bill 2023
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently Women Reservation Bill has been tabled in the Lok Sabha as the One Hundred Twenty-Eight Amendment Bill 2023.
Historical Background of Women’s Reservation Bill:
- 81st Constitutional Amendment Bill by Deve Gowda Govt: The Women Reservation Bill was first introduced in 1996 as 81st Constitutional Amendment Bill.
- The bill was referred to the select committee of parliament headed by Geeta Mukherjee.
- However the Bill lapsed with the dissolution of the Lok Sabha as no consensus could be formed over reservation for OBC women.
- The Bill was reintroduced by the NDA government in the 13th Lok Sabha in 1999 and was subsequently introduced twice in the year 2003.
- However the bills could not be passed and hence they lapsed.
- The UPA government in 2004 included reservation bill in its Common Minimum Programme and tabled it in Rajya Sabha to prevent it from lapsing again.
- Women’s Reservation Bill introduced as 108th Constitutional Amendment Bill 2008 was passed in the Rajya Sabha in 2010 and lapsed in the Lok Sabha.
- RJD, the JD(U) and the SP were its most vocal opponents.
- They demanded 33% reservation for backward groups within the 33% quota for women.
Key features of the Bill 2023:
- Reservation for women: The Bill reserves, as nearly as may be, one-third of all seats for women in Lok Sabha, state legislative assemblies, and the Legislative Assembly of the National Capital Territory of Delhi.
- This will also apply to the seats reserved for SCs and STs in Lok Sabha and states legislatures.
- Commencement of reservation: The reservation will be effective after the census conducted after the commencement of this Bill has been published.
- Based on the census, delimitation will be undertaken to reserve seats for women.
- The reservation will be provided for a period of 15 years.
- However, it shall continue till such date as determined by a law made by Parliament.
- Rotation of seats: Seats reserved for women will be rotated after each delimitation, as determined by a law made by Parliament.
Arguments in favour of the Bill:
- Increase in the political representation of women-According to the Inter-Parliamentary Union’s Women in Parliament’ Report (2021), India ranks lower than 140 other nations in terms of the number of women serving in their national legislatures.
- Rwanda (61 per cent), South Africa (43 per cent) and even Bangladesh (21 per cent), are ahead of India in this matter.
- Ability of women leadership in bringing change: Studies on panchayats have shown the positive effect of women reservation on empowerment of women and on allocation of resources.
- Ex-Woman Sarpanch of Dhani Mayan Khan GP in Haryana built a training centre for women and ensured that every village child went to school.
- Step towards decriminalisation of politics– Reserved seats for women would help in decriminalisation of Indian Politics.
- In the present Lok Sabha 159 MPs have declared serious criminal cases against them including those of rape, murder, attempt to murder, kidnapping, crimes against women.
- It will help in addressing crime against women in the society.
- Improvement of Economic Performance and Infrastructure: According to UN University, Women legislators improve the economic performance of their constituencies 1.8 per cent more than male legislatures.
- Evaluation of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana shows the share of incomplete road projects is 22 percentage points lower in female led constituencies.
- Increasing vote share but low representation: Though women’s vote share has increased, the number of women in positions of politics has not increased commensurately.
- Women in India vote at par with men but their representation is very low as compared to men.
- The bill will increase representation as well in the politics.
- Breaking the patriarchal Mold of Indian Politics- Indian Politics has been patriarchal with top party positions and positions of power have been occupied by male.
- It will dismantle this patriarchal nature of Indian politics.
- Changing Stereotypes: Increase in women politicians will help in changing the stereotyped image of women as only ‘homemakers’ and there will be gradual acceptance of women as lawmakers.
Challenges that have hindered the passage of the Bill:
- No separate OBC reservation: The Bill provides separate reservation to Scheduled castes and Scheduled Tribes women within the existing quota of one third reservation of seats.
- However OBC women which constitute 60% of women population have not been provided separate reservation within the quota.
- No reservation in the Rajya Sabha and legislative Councils: The Bill does not provide reservation to women in the Rajya Sabha and the legislative Councils.
- Conflict of Interests: Some political leaders worry that implementing the bill’s reservation quota for women may result in competition for seats between women candidates and those belonging to marginalized communities.
- This conflict of interests can create resistance to the bill, as political parties seek.
- Patriarchal norms: Deep-rooted patriarchal norms and gender biases in Indian society continue to be significant obstacles to women’s participation in politics.
- These norms can manifest in various ways, including the belief that women are less capable of leadership or that politics is a male-dominated domain.
- Family and societal pressures: Women often face family and societal pressures that discourage them from pursuing a career in politics.
- Concerns about safety, traditional gender roles, and societal expectations can dissuade women from taking an active role in politics.
- Violence and harassment: The political arena in India is not immune to gender-based violence and harassment.
- Women politicians and candidates have reported instances of threats, harassment, and violence, which can act as deterrents to their participation.
Way Forward:
Therefore the Women’s Reservation Bill 2023 is not merely a legislative proposal but it us a crucial step towards gender equality in India’s political landscape. It addresses deeply entrenched structural norms and prejudices that have hindered women’s participation in politics for generations. The Bill can serve as a catalyst for change, fostering an inclusive and gender-sensitive approach within the political arena.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 4 (Ethics)
Context: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming health care worldwide, and India has the potential to be at the forefront of this revolution.
About Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a simulation of human intelligence into a computer machine so that it can think and act like a human.
- AI systems are designed to simulate or replicate human cognitive abilities, such as perception, reasoning, learning, and problem-solving.
- AI rely on algorithms and computational models to process and analyze large amounts of data, extracting patterns and making predictions or decisions based on that information.
India’s journey and its achievements in Healthcare:
- Proton beam therapy technology: A significant milestone in this journey is the introduction of proton beam therapy technology, making India a regional leader in cancer treatment.
- Patients from across the globe are drawn to India for its world-class medical expertise, state-of-the-art infrastructure, and cost-effective care.
- Orthopaedic procedures: Orthopaedic procedures, including joint replacements and spinal surgeries, are conducted by highly skilled surgeons using minimally invasive techniques.
- This attracts patients seeking top-notch orthopaedic care at competitive prices.
- Robotic surgeries: Robotic surgery has also gained popularity, with India’s hospitals adopting robotic-assisted techniques for precision and faster recovery.
- The country’s expertise in this area draws international patients seeking minimally invasive, high-precision surgical interventions.
- Medical value travel (MVT): MVT is gaining strategic importance given its ability to create employment as well as earn foreign exchange.
- While India is already one of the leading destinations for patients seeking care abroad, there is adequate headroom for growth.
Significance of AI healthcare in India:
- According to the Indian AI Healthcare Market 2019-2025 report, AI in the Indian healthcare industry is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 50.9% during the forecast period.
- AI in healthcare have the potential to add $25-$35 billion to India’s GDP by 2025.
- Some of the AI healthcare start-ups in India that are reshaping the industry are:
- HealthifyMe: Harnesses AI to provide personalised diet and fitness information and coaching.
- Dozee: Contactless health monitors that enable early detection of any health deterioration.
- Niramai: Early-stage detection of breast cancer.
- Tricog: Offer virtual cardiology services to distant clinics.
Applications of AI in Healthcare:
- Personalized Treatment Plans: By considering a patient’s medical history, genetic information, and current condition, AI systems can recommend the most effective treatment options and dosages.
- Disease diagnosis: Machine learning algorithms can analyze patient data, including symptoms, medical records, and genetic information, to identify patterns and predict diseases.
- Medical Imaging: AI can assist in the interpretation of medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and mammograms to detect abnormalities, tumours, or other signs of diseases with high accuracy.
- AI Powered Virtual Assistants and Chatbots: They can provide patients with 24/7 access to medical information, answer questions about symptoms, medications, and provide healthcare guidance.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: AI-enabled devices can collect and analyze real-time patient data, such as vital signs, activity levels, and sleep patterns, allowing healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients.
- Robotics and Surgery: AI-powered robots can assist surgeons during complex procedures by providing real-time feedback, precision, and enhanced visualization.
- Drug Discovery and Development: AI can accelerate the process of drug discovery by analyzing vast amounts of biological and chemical data.
Challenges associated with the India’s healthcare system:
- No focus on Preventive Care: In India, there is a very low emphasis on preventive care, which can be proved very effective in solving a lot of problems for the patient in terms of misery or financial losses.
- Less emphasis on Medical Research: In India, there is no much impetus is being given to R&D and cutting-edge technology-led new initiatives.
- Such technologies could be useful in an unprecedented situation like Covid-19.
- Issue of Policymaking: For providing effective and efficient healthcare services policymaking is certainly an important aspect.
- In India, the problem is fundamental of supply than demand, where policymaking can be effective.
- Shortage of Medical Workforce: In India, there is a shortage of doctors, nurses, and other staff in the health sector.
- As per a report laid down by a minister in Parliament, there is a shortage of 600,000 doctors in India.
- Inadequate outlay for health: As per National Health Policy 2002, India contributes only 0.9 percent of its GDP to the Health care sector.
- India’s non-communicable diseases (NCD) burden: India is now the world’s diabetes capital; also, millions have hypertension, and its youth are succumbing to heart attacks, cancer, respiratory issues, depression and more.
- If left unchecked, India’s non-communicable diseases (NCD) burden will be nearly $4 trillion by 2030.
- India’s Struggle with Health indicators: India still faces issues like, poor Health, lack of adequate number of doctors, lack of expenditure on health, poor sanitation, lack of safe drinking water, increased drug resistance of many diseases, lack of infrastructure in remote locations, etc.
ICMR Guidelines for AI Use in the Health Sector: A way forward
- Accountability and Liability Principle: It underlines the importance of regular internal and external audits to ensure optimum functioning of AI systems which must be made available to the public.
- Autonomy Principle: It ensures human oversight of the functioning and performance of the AI system.
- Before initiating any process, it is also critical to attain consent of the patient who must also be informed of the physical, psychological and social risks involved.
- Data Privacy Principle: It mandates AI-based technology should ensure privacy and personal data protection at all stages of development and deployment.
- Collaboration Principle:This principle encourages interdisciplinary, international collaboration and assistance involving different stakeholders.
- Safety and Risk Minimization Principle: This principle aimed at preventing “unintended or deliberate misuse”, anonymized data delinked from global technology to avoid cyber-attacks, and a favourable benefit-risk assessment by an ethical committee among a host of other areas.
- Accessibility, Equity and Inclusiveness Principle: This acknowledge that the deployment of AI technology assumes widespread availability of appropriate infrastructure and thus aims to bridge the digital divide.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| National Park | Location |
| 1.Eravikulam National Park | Tamil Nadu |
| 2.Similipal National Park | Madhya Pradesh |
| 3.Silent Valley National Park | Karnataka |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
UN Convention on the International Effects of Judicial Sales of Ships was adopted in 2022.
Statement-II:
The convention is also known as the Beijing Convention on the Judicial Sale of Ships.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) With reference to the Segur elephant corridor, consider the following statements:
- It connects the Western and the Eastern Ghats.
- It has the Nilgiri Hills on its northeastern side.
- Moyar River Valley is on its southwestern side.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) How does Al help clinical diagnosis? Do you perceive any threat to privacy of the individual in the use of Al in healthcare? (250 words)
Q.2) What are the key reasons behind India’s low global ranking in terms of women’s political participation? Explain how the Women’s Reservation Bill could address these challenges and empower women in Indian politics. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 20th September 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 19th September – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – d











