IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: As per recent reports, the Parliamentary Committee is set to discuss the Uniform Civil Code in the upcoming meeting.
Background:-
- The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, Law and Justice will hold a meeting on the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) tomorrow.
- BJP Rajya Sabha MP Sushil Modi will head the Committee.
- The UCC proposes to formulate and implement personal laws of citizens, which apply to all citizens equally regardless of their religion.
About Uniform Civil Code:-

IMAGE SOURCE: The Times of India
- UCC is a generic set of governing laws for every citizen without taking into consideration religion.
- The Constitution in Article 44 requires the State to strive to secure for its citizens a Uniform Civil Code(UCC) throughout India. (UPSC CSE: Uniform Civil Code)
- Article 44:According to this article, “The State shall endeavor to secure for the citizens a uniform civil code throughout the territory of India”.
Historical Background:-
- The Supreme Court for the first time directed the Parliament to frame a UCC in the case of Mohammad Ahmed Khan v. Shah Bano Begum in the year 1985.
- In this case, Shah Bano claimed maintenance from her husband under Section 125 of the Code of Criminal Procedure after she was given triple talaq by him.
- However, the government overturned the Shah Bano case decision by way of the Muslim Women (Right to Protection on Divorce) Act, 1986 which curtailed the right of a Muslim woman to maintenance under Section 125 of the Code of Criminal Procedure.
Need of UCC:-
Gender Justice:–
- It is commonly observed that personal laws of almost all religions are discriminatory towards women.
- Men are usually granted upper preferential status in matters of succession and inheritance.
- Muslim men are allowed to marry multiple wives, but women are forbidden from having multiple husbands.
- Even after the 2005 amendment to the Hindu Succession Act, women are still considered part of their husband’s families after marriage.
- So, in case a Hindu widow dies without any heirs or will, her property will automatically go to her husband’s family.
- Men (fathers) are also treated as ‘natural guardians’ and are given preference under the Hindu Minority and Guardianship Act.
- A uniform civil code will establish gender justice by bringing both men and women to par.
Promote national unity:
- A unified personal law irrespective of gender, caste, creed, etc. will boost national unity and solidarity.
Simplification of laws: It will eliminate the overlapping of laws. Different personal laws (Codified and Uncodified) practised in India:-
- Hindu Personal Law
- Hindu personal law is codified in four bills: the Hindu Marriage Act, Hindu Succession Act, Hindu Minority and Guardianship Act, and Hindu Adoptions and Maintenance Act.
- The term ‘Hindu’ also includes Sikhs, Jains and Buddhists for the purpose of these laws.
- It was codified by the Parliament in 1956.
- Muslim personal laws
- A 1939 Act enacted by the British said that their personal Law (ie, the Shariat) would govern Muslims.
- The Muslim Personal Law (Shariat) Act, 1937 is a short statute with five provisions.
- It covers provisions of marriage, divorce, children’s custody or inheritance Intestate succession, dissolution of marriage etc.
- Secular’ laws:-
- These laws disregard religion altogether. These include:
- Special Marriage Act: for Inter-religion marriages and
- Guardians and Wards Act: establishes the rights and duties of guardians.
- Other laws:-
- In the Northeast, there are more than 200 tribes with their own varied customary laws.
- Apart from it, different personal laws also govern Christians and Jews.
- Thus, a UCC will simplify these laws into one standard.
Parliamentary Standing Committees
- These are the permanent and regular committees.
- They are constituted from time to time according to the provisions of an Act of Parliament or Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business.
- Both houses of Parliament, Rajya Sabha, and Lok Sabha have similar Committee structures with a few exceptions.
- Parliamentary committees draw their authority from:-
- Article 105: on privileges of Parliament members.
- Article 118: on Parliament’s authority to make rules for regulating its procedure and conduct of business.
MUST READ: Parliamentary Committees
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In essence, what does ‘Due Process of Law’ mean? (2023)
- The principle of natural justice
- The procedure established by law
- Fair application of law
- Equality before law
Q.2) In India, which one of the following (2023)
Constitutional Amendments were widely believed to be enacted to overcome the judicial interpretations of Fundamental Rights.
- 1st Amendment
- 42nd Amendment
- 44th Amendment
- 86th Amendment
Syllabus
- Prelims – Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the National Investigation Agency (NIA) conducted raids at multiple locations in Bihar, Gujarat, and Uttar Pradesh.
Background:-
- The NIA conducted raids at multiple locations in Bihar, Gujarat, and Uttar Pradesh in connection with a radicalized module run by Pakistan-based suspects – Ghazwa-e-Hind.
- During the raids, it seized incriminating material, including digital devices and documents.
About National Investigation Agency (NIA):-
- NIA is functioning as the Central Counter Terrorism Law Enforcement Agency in India.
- Establishment: 2008.
- National Investigation Agency Act, enacted on 31-12-08, established it. (UPSC MAINS: NIA)
- Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It is a central agency to investigate and prosecute offences:-
- Affecting the sovereignty, security and integrity of India, security of the State, and friendly relations with foreign States.
- Against atomic and nuclear facilities.
- Smuggling in High-Quality Counterfeit Indian Currency.
Objectives:-
- It implements international treaties, agreements, conventions and resolutions of the United Nations, its agencies and other international organisations.
Historical Background:-
- The agency at the Central level was created for the investigation of offences related to terrorism and certain other Acts post-2008 Mumbai terror attacks.
Functions of NIA:-
- In-depth professional investigation of scheduled offences using the latest scientific methods.
- Ensuring effective and speedy trials.
- Developing into a thoroughly professional, result-oriented organization.
- Developing a professional workforce through regular training and exposure to the best practices and procedures.
- Maintaining professional and cordial relations with the governments of States and Union Territories and other law enforcement agencies in compliance with the legal provisions of the NIA Act.
- Assist all States and other investigating agencies in the investigation of terrorist cases.
- Build a database on all terrorist-related information.
- Share the database available with the States and other agencies.
- Study and analyze laws relating to terrorism in other countries.
- Evaluate the adequacy of existing laws in India and propose changes as and when necessary.
- To win the confidence of the citizens of India through selfless and fearless endeavors.
MUST READ: Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following organizations/ bodies in India: (2023)
- The National Commission for Backward Classes
- The National Human Rights Commission
- The National Law Commission
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
How many of the above are constitutional bodies?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) With reference to Home Guards, consider the following statements: (2023)
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the Central Government.
- The role of the Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary force to the police in the maintenance of internal security.
- To prevent infiltration on the international border/ coastal areas, the Border Wing Home Guards Battalions have been raised in some states.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Organizations
Context: Recently, National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) has nearly doubled coal production during the first quarter of the financial year 2023 – 2024.
Background:-
- NTPC nearly doubled coal production in the first quarter (Q1) of the financial year 2023 – 202 as compared to the production during Q1 of the previous year.
- It achieved impressive coal production of 8.48 million metric tonnes (MMT) during Q1 of FY24, compared to 4.27 MMT in Q1 of FY23.
- In addition, coal dispatch has more than doubled during Q1 of 2023 – 2024, relative to the first quarter of 2022 – 2023.
About National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC):-
- NTPC is India’s largest energy conglomerate with roots planted back in 1975 to accelerate power development in India. (UPSC CSE: NTPC’s Energy Compact Goals)
- It is a central Public Sector Undertaking (PSU).
- Establishment: 1975.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Ministry: Ministry of Power.
- Objective: To provide reliable power and related solutions in an economical, efficient and environment-friendly manner, driven by innovation and agility.
- It became a Maharatna company in
- NTPC Limited is India’s largest integrated power utility.
- It contributes 1/4th of the power requirement of the country.
- It has a diverse portfolio of thermal, hydro, solar, and wind power plants.
- It is dedicated to delivering reliable, affordable, and sustainable electricity to the nation.
- The company is committed to adopting best practices, fostering innovation, and embracing clean energy technologies for a greener future.
MUST READ: India’s Power Crisis
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following has been constituted under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986?
- Central Water Commission
- Central Ground Water Board
- Central Ground Water Authority
- National Water Development Agency
Q.2) “R2 Code of Practices” constitute a tool available for promoting the adoption of
- Environmentally responsible practices in the electronics recycling industry
- Ecological management of ‘’Wetlands of International Importance” under the Ramsar Convention
- Sustainable practices in the cultivation of agricultural crops in degraded lands
- ‘’Environmental Impact Assessment’’ in the exploitation of natural resources
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: The Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio of Scheduled Commercial Banks has fallen to 10-year low of 3.9 per cent in March 2023 as per recent reports.
Background:-
- Reserve Bank of India has informed that the Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio of Scheduled Commercial Banks has fallen to 10-year low of 3.9 per cent in March 2023.
About Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) ratio:-
- Non-Performing Assets (NPA): NPAs are loans or advances made by a financial institution, on which both principal or interest is unpaid for a specified period.
- Gross Nonperforming assets (GNPA) is an absolute amount.
- Net non-performing assets (NNPA) ratio declined to 1 per cent.
- NNPA: This amount is realized after the provision amount has been deducted from the gross non-performing assets.
- Gross Nonperforming assets – Provisioning = Net Nonperforming assets.
- It tells the total value of gross non-performing assets for the bank in a particular quarter or financial year, as the case may be.
- GNPA ratio is the ratio of total gross non-performing assets to total loans of the bank.
- Interpretation: A very high GNPA means the institution’s asset quality is in bad shape.
- Significance: The GNPA ratio estimate is to assess the resilience of banks to unforeseen shocks emanating from the macroeconomic environment.
Types of NPA:-
- Standard Assets: assets that carry a normal risk and are not NPA in the real sense of the word.
- No special provisions are required for standard assets.
- Sub Standard: is an asset where repayment has not been done for up to twelve months.
- Doubtful: an asset that has remained as an NPA for a period exceeding twelve months.
- Loss: one where loss has already been identified by the bank or an external institution, but it is not yet completely written off.
Impacts of rise in NPAs:-
- Lenders suffer a lowering of profit margins.
- Stress in the banking sector causes less money available to fund other projects, therefore, a negative impact on the larger national economy.
- Higher interest rates by the banks to maintain the profit margin.
- As investments got stuck, it may result in
- Investors do not get rightful returns.
- Both the banks and the corporate sector have stressed the balance sheet, which causes the halting of the investment-led development process.
- NPAs-related cases add more pressure to already pending cases with the judiciary.
MUST READ: RBI issues revised PCA framework for banks
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following .activities of the Reserve Bank of India is considered to be part of ‘sterilization’? (2023)
- Conducting ‘Open Market Operations
- Oversight of settlement and payment systems
- Debt and cash management for the Central and State Governments
- Regulating the Functions of Nonbanking Financial Institutions
Q.2) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2022)
- A share of the household’s financial savings goes towards government borrowings.
- Dated securities issued at market-related rates in auctions form a large component of internal debt.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recent reports suggest that the Centre’s Jal Jeevan Mission may miss the 2024 target.
About Jal Jeevan Mission:-

IMAGE SOURCE: IASBABA
- Launched in 2019.
- Ministry: Ministry of Jalshakti. (UPSC CSE: JAL JEEVAN MISSION)
- It aims to provide safe and adequate drinking water through individual household tap connections to all households in rural India by 2024.
- Funding: The fund-sharing pattern between the Centre and states is 90:10 for Himalayan and North-Eastern States, 50:50 for other states, and 100% for Union Territories.
Objectives of JJM:-
- To provide Functional Household Tap Connections (FHTC) to every rural household.
- To provide functional tap connection to Schools, Anganwadi centers, Gram Panchayat buildings, etc.
- To monitor the functionality of tap connections.
- To promote and ensure voluntary ownership among the local community by way of contribution in cash, kind and/ or labor and voluntary labor.
- To assist in ensuring the sustainability of the water supply system, i.e. water source, water supply infrastructure etc.
- To empower and develop human resources in the sector such that the demands of construction, plumbing, electrical, water quality management etc.
- To bring awareness on various aspects and significance of safe drinking water and involvement of stakeholders in a manner that make water everyone’s business
Components Under JJM:-
- Development of in-village piped water supply infrastructure: to provide tap water connection to every rural household.
- Development of reliable drinking water sources: to provide long-term sustainability of water supply system.
- Bulk water transfer, treatment plants and distribution network: to cater to every rural household.
- Technological interventions for removal of contaminants where water quality is an issue.
- Greywater management: Greywater is wastewater generated from activities such as washing dishes, doing laundry, and bathing.
- It can be treated and reused for non-potable purposes such as flushing toilets, watering plants, or irrigating lawns.
SOURCE: HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in relation to Janani Suraksha Yojana : (2023)
- It is a safe motherhood intervention of the State Health Departments.
- Its objective is to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality among poor pregnant women.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women.
- Its objective includes providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2 With reference to Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Private and public hospitals must adopt it.
- As it aims to achieve universal health coverage, every citizen of India should be part of it ultimately.
- It has seamless portability across the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recent studies suggest new theories about Dark matter.
About Dark matter:-

IMAGE SOURCE: IASBABA
- Dark matter is made up of particles that do not have a charge.
- These particles are “dark”, because they do not emit light.
- They are called “matter” because they possess mass like normal matter and interact through gravity.
- Scientists estimate that up to 85% of the matter in the universe could be made of dark matter.
- About 27% of the universe is dark matter and 68% is dark energy.
- Dark energy: It is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales.
- While dark matter attracts and holds galaxies together, dark energy repels and causes the expansion of the universe.
Historical Background:-
- In the 19th century, Lord Kelvin, a Scottish-Irish physicist, wanted to estimate the mass of our galaxy, the Milky Way.
- However, Kelvin found discrepancies or anomalies in the data, things which could not be explained.
- These were attributed to “dark bodies” that we could not see.
- Swiss American astronomer Fritz Zwicky first inferred dark matter’s existence in 1933.
- He discovered that the mass of all the stars in the Coma cluster of galaxies provided only about 1 per cent of the mass needed to keep the galaxies from escaping the cluster’s gravitational pull.
- 1970s: The reality of this missing mass remained in question for decades, until when American astronomers Vera Rubin and W. Kent Ford confirmed its existence.
- They observed that the mass of the stars visible within a typical galaxy is only about 10 per cent of that required to keep those stars orbiting the galaxy’s center.
Significance of Dark Matter:-
- Dark matter attracts and holds galaxies together.
- It exerts its influence on individual galaxies as well as the universe at large.
- Dark matter’s gravitational effects are also necessary to explain the motions of clusters of galaxies and the structure of the entire Universe at the largest scale.
- Galaxy: any of the systems of stars and interstellar matter that make up the universe.
- Galaxy clusters: are gravitationally bound groupings of galaxies, numbering from the hundreds to the tens of thousands.
New theories about dark matter:-
- Doubting the existence of dark matter: Some scientists argue that if there were invisible forces in the universe, we would have found them already.
- They suggest we should think outside of the Standard Model.
- Physicist Mordehai Milgrom has developed an alternative theory of gravity.
- It suggests that gravitational force operates differently at different distances from the core of a galaxy.
- While Newton’s theory of gravity explains most large-scale movements in the cosmos, Milgrom’s Modified Newtonian Dynamics suggests that a force acts differently when it is weak, such as at the edge of a galaxy.
- Advocates of the theory say it predicts the rotation of galaxies and the speed of the stars better than Newton’s theory.
MUST READ: Dark energy
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (2023)
- Australia
- Canada
- Israel
- Japan
Q.2) Consider the following pairs: (2023)
Objects in space Description
- Cepheids Giant clouds of dust and gas in space
- Nebulae Stars which brighten and dim periodically
- Pulsars Neutron stars are formed when massive starsrun out of fuel and collapse
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Groundwater status in India
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Geography) and GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The excessive extraction of groundwater for drinking and irrigation has shifted the Earth’s axis of rotation, according to a new study.
Key findings of the study:
- The study says that humans pumped out around 2,150 gigatons of groundwater between 1993 and 2010 and this has led the planet’s axis to drift at the rate of 4.36 cm per year towards the east.
Groundwater status in India:
- India is the largest user of groundwater with a fourth of the total global withdrawal.
- Indian cities cater to about 48 per cent of its water supply from groundwater.
- The unmanaged groundwater and increasing population may result in seasonal water shortages by 2050 for an estimated 3.1 billion people and perpetual water shortage for almost a billion.
- Water and food security will also be compromised and lead to poverty in the cities despite having good infrastructure development.
About Earth’s Axis:
- The Earth’s axis is the imaginary line through the earth that extends from the North Pole to the South Pole.
- At present, the Earth’s axis is tilted 23.5 degrees from the plane of its orbit around the Sun.
- During a cycle that averages about 40,000 years, the tilt of the axis varies between 22.1 and 24.5 degrees.
- Scientists for years have known that the poles and the axis keep shifting naturally as the mass distribution in and on the planet changes. This phenomenon is known as “polar motion”.
- For instance, rocks slowly circulating inside Earth’s mantle causes the planet’s mass to shift, leading to a change in the position of the rotational axis.
- There are several other reasons responsible for polar motion like ocean currents and even hurricanes.
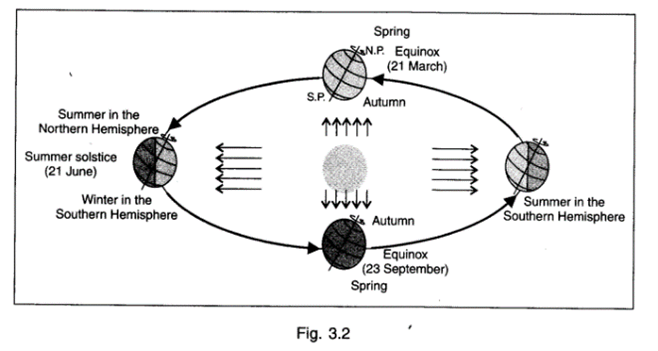
Source: Ncert
Impact of Climate Change on Polar Motion:
- Changes in Water Mass Distribution: Climate change is causing significant changes in the distribution of water masses on Earth.
- This alteration in water mass distribution affects the planet’s rotational dynamics, including polar motion.
- Melting of Greenland’s Ice: Greenland’s ice sheet is particularly susceptible to climate change.
- As it melts, vast amounts of water are discharged into the surrounding oceans.
- This influx of water alters the distribution of mass on Earth, leading to shifts in the rotational axis.
- Accelerated Rotational Axis Shift: Recent studies suggest that climate change has accelerated the shift of Earth’s rotational axis since the 1990s.
Major reasons for groundwater depletion:
- Green Revolution: Green Revolution enabled water intensive crops to be grown in drought prone/ water deficit regions, leading to over extraction of groundwater.
- Frequent pumping of water from the ground without waiting for its replenishment leads to quick depletion.
- Further, Subsidies on electricity and high MSP (Minimum Support Price) for water intensive crops.
- Industries Requirement: Water contamination as in the case of pollution by landfills, septic tanks, leaky underground gas tanks, and from overuse of fertilizers and pesticides leading to damage and depletion of groundwater resources.
- Inadequate Regulation: Inadequate regulation of groundwater encourages the exhaustion of groundwater resources without any penalty.
- Federal Issue: Water being a State subject, initiatives on water management including water conservation and water harvesting and making available adequate drinkable water to citizens in the Country is primarily States’ responsibility.
Impacts:
- Lowering of the water table: Groundwater depletion may lower the water table leading to difficulty in extracting groundwater for usage.
- Reduction of water in streams and lakes: A substantial amount of the water flowing in rivers comes from seepage of groundwater into the streambed.
- Depletion of groundwater levels may reduce water flow in such streams.
- Subsidence of land: Groundwater often provides support to the soil. When this balance is altered by taking out the water, the soil collapses, compacts, and drops leading to subsidence of land.
- Increased cost for water extraction: As the depleting groundwater levels lower the water table, the user has to delve deep to extract water.
- This will increase the cost of water extraction.
- Contamination of groundwater: Groundwater that is deep within the ground often intermingles with saltwater that we shouldn’t drink.
Initiatives taken by the Government:
- Atal Bhujal Yojana (Atal Jal): It is a Rs. 6000 crore Central Sector Scheme with World Bank assistance, for sustainable management of ground water resources with community participation.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA): It was launched in 2019 in 256 water stressed districts in the country to improve water availability including ground water conditions in these areas.
- It has special emphasis on creation of recharge structures, rejuvenation of traditional water bodies, intensive afforestation etc.
- Aquifer Mapping and Management Programme: The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) has taken up Aquifer Mapping and Management Programme.
- The program is aimed to delineate aquifer disposition and their characterization for preparation of aquifer/ area specific groundwater management plans with community participation.
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT): The Mission focuses on development of basic urban infrastructure in the AMRUT cities, such as water supply, sewerage & septage management, storm water drainage, green spaces and parks, and non-motorized urban transport.
Way Forward:
The study’s results emphasize the need to recognize the far-reaching consequences of human activities on the Earth’s delicate equilibrium. Groundwater extraction, driven by agricultural and freshwater needs, has been found to impact the planet’s rotational axis, leading to polar motion and contributing to global sea level rise.
Therefore, understanding these interactions is crucial for effective environmental management and sustainable practices to mitigate the adverse effects of human-induced changes on our planet.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: The 20-member Africa Expert Group (AEG), established by the Vivekananda International Foundation (VIF), recently presented the Report entitled ‘India-Africa Partnership: Achievements, Challenges and Roadmap 2023’.
Findings of the Report:
- The VIF report notes that India has a substantive partnership with Africa and a rich fund of goodwill, but it is “essential for India to review its Africa policy periodically, stay resilient by making the required changes, and place a razor-like focus on its implementation”.
- This can best be secured through close collaboration between the Ministry of External Affairs and the National Security Council Secretariat through a team of officials working under the joint leadership of the Secretary, Africa in the MEA, and a designated Deputy National Security Adviser.
India – Africa Relations:
Evolution of Ties:
- Historical Ties: India and Africa have a long history of interaction, primarily through trade routes connecting the Indian Ocean region and the East African coast.
- This historical connection forms the basis of cultural and people-to-people ties that continue to influence contemporary relations.
- Decolonization and South-South Cooperation: Following the wave of decolonization in Africa during the mid-20th century, India played a significant role in supporting African nations’ struggles for independence.
- India’s own experience of colonial rule resonated with African nations, leading to the establishment of strong diplomatic and political ties.
- India’s leaders, such as Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru, played a crucial role in fostering solidarity and cooperation between India and Africa.
- Non-Aligned Movement (NAM): Both India and many African countries were founding members of the Non-Aligned Movement, which emerged during the Cold War era.
- NAM aimed to provide a platform for countries to maintain neutrality and pursue their own development agendas, free from the influence of major power blocs.
Trade and Investment:
- India is the fifth-biggest investor in Africa with investments over the past 20 years amounting to $54 billion or 19.2% of Africa’s foreign direct investment.
- Pharmaceuticals, ICT and services, the automobile sector and the power sector could help boost Indian trade and investment in the continent. The bilateral trade stood at $ 62 billion in 2017-18 and the goal of hitting $ 100 billion is still distant.
- A huge population of Africa can serve as an attractive destination for exports and investment under ‘Make in India’.
- Africa has ample agricultural land which can address India’s food security. India is looking at leasing land in Africa to overcome the land deficit that we face in terms of arable land.
Soft Power:
- It is amplified by the presence of Indian Diaspora in countries like Mauritius.
- This helps in building trust between the nations and effective implementation of joint projects.
- Women consist of 90% of Africa’s labor force in the informal sector, engaged mainly in education, healthcare, and tertiary services.
- India’s efforts in these areas under the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) would enhance its brand image across the continent.
Common Agendas:
- Most African nations are developing in nature just like India which creates a common understanding on multiple issues.
- India and Africa share common grounds on reformation of the UNSC, Climate change agreements, Trade Issues and WTO negotiations etc.
Geopolitical
- India has been actively involved in peace and stability of African countries through UN Peace keeping operations. India is involved in capacity building of African countries.
- Africa, through forums such as BRICS and IBSA, can voice the concerns of developing and least developed countries at international climate change conferences and investment summits.
- Indian aid to Africa: India must revive the infrastructure projects already going on in Africa through its aid.
- India being a peaceful democratic nation can help African countries to establish political stability.
Regional Groupings and Forums for India-Africa Relations:
- India-Africa Forum Summit (IAFS): The IAFS is a major platform for India-Africa cooperation.
- It is a summit-level meeting held periodically to enhance and strengthen the partnership between India and African countries.
- BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa): India and Africa engage through the BRICS platform, which is a grouping of five major emerging economies.
- Asia-Africa Growth Corridor (AAGC): The AAGC is an economic cooperation agreement between India and Japan aimed at promoting socio-economic development in Asia and Africa.
- International Solar Alliance (ISA): The ISA is an initiative launched by India and France to promote solar energy deployment globally.
- It provides a platform for collaboration and technology transfer in the field of solar energy, including for African countries.
- India-Africa Science and Technology Initiative (IASTI): The IASTI is an initiative that promotes cooperation between India and African countries in the field of science and technology.
Challenges in India-Africa Relations:
- Competition with China: China has established a significant presence in Africa, particularly in sectors like infrastructure, mining, and energy. India faces competition from China in terms of investment, trade, and influence in Africa.
- Limited Resources: India’s resources for providing financial assistance and infrastructure development in Africa are comparatively limited.
- India cannot match China’s vast financial capabilities, which can result in challenges in competing for major projects and trade opportunities.
- Lack of Connectivity: Adequate city-to-city connectivity between India and Africa is lacking, hindering people-to-people contact and impeding the growth of mutual understanding and cooperation.
- Perception and Image: India needs to address concerns among African citizens who view Indian investments as neo-colonialism or exploitative. Incidents of racial attacks on African nationals in India have damaged India’s image and could potentially strain relations.
- Different Priorities: India’s focus on Africa is not its primary foreign policy priority, as it also engages with other major powers like the United States, the European Union, and neighboring countries. Balancing multiple priorities can pose challenges in effectively pursuing India-Africa relations.
Way Forward:
India has a substantive partnership with Africa and a rich fund of goodwill, but it is “essential for New Delhi to review its Africa policy periodically, stay resilient by making the required changes, and place a razor-like focus on its implementation”.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
National Investigation Agency was established in 2008.
Statement-II:
National Investigation Agency’s headquarters is in Mumbai.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-11 is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q2) Consider the following pairs:
- Sub Standard : NPA for a period exceeding 12 months.
- Doubtful : NPA for a period not exceeding twelve months.
- Loss assets : NPA not yet completely written off.
- Standard Assets: assets that carry a normal risk and are not NPA in a real sense.
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Dark matter attracts and holds galaxies together.
Statement-II:
Dark matter emits light.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-11 is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 3rd July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 1st July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – a