IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, Union Home Minister Amit Shah hailed the team of National Automated Fingerprint Identification System (NAFIS) of National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) for winning the Gold Award.
Background:-
- NAFIS won the Gold Award under the Excellence in Government Process Reengineering for Digital Transformation Category-1 of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
About National Automated Fingerprint Identification System (NAFIS)
- Managed by: National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) at the Central fingerprint bureau, based in New Delhi.
- Objective: to collect fingerprint data of all the criminals from all the states and the Union Territories.
- It is a web-based application project. ( NAFIS)
- It is a country-wide searchable database of crime- and criminal-related fingerprints.
Working of NAFIS:-
- NAFIS assigns a unique 10-digit National Fingerprint Number (NFN) to each person arrested for a crime.
- This unique ID will be used for the person’s lifetime, and different crimes registered under different FIRs will be linked to the same NFN.
Uses:-
- It enables law enforcement agencies to upload, trace, and retrieve data from the database in real-time on a 24×7 basis.
- It would help in the quick and easy disposal of cases with the help of a centralized fingerprint database.
National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB)
- Established: 1986.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Objective: To function as a repository of information on crime and criminals so as to assist the investigators in linking crime to the perpetrators.
- It was set up based on the recommendations of the National Police Commission (1977-1981) and the MHA’s Task Force (1985).
Important publications of NCRB:-
- Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India. (NCRB Report )
- Prison Statistics India.
- Fingerprints in India. (Facial recognition technology)
- Report on missing women and children in India.
MUST READ: NATGRID and NCRB
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-speech conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 3, and 5 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 2, 4, and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) In India, the term “Public Key Infrastructure” is used in the context of (2020)
- Digital security infrastructure
- Food security infrastructure
- Health care and education infrastructure
- Telecommunication and transportation infrastructure
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Luna 25 mission was launched by Russia.
Background:-
- Russia launched its first mission to the surface of the Moon in nearly half a century, in a bid to be the first country to land on the lunar south pole.
About Luna 25 mission:-
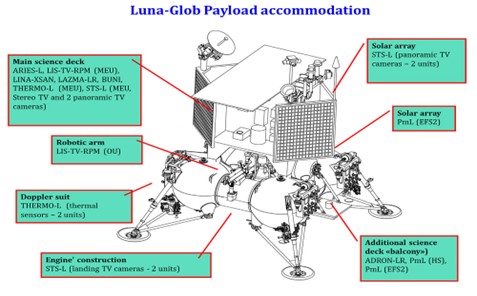
IMAGE SOURCE: iki.rssi.ru
- Launched: 2023.
- Launched by: Roscosmos.
- Roscosmos: the State Space Corporation of Russia that is responsible for space flights, aerospace research, and cosmonautics programmes.
- Take off: Vostochny cosmodrome, Russia.
- Landing Site: southwest of the Manzini crater.
- It is also called the Luna-Glob-Lander.
- It is a Russian lunar lander mission.
- It is to carry thirty kilo grams of scientific instruments including a robotic arm and drilling hardware to collect soil samples.
- It will study the south pole of the moon. ( Moon’s Wobble Effect)
Objectives of Luna 25 mission:-
- To study the composition of the polar regolith.
- To study the plasma and dust components of the lunar polar exosphere.
MUST READ: Supermoon
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth? (2022)
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur in equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 4, and 5 only
- 2, 3, 5, 6, and 7 only
- 1, 3, 4, 6, and 7 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Q.2) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same surface. speed and places a probe on it.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, a two-year-old female tiger from Nagzira National Park, was killed after being run over by a speeding car.
About Nagzira National Park:-
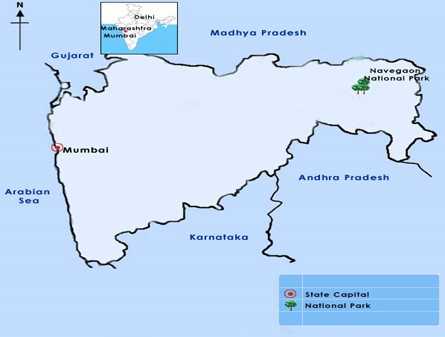
IMAGE SOURCE: toptourguide.com
- Location: Gondia and Shandara Districts of Maharashtra.
- It has connectivity with the major tiger reserves in Central India like, Kanha and Pench tiger reserve in Madhya Pradesh, Tadoba-Andhari Tiger reserve in Maharashtra, etc.
- Topography: The landscape of Navegaon Nagzira National Park is characterized by undulating terrain with gentle hills and valleys.
- Water bodies: The prominent water bodies within the national park include Navegaon Lake, Nagzira Lake, and the Itiadoh Dam.
- Climate: It experiences a tropical monsoon climate.
- Vegetation: Southern Tropical Dry Deciduous Forest which includes dry mixed forests to moist forest type.
- Flora: Terminalia tomentosa, Lagerstroemia parviflora, Anogeisus lotifolia, Pterocarpus marsupium, Diospyrus melanoxylon, etc.
- Fauna: Tiger, Panther, Small Indian Civet, Palm Civet, Wolf, Jackal, Wild Dog, Sloth Bear Flying Squirrel, Gaur, Sambar, etc.
Timeline:-
- 1970: It was declared a Wildlife Sanctuary. ( Navegaon-Nagzira Tiger Reserve)
- 2012: the state government announced to merging this sanctuary with another national park to include in Tiger Project.
- 2013: It was notified as 46th tiger reserve of India.
Other Tiger Reserves in Maharashtra:-
- Melghat Tiger reserve (1974)
- Tadoba Tiger Reserve (1993)
- Pench Tiger Reserve (1999)
- Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (2007)
- Bor Tiger Reserve (2014)
MUST READ: Tiger Estimation
SOURCE: INDIA TODAY
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following ‘fauna: (2023)
- Lion-tailed Macaque
- Malabar Civet
- Sambar Deer
How many of the above are generally nocturnal or most active after sunset?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding the Indian squirrels: (2023)
- They build nests by making burrows in the ground.
- They store their food materials like nuts and seeds in the ground.
- They are omnivorous.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: The Railways Ministry has announced plans to establish Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Kendras at railway stations across the country.
Background:-
- Railways Ministry aims to make available quality medicines to all at an affordable price through these initiatives.
About Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Kendras:-
- Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Kendras are set up under Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana(PMJP).
- Objective of PMBJP: to provide quality medicines at affordable prices for all, particularly the poor, so as to reduce out-of-pocket expenses in healthcare.
- It is a medical outlet opened under the scheme which makes quality medicines available at affordable prices for all.
- It has been set up to provide generic drugs at lesser prices that are equivalent in quality and efficacy to expensive branded drugs. (Pradhan Mantri Janaushadhi Kendra (PMJK))
- Bureau of Pharma PSUs in India (BPPI) supports Janaushadhi Kendras as a part of PMBJP.
- It has been established under the Department of Pharmaceuticals.
- It coordinates the procurement, supply, and marketing of generic drugs through Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana Kendra.
- Funding: Financial Support is provided by the government to eligible NGOs/Trusts/agencies/individuals to establish Jan Aushadhi stores.
- One-time financial assistance up to ₹2.50 lakh.
- Target: The Government has set a target to increase the number of Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Kendras (PMBJKs) to 10,500 by the end of March 2025.
Eligibility to open a Jan Aushadhi Kendra:-
- State Governments or any organization / reputed NGOs / Trusts / Private hospitals / charitable institutions / Doctors / Unemployed pharmacists/ individual entrepreneurs are eligible to apply for the new Jan Aushadhi Kendra.
- The applicants shall have to employ one B Pharma / D Pharma degree holder as Pharmacist in their proposed store.
About Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana(PMJP):-
- Launched: 2008.
- Ministry: Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers. ( PMJP)
- Implementing Agency: Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI).
- Objectives of PMBJP: to provide quality medicines at affordable prices to people through special Kendras known as Pradhan Mantri Bharatiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana Kendra.
- Funding: Financial Support is provided by the government to eligible NGOs/Trusts/agencies/individuals to establish Jan Aushadhi stores.
- Benefit: The scheme ensures easy reach to affordable medicine to the people in every nook and corner of the country.
MUST READ: Towards affordable healthcare in India: ‘Jan Aushadhi’ to ‘Jan Upyogi’
SOURCE: NEWS ON AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under the Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy: (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for preschool children, adolescents, and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with a special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies, and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements in relation to Janani Suraksha Yojana (2023)
- It is a safe motherhood intervention of the State Health Departments.
- Its objective is to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality among poor pregnant women.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women.
- Its objective includes providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy/Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC) delivered record performances in Fiscal Year 2023-2024.
Background:-
- The NMDC is paving the way towards becoming a 100 Million Tonnes (MT) mining company.
- The Ministry of Steel said the Corporation has reported record-breaking production for the period up to July 2023.
About National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC):-
- Establishment: 1958.
- Ministry: Ministry of Steel. ( Integrated Steel Hub)
- HQ: Hyderabad.
- Vision: To emerge as a global Environment-friendly Mining Organization and as a quality Steel producer with a positive thrust on Social Development. (Iron-Ore Policy 2021)
- It is India’s largest iron ore producer.
- The company has been categorized by the Department of Public Enterprises as a “Navratna” Public Sector Enterprise in 2008.
Objectives of NMDC:-
- To expand the operations in the areas of Mining and Mineral Processing to meet the growing demands from domestic and international Markets.
- Achieve international standards in per capita productivity, value addition, and cost-effectiveness.
- To increase the iron ore production capacity to 67 MTPA by FY 2025. (Iron Ore)
- To conserve mineral resources through scientific mining.
MUST READ: Decarbonizing India: Iron and Steel Sector report
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Steel slag can be the material for which of the following? (2020)
- Construction of base road
- Improvement of agricultural soil
- Production of cement
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) In the ‘Index of Eight Core Industries’, which one of the following is given the highest weight? (2015)
- Coal production
- Electricity generation
- Fertilizer production
- Steel production
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Recently, the Geological Survey of India (GSI) has discovered the oldest fossil remains of a long-necked, plant-eating dicraeosaurid dinosaur in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan.
About the Study:-
- The scientists from IIT-Roorkee and the Geological Survey of India (GSI) conducted this research.
Findings:-
- The remains are 167 million years old.
- They belong to a new species unknown to scientists thus far.
- It has been named ‘Tharosaurus indicus’.
- The first name refers to the ‘Thar desert’ where fossils were found.
- The second name is after its country of origin.
- The fossils of dicraeosaurid dinosaurs have been found previously in North and South Americas, Africa, and China, but such fossils were not known from India.
- The rocks in which the fossils were found are dated to be around 167 million years old.
- It makes this new Indian sauropod not only the oldest known dicraeosaurid but also globally the oldest diplodocoid.
- Diplodocoid: a broader group that includes dicraeosaurids and other closely related sauropods.
- Theories so far had suggested that the oldest dicraeosaurid was from China (about 166-164 million years old).
About the Geological Survey of India:-
- Establishment: 1851.
- Ministry: Ministry of Mines.
- HQ: Kolkata. ( GSI)
- It has six Regional offices located at Lucknow, Jaipur, Nagpur, Hyderabad, Shillong, and Kolkata.
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) is a scientific agency.
- It is one of the oldest of such organizations in the world and the second oldest survey in India after Survey of India (founded in 1767). ( Survey of India)
- It uses the latest computer-based technologies for the dissemination of geoscientific information and spatial data, through cooperation and collaboration with other stakeholders in the Geo-informatics sector.
Role of GSI:-
- Conducting geological surveys and studies of India.
- Prime provider of basic earth science information to government, industry, and the general public.
- conduct multidisciplinary as well as fundamental geological research and studies.
- Coordinate geoscientific activities with stakeholders in all areas related to geosciences.
- Actively participate in international collaborative projects to improve our understanding of the Earth and its ecosystems and its geology.
- Maintain a leadership role in the geological field and develop partnerships with central, state, and other institutions.
MUST READ: Abnormal’ dinosaur egg in India
SOURCE: TIMES OF INIDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Monazite is a source of rare earth.
- Monazite contains thorium.
- Monazite occurs naturally in the entire Indian coastal sands in India.
- In India, Government bodies only can process or export monazite.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1, 2, and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and
Q.2) The word ‘Denisovan’ is sometimes mentioned in media in reference to (2019)
- fossils of a kind of dinosaurs
- an early human species
- a cave system found in North-East India
- a geological period in the history of the Indian subcontinent
The Bharatiya Sanhita Suraksha Bill, 2023
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The Bharatiya Sanhita Suraksha Bill, 2023 was introduced in Lok Sabha to replace the Indian Penal Code, Code of Criminal Procedure and Indian Evidence Act.
Highlights of the Bill:
- The Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita Bill 2023 prescribes capital punishment as the maximum sentence for mob lynching.
- The bill suggests 10 years of imprisonment for sexual intercourse with women on the false promise of marriage.
- The bill states that sexual intercourse by a man with his wife, when the wife is not under 18 years of age, is not considered rape.
Repeal of Sedition Section
- The bills provide definitions for terrorism and offences such as separatism, armed rebellion against the government, and challenging the sovereignty of the country.
- Confiscation of property can be done based on court orders.
- The bills aim to provide speedy justice and create a legal system that aligns with contemporary needs and aspirations.
- In cases of sexual violence against women, the video recording of survivor statements is made compulsory.
- Police must inform about the status of a complaint within 90 days.
- Consultation with the victim is required before withdrawing a case punishable by seven years or more.
- Community service is being introduced for specific crimes.
- The maximum time to file a charge sheet is fixed at 180 days.
- In additional 90 days can be granted by the court, but it cannot exceed that.
- The government must decide prosecution sanctions against police officers and civil servants within 120 days, or it will be deemed permitted.
- Videography of search and seizure is made compulsory, and a charge sheet will not be accepted without it.
- Forensic collection of evidence is made compulsory for all crimes punishable by seven years.
- A designated police officer will certify the custody of an accused to their relatives, both online and physically.
- Rules for remission of sentences are stricter to prevent individuals with political influence from benefiting disproportionately.
Significance of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita Bill:
- It will consolidate and amend the law relating to criminal procedure and calls for specific timelines for time-bound investigations, trials and judgements.
- It will ensure speedy delivery of justice.
- The draft legislation falls in line with the government’s Digital India initiative.
- For example, it provides for admissibility of digital or electronic record as evidence, which shall have the same legal validity and enforceability as a paper record.
- A ‘Zero FIR’ can be lodged at any police station and the FIR must be transferred within 15 days to the police station having jurisdiction over the place of crime.
- Unlike an FIR, which is restricted by jurisdiction, a zero FIR can be filed in any police station, regardless of whether the offence was committed under the jurisdiction of that particular police station.
- It will promote a human rights-based approach that respects the dignity and rights of all stakeholders in the criminal justice process.
- It will enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the criminal justice system by reducing delays, pendency, backlog, and corruption.
- It will improve the quality and credibility of justice delivery by ensuring transparency, accountability, and professionalism.
- It will foster a culture of peace and harmony in society by preventing and curbing crimes that threaten social order and security.
- It will address the root causes of crimes by addressing socio-economic inequalities and injustices.
- It will strengthen the rule of law and democracy in India by upholding constitutional values and principles.
Challenges:
- The bills may face opposition and resistance from some quarters who may perceive them as an infringement on their rights, interests, or autonomy.
- It may face legal challenges and scrutiny from the courts on the grounds of constitutionality, validity, or interpretation of certain provisions.
- It may face practical difficulties and bottlenecks in implementation due to a lack of awareness, cooperation, or coordination among various agencies or stakeholders.
- It may face unforeseen consequences or implications that may require further amendments or modifications in the future.
Way Forward:
The criminal justice system is the backbone of any democracy. It is essential to ensure that it is fair, efficient, and responsive to the needs and aspirations of the people. The introduction of these bills is a historic opportunity to achieve this goal. It is hoped that these bills will usher in a new era of criminal justice reform in India and make it a model for other countries to emulate.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Economy)
Context: The Indian government is promoting technology-enabled sustainable farming, including natural, regenerative and organic systems, during its G20 presidency.
Status of Agriculture in India:
- Agriculture and allied sectors are central to the Indian economy.
- India is one of the major players in the agriculture sector worldwide and it is the primary source of livelihood for ~55% of India’s population.
- India:
- Has the world’s largest cattle herd (buffaloes),
- Has largest area planted to wheat, rice, and cotton, and it is the largest producer of milk, pulses, and spices in the world.
- It is the second-largest producer of fruit, vegetables, tea, farmed fish, cotton, sugarcane, wheat, rice, cotton, and sugar.
- Agriculture sector in India holds the record for second-largest agricultural land in the world generating employment for about half of the country’s population.
Technological Advancement made in Seed Industry:
- Genetic advancement: Seed technology used today combines genetic advancement with applied technologies to provide quality-enhanced seeds with the ability to withstand a range of biotic and abiotic stressors.
- Priming and enhancement technologies: Priming and enhancement technologies are emerging as an essential package of practices to ensure that seeds perform well under a wide range of growing conditions.
- Film coating technology: Film coating technology is applied to organic and inorganic cultivation to improve seed handling, precision planting and use as carriers of pesticides and nutrients.
Significance of Seed Technology in Indian Agriculture:
- Higher Productivity: Seed technology can increase the yield potential of crops by developing improved varieties that have desirable traits, such as high grain or fruit quality, resistance to pests and diseases, tolerance to drought or salinity, etc.
- Seed technology can also improve the germination rate, seedling vigour, and plant establishment of seeds by using priming or physiological advancement protocols.
- Higher Input Use Efficiency: Seed technology can reduce the amount and cost of inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides, and water by using film coating, pelleting, or seed treatments that can deliver these inputs directly to the seeds or plants in optimal doses.
- Seed technology can also enhance the nutrient uptake and utilization of plants by using bio-stimulants and nutrients that can stimulate plant growth and metabolism.
- Higher Resilience: Seed technology can improve the adaptability and stability of crops under changing and unpredictable climatic conditions by using genetic manipulation, speed breeding, gene-editing tools, or AI-responsive sensors or substances that can modulate plant responses to external stimuli.
- Seed technology can also improve the diversity and health of crops by using biologicals or microbial inoculum that can enhance plant immunity and soil fertility.
Challenges:
- Demand and affordability: Though India has achieved food security with the production of food grains reaching 330 MT; the demand for coarse cereals, pulses, oilseeds and vegetables is not fully met.
- In addition, they are not affordable for a large part of the population, leading to a high proportion of the under/malnourished population, with a sizable percentage of child wasting (19.3 percent).
- Crop productivity: India is much lower than other advanced and emerging market economies due to various factors, like fragmented landholdings, lower farm mechanization and lower public and private investment in agriculture.
- Irrigation: Although India is the second largest irrigated country of the world after China, only one-third of the cropped area is under irrigation. Irrigation is the most important agricultural input in a tropical monsoon country like India.
- Conventional method of cultivation: In spite of the large-scale mechanization of agriculture in some parts of the country, most of the agricultural operations in larger parts are carried on by human hand using simple and conventional tools and implements like wooden plough, sickle, etc.
- Significant challenges: Depleting natural resources, a burgeoning population, extreme weather conditions and natural disasters because of climate change pose bigger challenges to Indian and regional agriculture, dominated by smallholder farmers.
- India’s performance in achieving the SDGs, especially goals one, two and three, ones linked to agriculture, are yet to reach desired levels.
Suggestive measures: Way Forward
- Millet production: Being nutrient-rich, hardy and grown in a short cycle, millets are recognised as well suited for sustainable agriculture.
- India is the global leader in millet production.
- By producing quality-assured seeds of improved varieties of millets, especially minor millets, it has the potential to capture the global seed market.
- Seed technology: While crop variety development will become faster and more precise in the coming years by using molecular technologies, speed breeding and gene-editing tools, applied seed technologies would ensure good performance even under less favourable, unpredictable, and harsh environments.
- Hence, seed technology today must combine genetic advancement with applied technologies.
- These must ensure to provide quality-enhanced seeds of improved varieties having higher productivity, high input use efficiency and the ability to withstand a range of biotic and abiotic stressors.
- Role of public and private sectors: The R&D efforts of the public and private sectors can complement each other in developing environment-friendly, better-performing seeds at affordable costs.
- “Next Gen” technologies: “Next Gen” technologies may also introduce AI-based responses from seeds under specific external conditions (for example, moisture, temperature); or incorporate such molecules or metabolites that act as metabolic cues in biological pathways, which will require appropriate guidelines for application.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Tiger Reserve | Location |
| 1.Melghat Tiger Reserve | Karnataka |
| 2.Palamau Tiger reserve | Bihar |
| 3.Nawegaon-Nagzira Tiger Reserve | Maharashtra |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
National Automated Fingerprint Identification System (NAFIS) assigns a unique 10-digit National Fingerprint Number (NFN) to each person arrested for a crime.
Statement-II:
It would help in the quick and easy disposal of cases.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
GSI is under the Ministry of Earth Science.
Statement-II:
It uses the latest computer-based technologies for the dissemination of geoscientific information and spatial data.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains practice Questions
Q.1) What is the significance of criminal justice system reforms in India and major challenges impede their implementation. What strategies can be envisioned to lead the way forward towards a more just and effective system? (250 words)
Q.2) Technology can play a vital role in boosting Indian agriculture by enhancing the productivity, profitability, and resilience of its farming sector. Critically analyse. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 14th August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 12th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – c
Q.3) -d











